Back
Rahul Agarwal
Founder | Agentic AI... • 2m
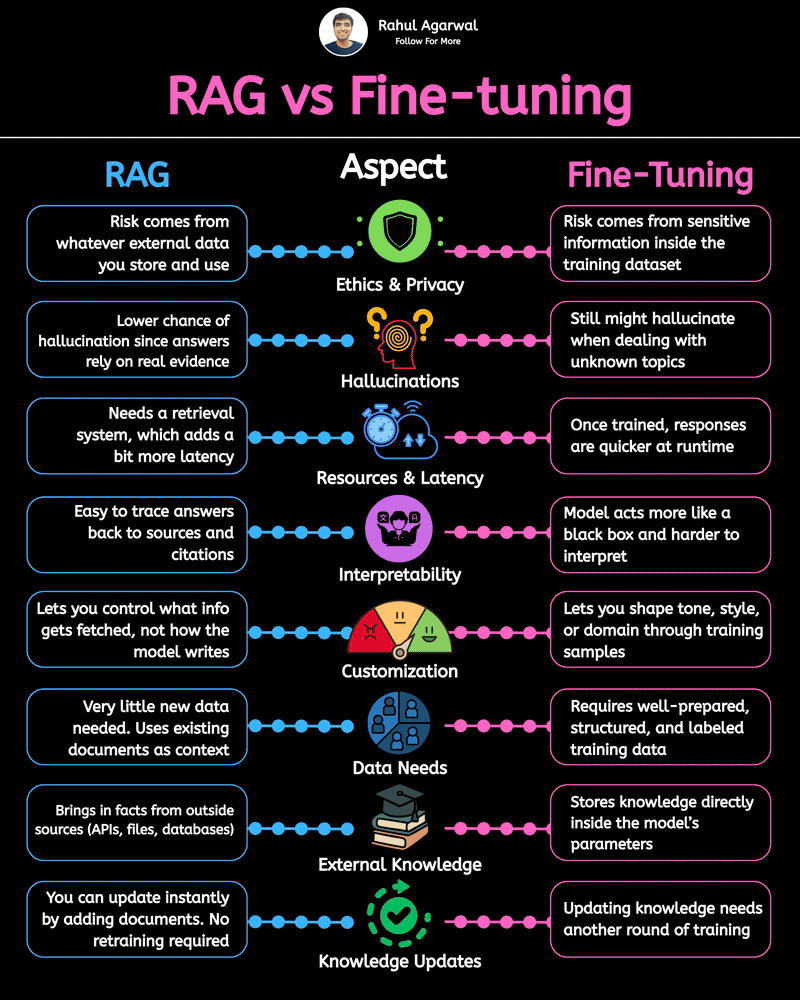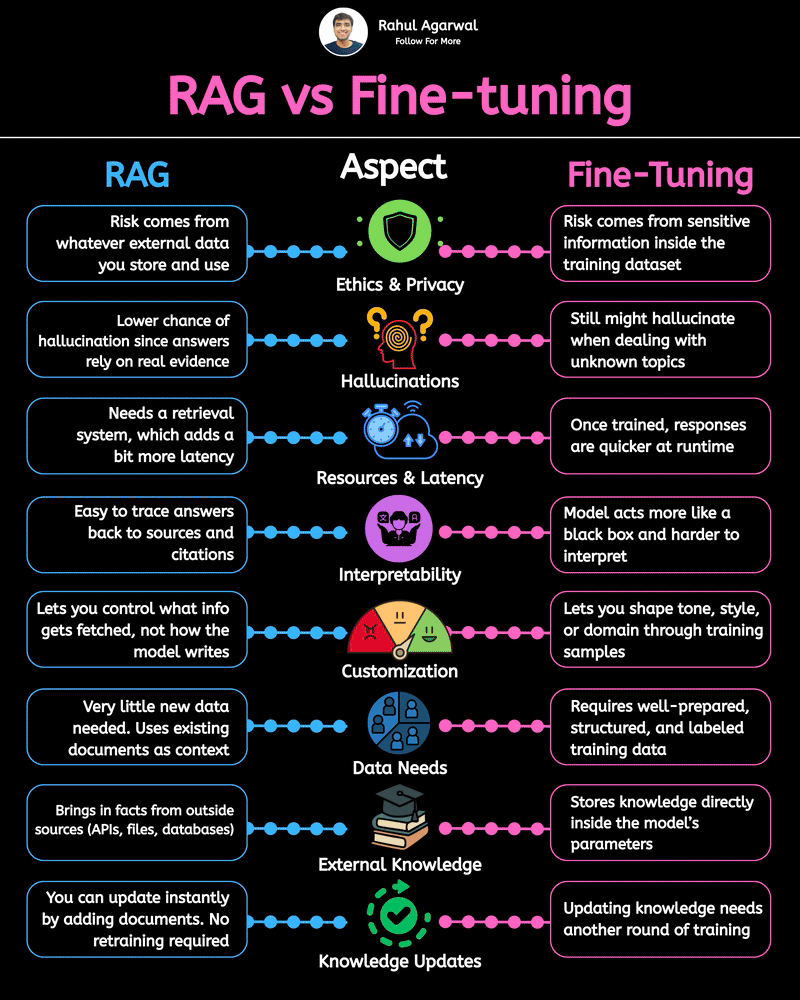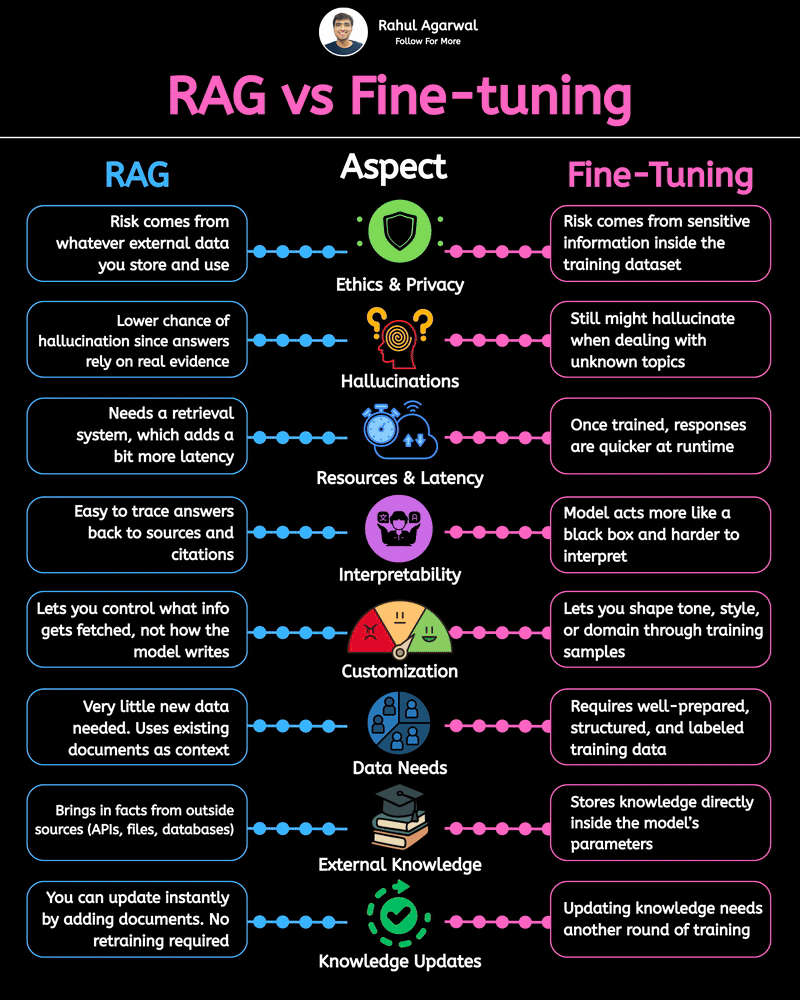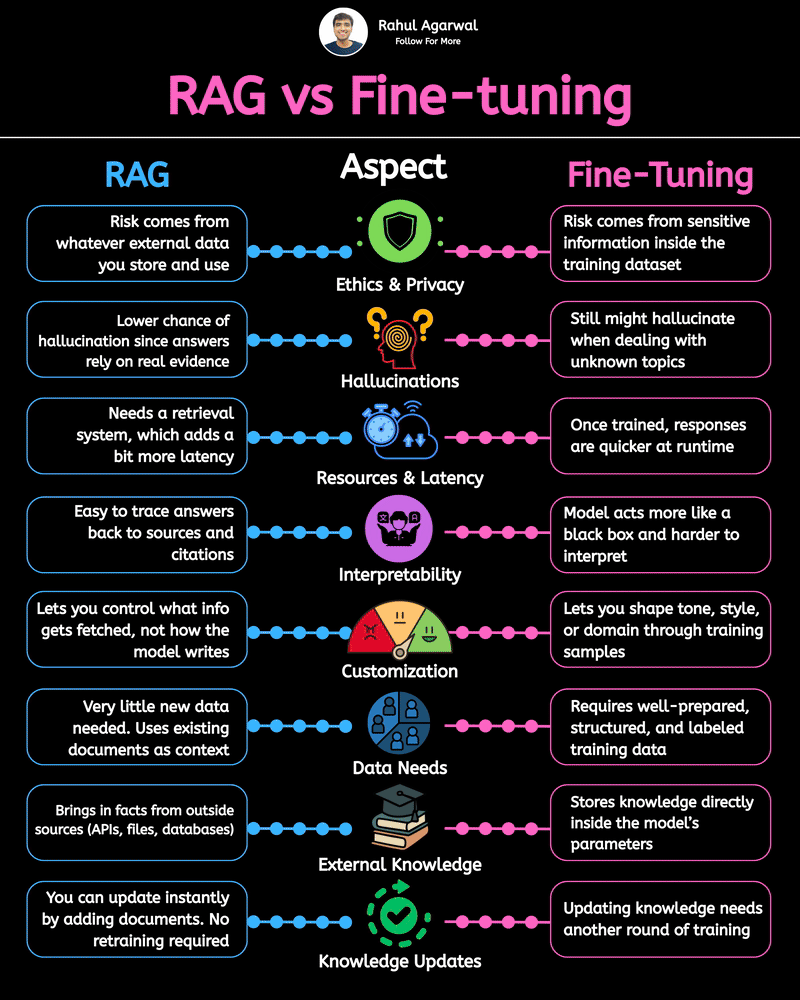
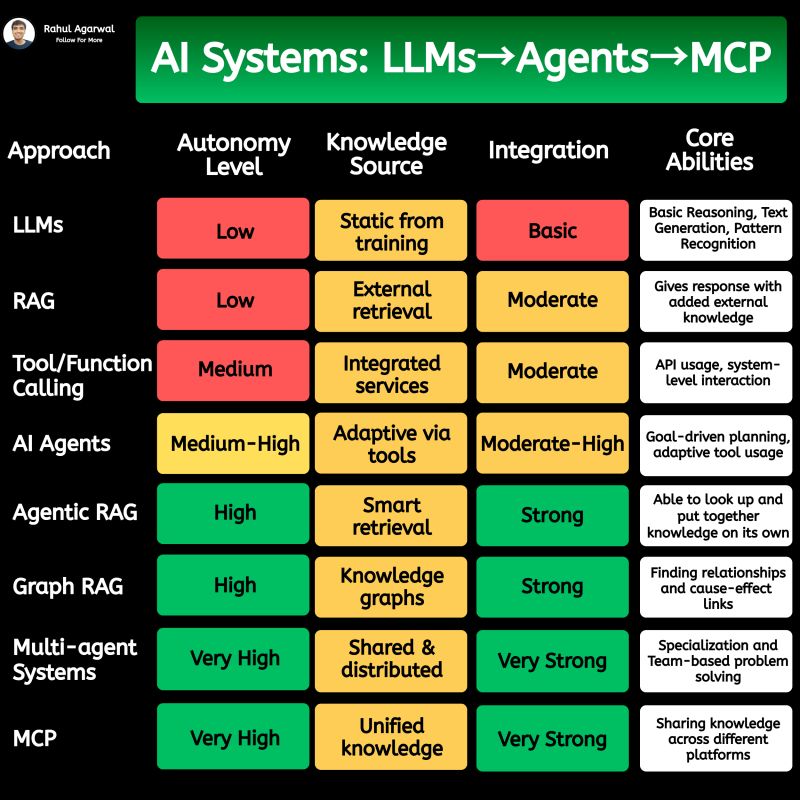
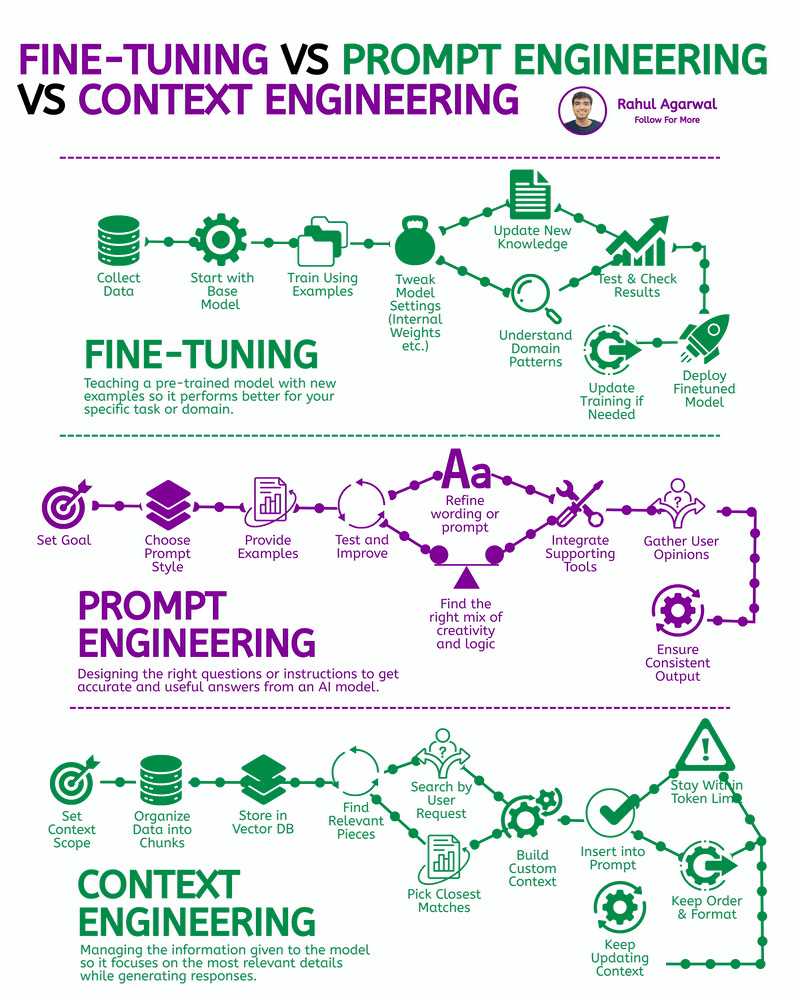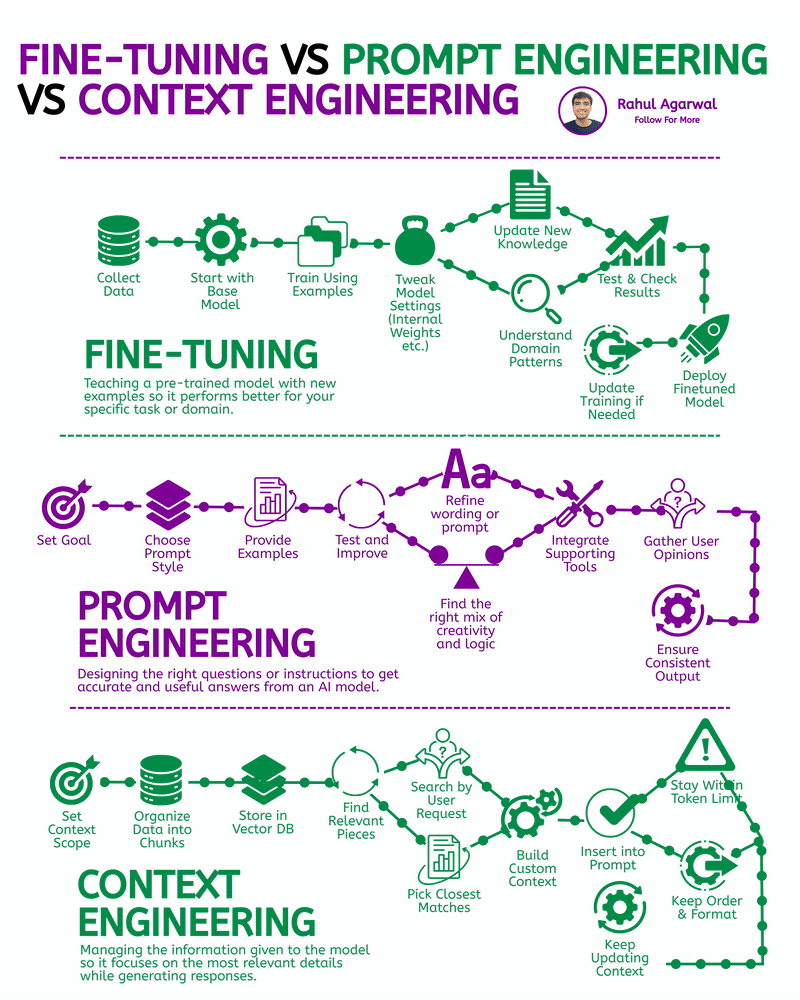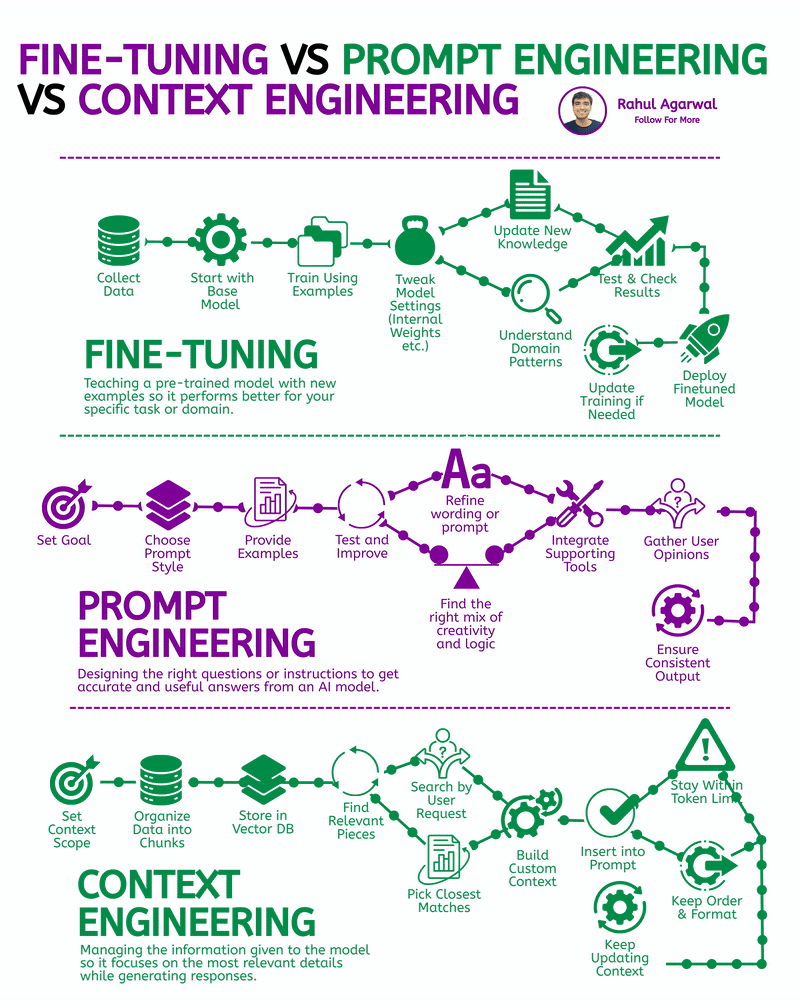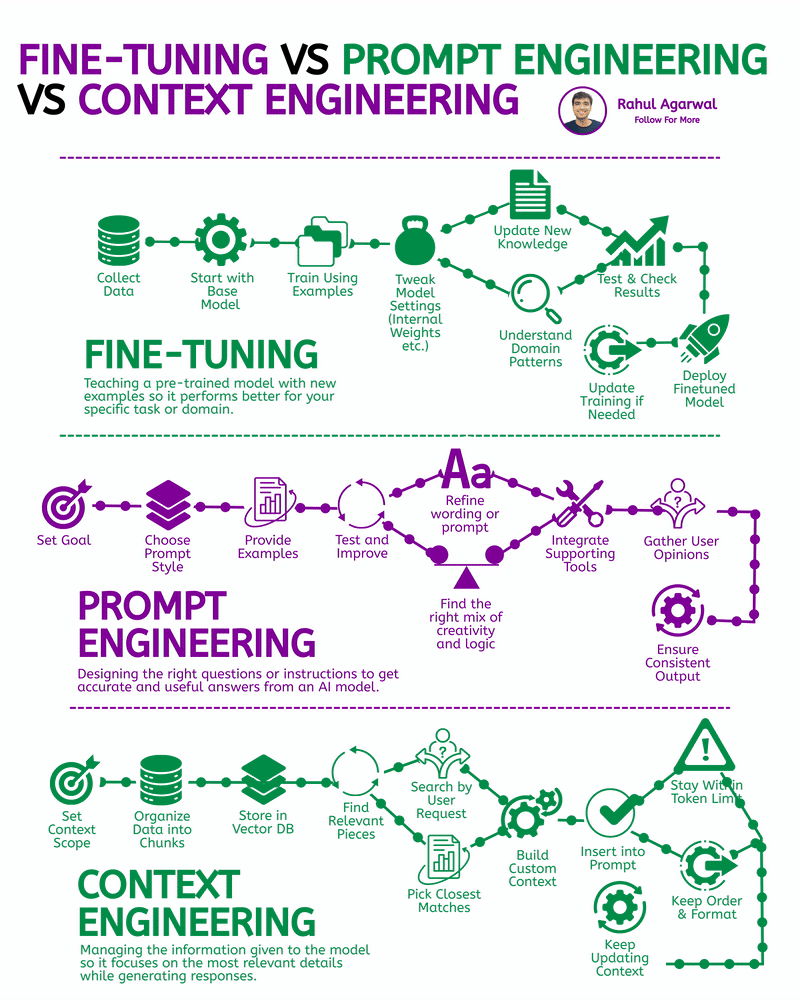
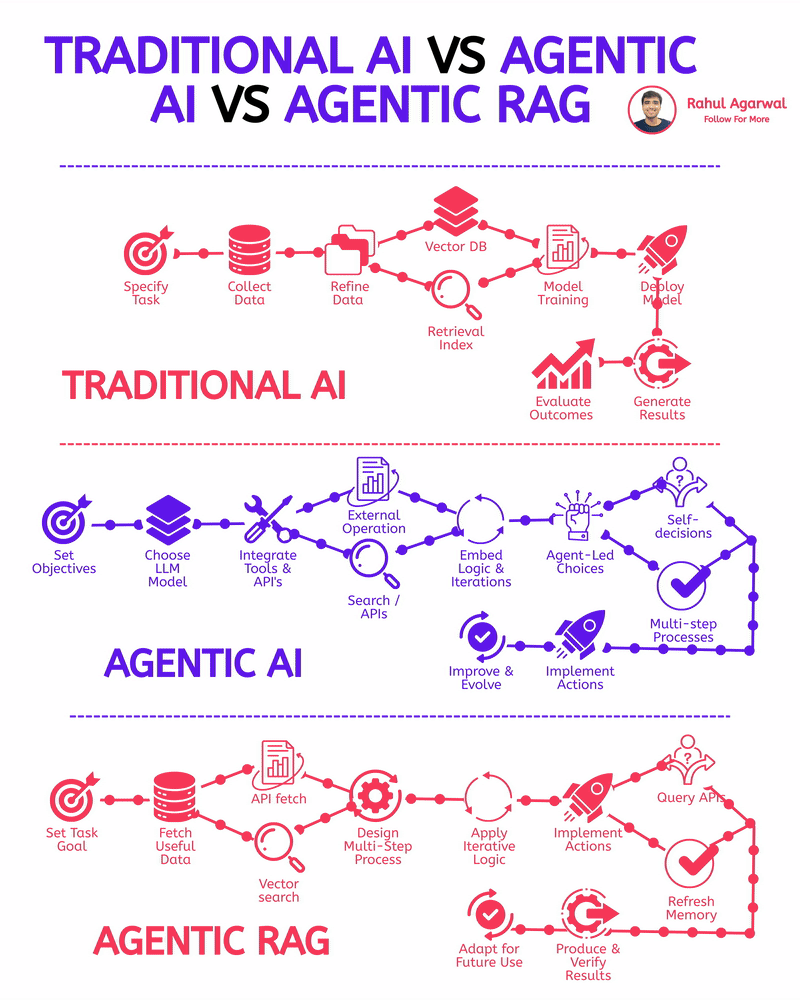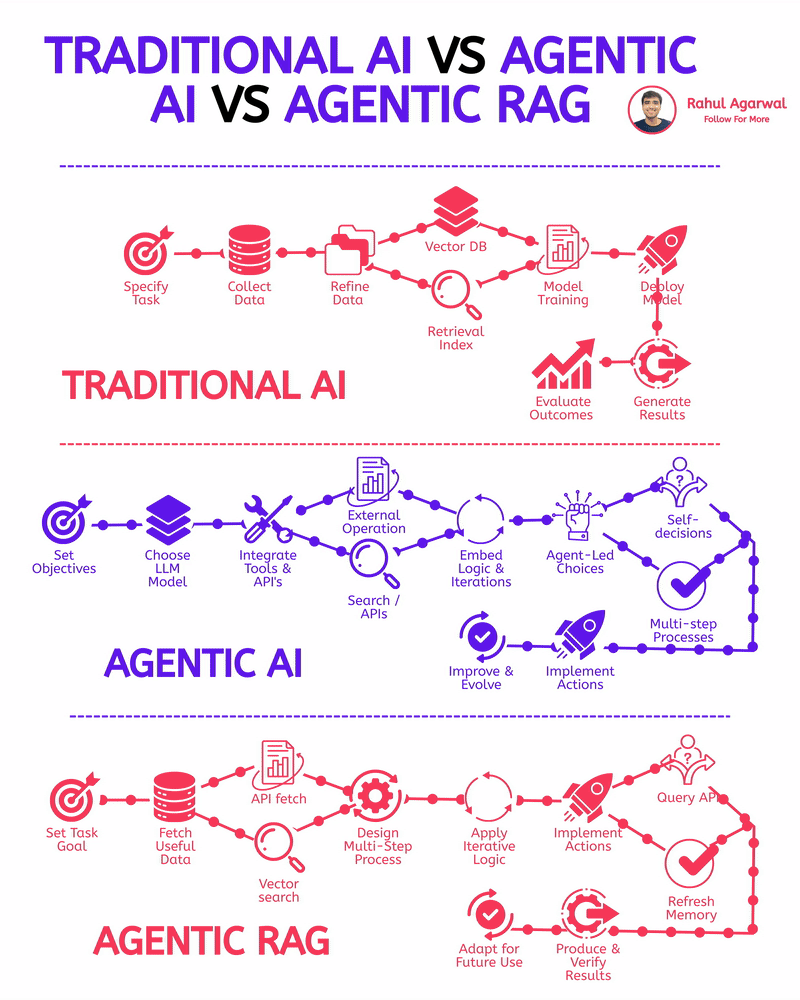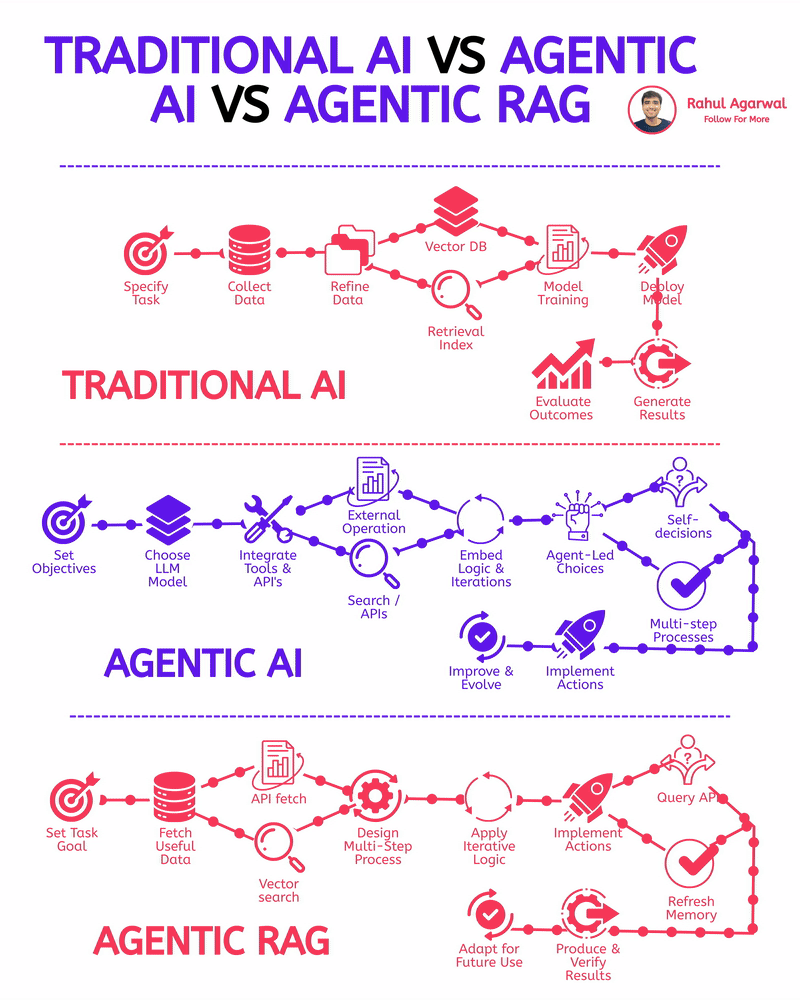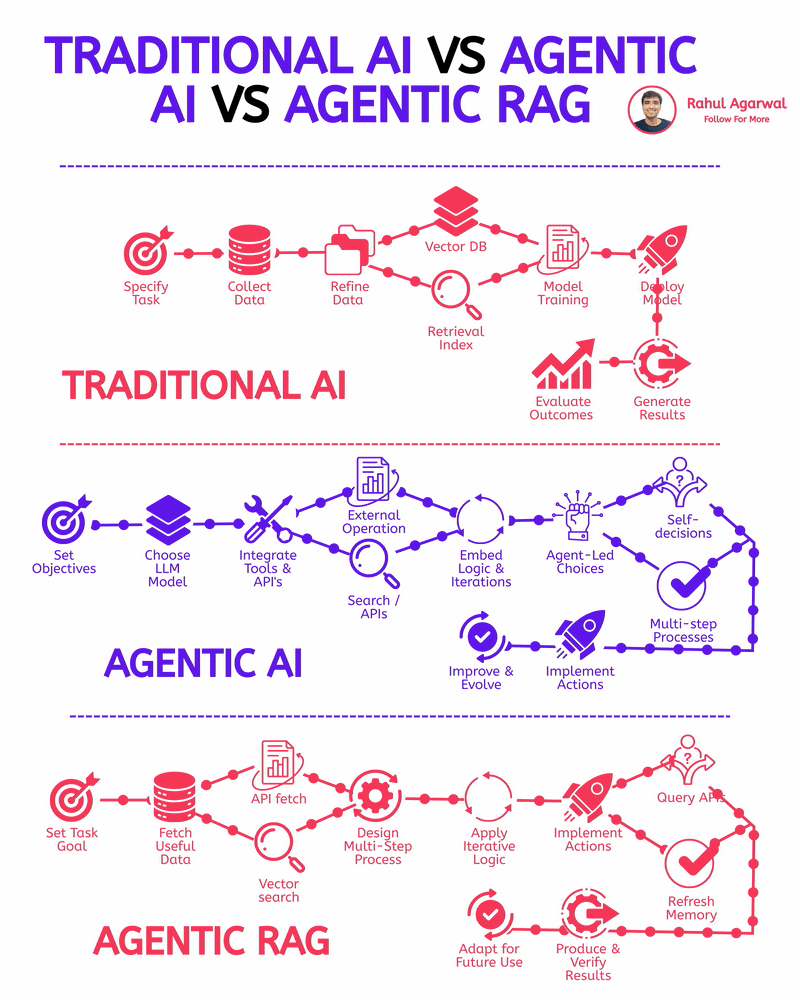
