Back
vishakha Jangir
•
Set2Score • 10m
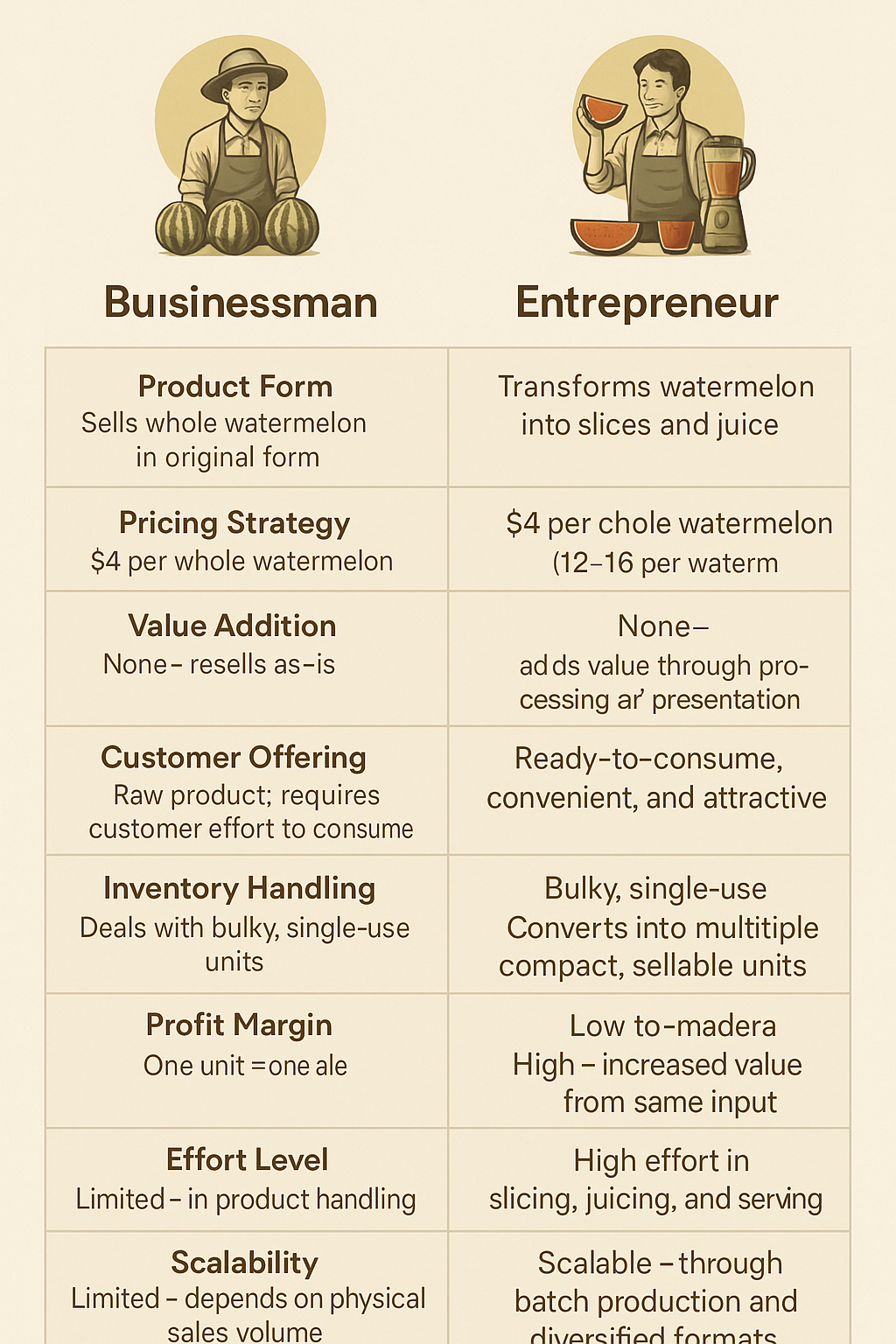
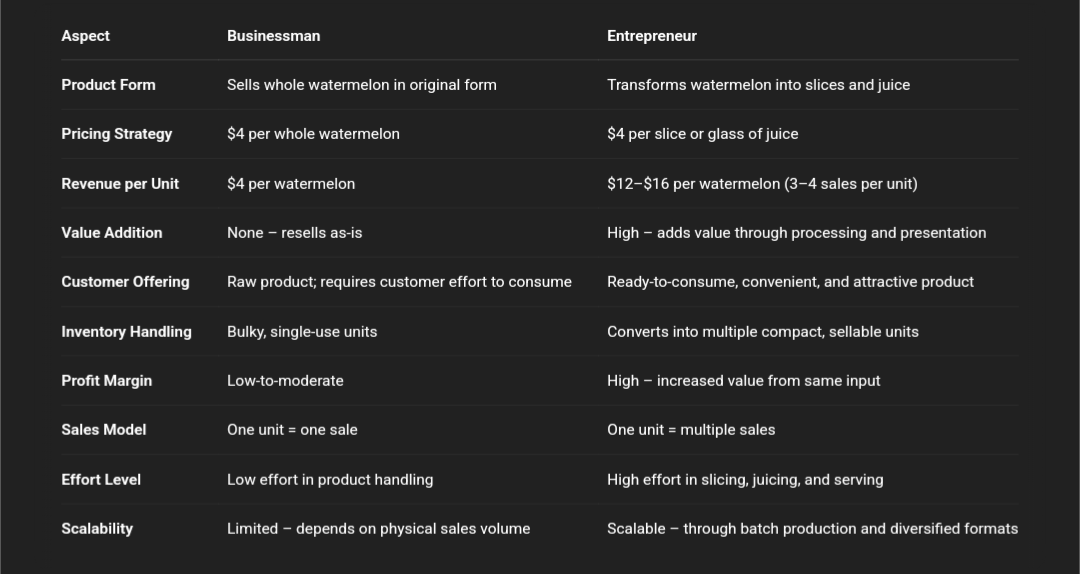
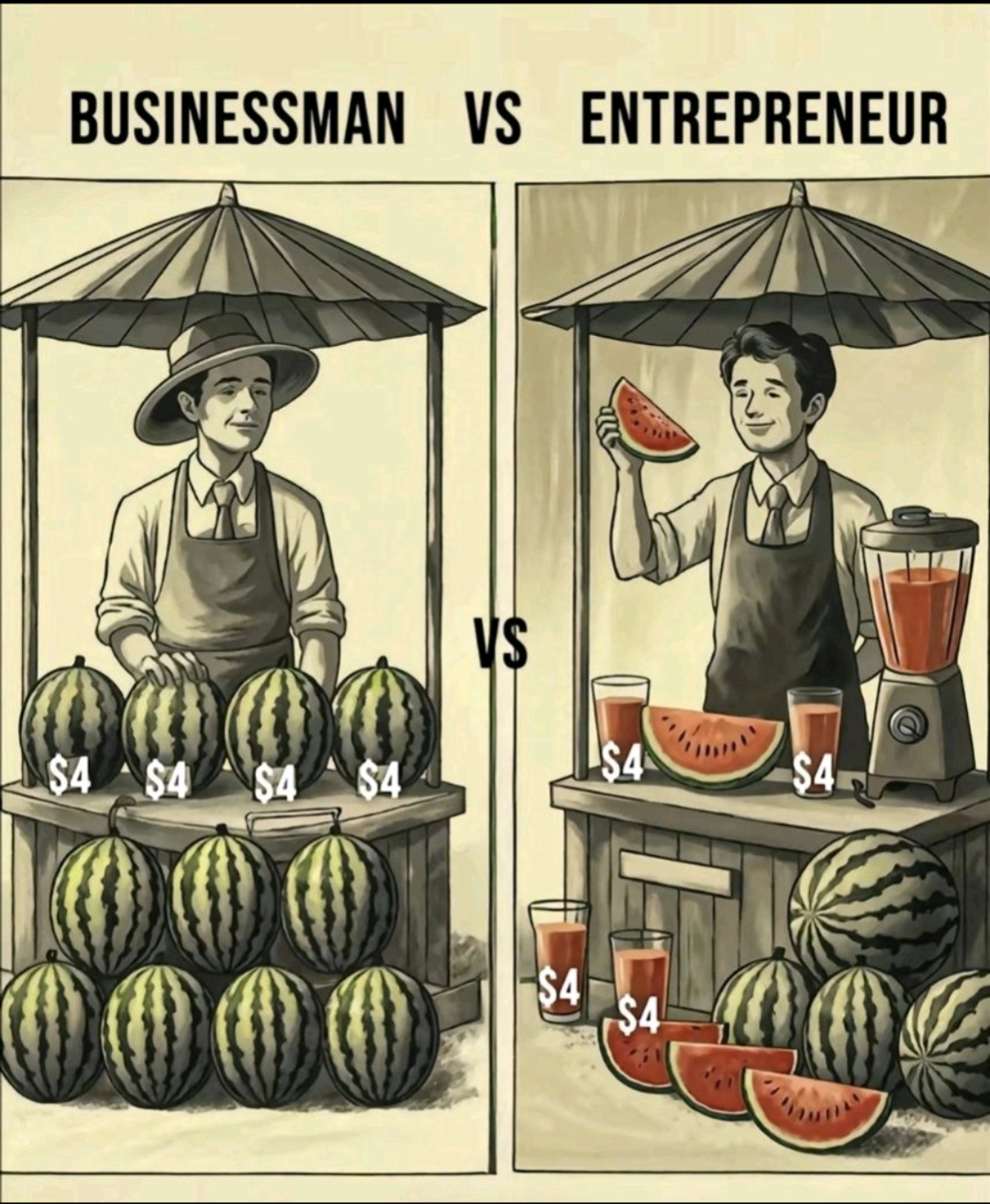
𝗕𝘂𝘀𝗶𝗻𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗺𝗮𝗻 𝗩𝘀 𝗘𝗻𝘁𝗿𝗲𝗽𝗿𝗲𝗻𝗲𝘂𝗿 : 𝗕𝘂𝘀𝗶𝗻𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗺𝗮𝗻 : Product Form: Sells whole watermelons in their raw, original state. Pricing Strategy: Fixed price of $4 per watermelon. Revenue per Unit: Earns only $4 per watermelon, regardless of size or content. Value Addition: No value added—product is sold as received. Customer Offering: Customer must do the cutting/preparation themselves. Inventory Handling: Deals with bulkier inventory; space and handling required for whole melons. Profit Margin: Low-to-moderate, depends on purchase cost vs. selling price. Sales Model: Linear—one product sold equals one transaction. Effort Level: Low effort in processing, moderate in logistics. Scalability: Limited by number of whole melons sold; no product differentiation. 