Back
SHIV DIXIT
CHAIRMAN - BITEX IND... • 1y
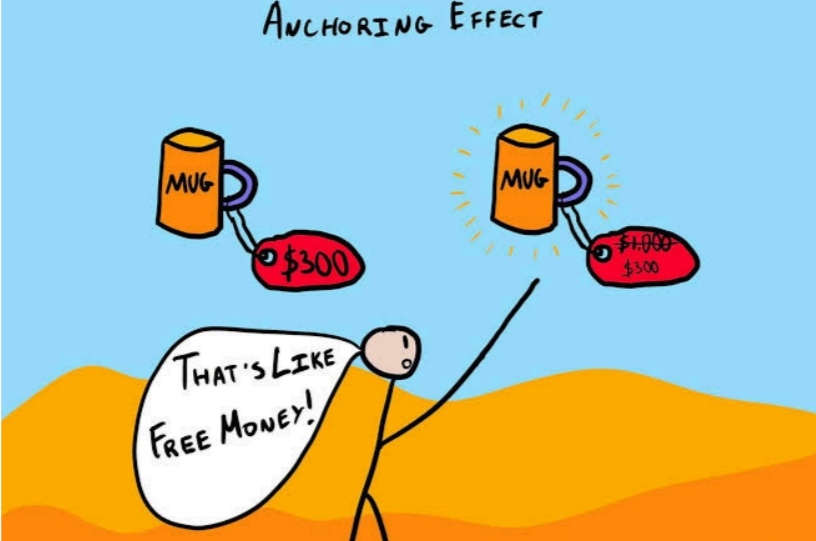
📖 DAILY BOOK SUMMARIES 📖 🔗 DIRECT FREE E-BOOK DOWNLOAD LINK AVAILABLE — https://drive.google.com/file/d/18xOMsRbe8b4vP3zYKobcbsDj4FWlRcMi/view?usp=drivesdk 🔥 Thinking, Fast and Slow 🔥 🚀 20 Lessons By 👉 ✨ Daniel Kahneman ✨ 1. Two Systems of Thinking: • System 1 is fast, intuitive, and automatic; System 2 is slow, deliberate, and analytical. 2. Cognitive Biases Influence Decisions: • Biases like anchoring, availability, and confirmation impact decision-making, often unconsciously. 3. Heuristics Simplify Complex Judgments: • People use mental shortcuts to make decisions quickly but sometimes inaccurately. 4. Overconfidence Effect: • People tend to overestimate their knowledge and judgment, leading to biased conclusions. 5. Prospect Theory and Loss Aversion: • Losses are psychologically more powerful than equivalent gains, influencing risk-taking behavior. 6. Endowment Effect: • People assign higher value to things they own compared to items they don’t own. 7. Framing Effects on Decisions: • How information is presented (framed) influences the choices people make, even if the facts are the same. 8. Anchoring Bias: • Initial exposure to a number or idea affects subsequent judgments and estimates. 9. Priming Affects Behavior: • Exposure to certain words or images can subconsciously influence behavior and choices. 10. Understanding Regression to the Mean: • Extreme performances or events are likely to be followed by more typical outcomes, but this concept is often misunderstood. 11. Planning Fallacy: • People tend to underestimate the time, costs, and risks of future actions, even with past experience showing otherwise. 12. Availability Heuristic: • People judge the probability of events by how easily examples come to mind, which can skew risk assessment. 13. Halo Effect: • An initial positive impression in one area leads to an overall positive perception, even in unrelated areas. 14. Sunk Cost Fallacy: • People irrationally continue investing in a losing endeavor because of prior investment, rather than cutting losses. 15. WYSIATI (What You See Is All There Is): • People make decisions based only on the information they have, ignoring what they don’t know. 16. Optimism Bias: • People tend to be overly optimistic about their own outcomes, often underestimating risks or difficulties. 17. Substitution: • When faced with a difficult question, people often answer an easier question instead, without realizing it. 18. Representativeness Heuristic: • People judge probabilities based on how much something resembles a typical case, which can lead to stereotyping. 19. Base Rate Neglect: • People often ignore general statistical information (base rates) in favor of specific information, leading to flawed judgments. 20. Remembering vs. Experiencing Self: • People’s memories of an experience often differ from what they actually felt at the time, affecting future decisions.

Replies (1)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Suman solopreneur
Exploring peace of m... • 1y
Behavioral Finance examines how emotions and biases affect financial decisions, leading to irrational behavior. Unlike traditional finance, it acknowledges that people often make decisions influenced by psychology. Key points include: 1. Loss Avers
See MoreOnly Buziness
Everything about Mar... • 9m
“Anchoring Effect: The First Price You See Changes Everything” The Anchoring Effect is a cognitive bias where people rely too heavily on the first piece of information (the “anchor”) they see when making decisions — especially in pricing. Businesses
See MoreAditi
Will become a inspir... • 9m
It’s All in the Wording: How the Framing Effect Shapes What We Buy” The Framing Effect is a cognitive bias where people make decisions based on how information is presented rather than the facts themselves. In business, marketers use this to shape p
See MoreOnly Buziness
Everything about Mar... • 9m
“Set and Selected: How the Default Effect Quietly Influences Customer Choices” The Default Effect is a psychological bias where people are more likely to go with pre-selected or automatic choices, simply because it requires less effort. Businesses u
See MoreOnly Buziness
Everything about Mar... • 9m
“Same Facts, New Feeling: How the Framing Effect Shapes Customer and Audience Behavior” The Framing Effect is the idea that the way information is presented—rather than the facts themselves—can dramatically influence decisions. In business and media
See MoreVikas Acharya
Building Reviv | Ent... • 1y
day 1 - THE HALO EFFECT The Halo Effect is a type of cognitive bias where our overall impression of a person influences how we feel and think about their character or abilities. Here's a simple way to understand it: Imagine you meet someone who lo
See More
Only Buziness
Everything about Mar... • 9m
“Setting the Stage: How Priming Subconsciously Influences Customer Choices” Priming is a psychological effect where exposure to certain stimuli influences a person’s response to future information—often subconsciously. In business, priming is used t
See MoreDownload the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.















/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)


