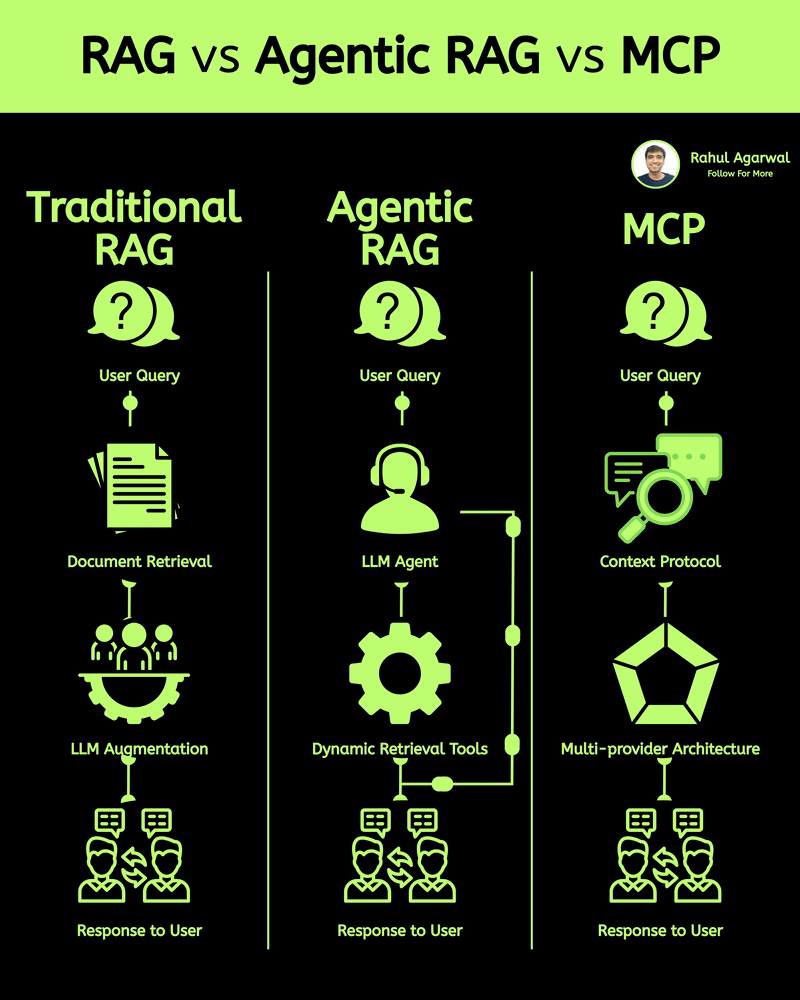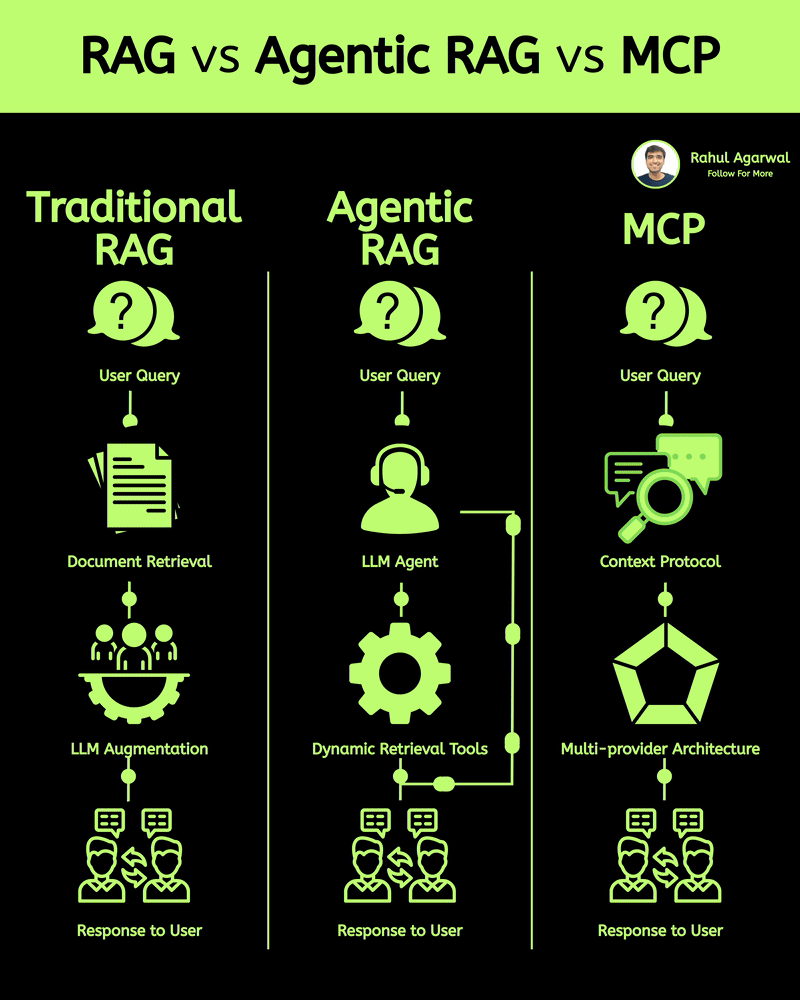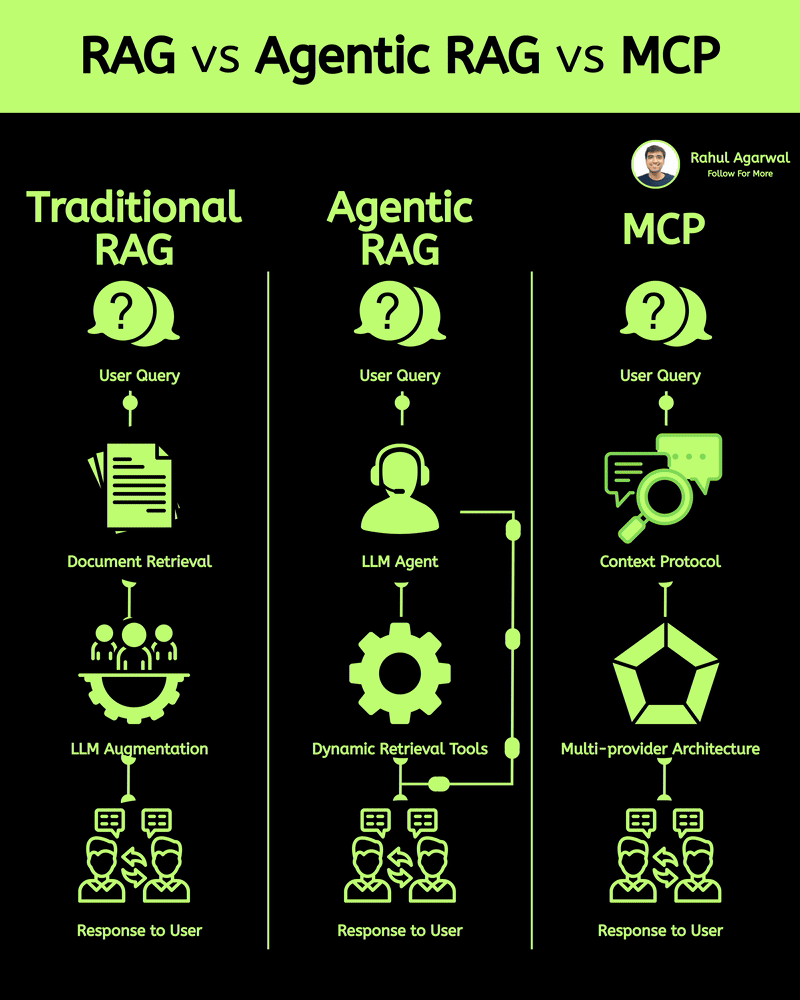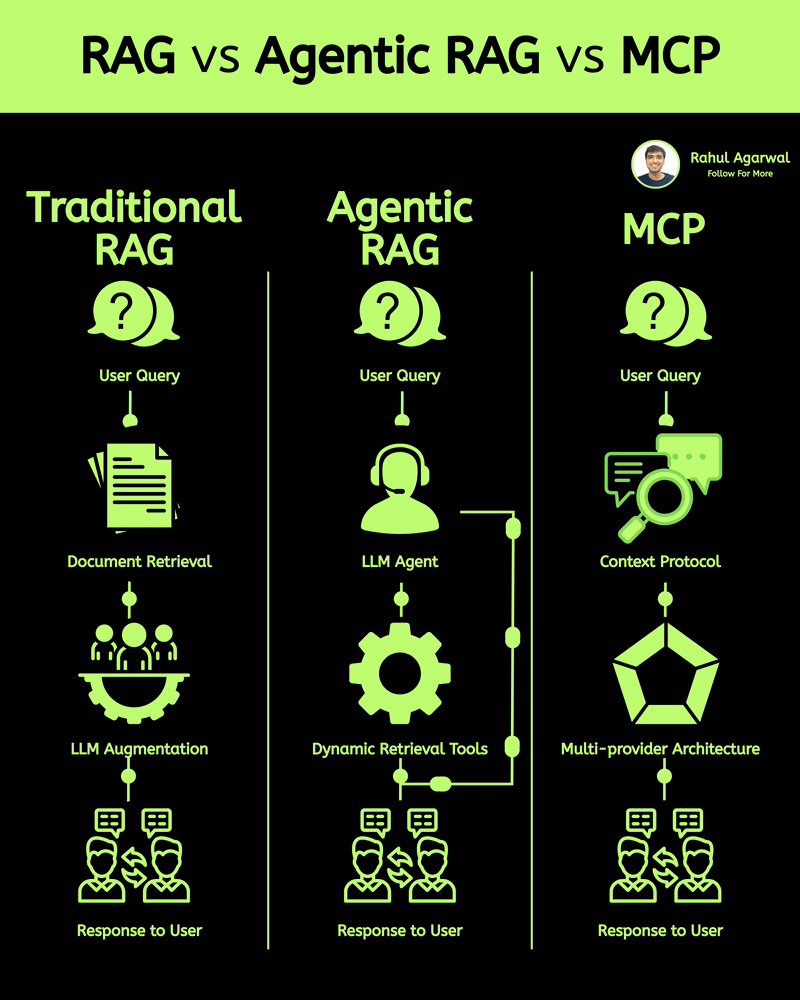
2 core ways AI learns and when to use each. I’ve explained each in a simple, detailed way below. 𝗣𝗼𝗶𝗻𝘁 1: 𝗘𝘅𝘁𝗲𝗿𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗞𝗻𝗼𝘄𝗹𝗲𝗱𝗴𝗲 𝗥𝗔𝗚 • Pulls information from outside sources like APIs, PDFs, or databases • Answers are based on real documents retrieved at query time • Knowledge lives 𝗼𝘂𝘁𝘀𝗶𝗱𝗲 the model 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗲-𝗧𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 • Stores information inside the model’s parameters • Model uses what it has learned