𝗘𝗻𝘁𝗿𝗲𝗽𝗿𝗲𝗻𝗲𝘂𝗿 : Product Form: Transforms whole watermelons into slices and juice. Pricing Strategy: Sells each slice or juice glass for $4. Revenue per Unit: Extracts 3–4 slices or juices from one watermelon = $12–$16 per melon. Value Addition: High value addition through processing and presentation. Customer Offering: Ready-to-consume product; adds convenience and appeal. Inventory Handling: Converts bulky items into multiple compact, sellable units. Profit Margin: High, due to increased perceived value and markup on portions. Sales Model: Multi-point sale from one base unit (one watermelon = multiple transactions). Effort Level: High effort in preparation, but higher returns. Scalability: Scalable through batch production, branding, and upselling convenience. Follow vishakha Jangir for more such business insights.
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Mandeep Patel
CA | Fractional CFO • 1y
The end value addition of Q-commerce, devastating for the riders involved. The median payout in Tier-I city after working for 10 hours a day is coming ~18k generously. As per the living cost across metros, it will become increasingly tough for them t
See MoreBhargav Bhadresa
Grow with the flow • 9m
we have made the packaging of our D2C and B2B frozen food brand we are starting from Ahmedabad first then we will target the whole Gujarat and move forward as per the process Any ideas to start or any suggestions to keep in mind during launch thi
See More



Nawal
Entrepreneur | Build... • 1y
Swiggy makes over ₹40 crore 🔥 a year just through rounding off—something most users hardly notice. Have you ever observed that the handling fee on a Swiggy Instamart order is ₹7.30? While most platforms stick to whole numbers, this seemingly odd 30
See More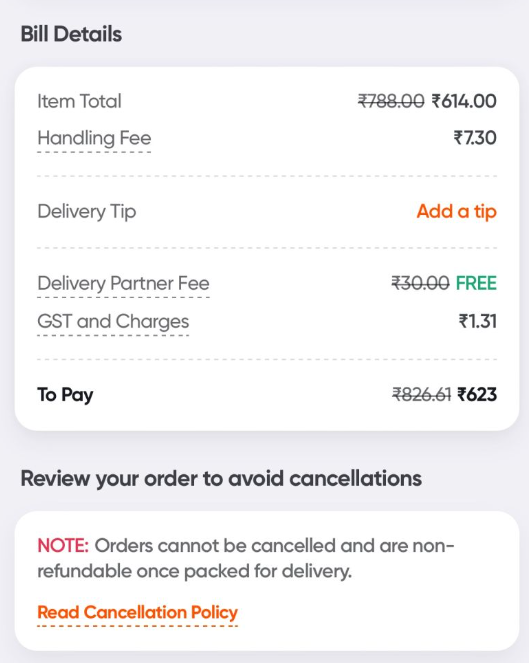
Naman Rathi
Student of Computer ... • 1y
📍 Smart Product Locator for Supermarkets – Game Changer or Not? 🤔 Ever wandered around a supermarket, struggling to find a product? Imagine an AI-powered Product Locator that helps you find items instantly, saving time and effort. Sounds useful, r
See MoreDownload the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.














/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)


