during training • Doesn’t rely on external documents at runtime 𝗣𝗼𝗶𝗻𝘁 2: 𝗛𝗮𝗹𝗹𝘂𝗰𝗶𝗻𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀 𝗥𝗔𝗚 • Less likely to make things up because answers depend on retrieved facts • If retrieval is accurate, hallucinations stay low 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗲-𝗧𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 • May still hallucinate when the model faces something unfamiliar • Fills gaps by guessing patterns learned during training 𝗣𝗼𝗶𝗻𝘁 3: 𝗞𝗻𝗼𝘄𝗹𝗲𝗱𝗴𝗲 𝗨𝗽𝗱𝗮𝘁𝗲𝘀 𝗥𝗔𝗚 • Updating is instant, just add or modify documents • No model retraining needed 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗲-𝗧𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 • Updating knowledge requires collecting new examples • Needs another training cycle to reflect new facts 𝗣𝗼𝗶𝗻𝘁 4: 𝗘𝘁𝗵𝗶𝗰𝘀 & 𝗣𝗿𝗶𝘃𝗮𝗰𝘆 𝗥𝗔𝗚 • Risk depends on what data you store in external systems • Sensitive files or databases might get exposed if not secured 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗲-𝗧𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 • Risk comes from private information inside the training set • Model can leak or recall sensitive content it memorized 𝗣𝗼𝗶𝗻𝘁 5: 𝗥𝗲𝘀𝗼𝘂𝗿𝗰𝗲𝘀 & 𝗟𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗻𝗰𝘆 𝗥𝗔𝗚 • Needs a retrieval system, which adds a bit of delay • Requires storage + indexing + the model 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗲-𝗧𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 • Once trained, the model responds faster at runtime • No retrieval step in between 𝗣𝗼𝗶𝗻𝘁 6: 𝗜𝗻𝘁𝗲𝗿𝗽𝗿𝗲𝘁𝗮𝗯𝗶𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆 𝗥𝗔𝗚 • Answers can be traced back to specific documents • Easy to show citations or evidence 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗲-𝗧𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 • Works like a black box, no direct source for each answer • Harder to justify or audit responses 𝗣𝗼𝗶𝗻𝘁 7: 𝗖𝘂𝘀𝘁𝗼𝗺𝗶𝘇𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗥𝗔𝗚 • Controls 𝘸𝘩𝘢𝘵 information is provided (through retrieved files) • Doesn’t deeply control tone or writing style 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗲-𝗧𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 • You can shape tone, writing style, and domain expertise • Model adapts to patterns in training examples 𝗣𝗼𝗶𝗻𝘁 8: 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗮 𝗡𝗲𝗲𝗱𝘀 𝗥𝗔𝗚 • Doesn’t require special labeled datasets • Uses existing text, documents, and files as context 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗲-𝗧𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 • Needs structured, curated, high-quality training data • Must prepare examples that teach the model exactly how to behave ✅ 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗙𝗹𝗼𝘄 1. Understand where knowledge comes from (external vs internal) 2. Compare how each method handles hallucinations 3. Review how easy it is to update information 4. Check privacy risks on both sides 5. Consider compute and latency needs 6. Look at how traceable the answers are 7. Evaluate how much customization you need 8. Estimate the type and amount of data required ✅ Repost for others in your network who want to build AI systems.
Replies (1)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Aryan patil
Intern at YourStory ... • 1y
In traditional programming, the focus is on using rules and data to find answers. This is typically represented as rules + data = answers. In contrast, AI/ML takes a different approach: Answers + data = rules. In AI/ML, we train models by providing
See More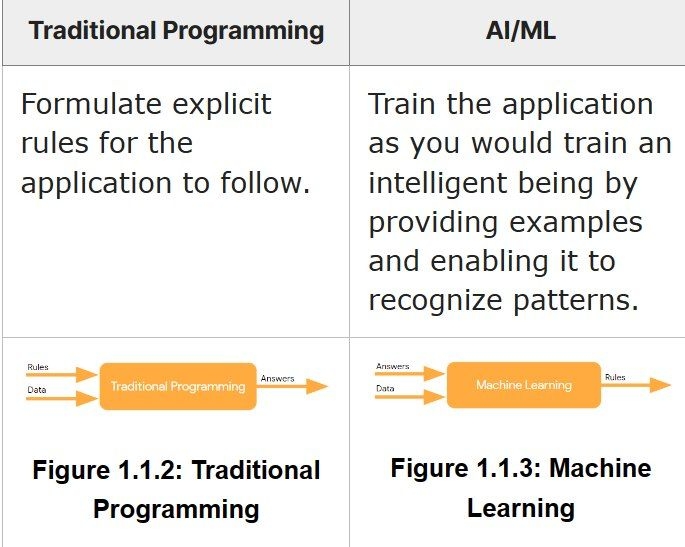
Download the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.












/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)





















