Back
SHIV DIXIT
CHAIRMAN - BITEX IND... • 1y
• Advanced Cost Concepts 1. Economies of Scale Cost advantages achieved by increasing production. Types: Internal (e.g., bulk purchasing), External (e.g., industry-wide benefits). 2. Diseconomies of Scale Increased costs due to inefficiencies in large-scale operations. 3. Fixed-to-Variable Cost Ratio Analyzing cost structure to determine flexibility and risk. 4. Incremental Costs Costs incurred due to additional production. 5. Absorption vs. Variable Costing Absorption Costing: Includes all fixed and variable costs in product cost. Variable Costing: Only variable costs included in product cost. • Cost Reduction Strategies 1. Operational Efficiency Streamline workflows and automate repetitive tasks. 2. Supplier Negotiations Negotiate better rates or bulk discounts. 3. Outsourcing Reduce fixed costs by outsourcing non-core tasks. 4. Energy Efficiency Invest in energy-saving equipment to lower utility costs. 5. Inventory Optimization Implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems to reduce storage costs. 6. Lean Production Minimize waste during manufacturing processes. 7. Regular Cost Audits Identify and eliminate unnecessary expenses. • Main Cost Management Metrics 1. Cost Efficiency Ratio Measures the efficiency of cost usage. Efficiency Ratio = Total Costs ÷ Revenue × 100 2. Cost Variance (CV) Difference between estimated and actual costs. CV = Budgeted Cost - Actual Cost 3. Gross Margin Gross Margin = (Revenue - COGS) ÷ Revenue × 100 4. Operating Margin Operating Margin = (Operating Income ÷ Revenue) × 100 • Practical Examples 1. Scenario 1: Break-Even Analysis A startup with ₹50,000 fixed costs produces 1,000 units at a variable cost of ₹200/unit. Selling price is ₹300/unit. BEP: ₹50,000 ÷ (₹300 - ₹200) = 500 units 2. Scenario 2: Marginal Cost Analysis A bakery incurs ₹2,000 in costs to produce 100 cakes. Producing an additional cake costs ₹20. MC: ₹20 per cake 3. Scenario 3: Opportunity Cost Choosing between investing ₹1,00,000 in marketing (expected revenue: ₹5,00,000) or a new product launch (expected revenue: ₹4,50,000). Opportunity Cost: ₹50,000 • Tips and Tricks for Cost Management 1. Track costs regularly using accounting software like QuickBooks or Zoho Books. 2. Distinguish between necessary and unnecessary expenses. 3. Always calculate the ROI before incurring significant costs. 4. Negotiate long-term contracts with suppliers for stability. 5. Focus on high-margin products to maximize profitability
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
SHIV DIXIT
CHAIRMAN - BITEX IND... • 1y
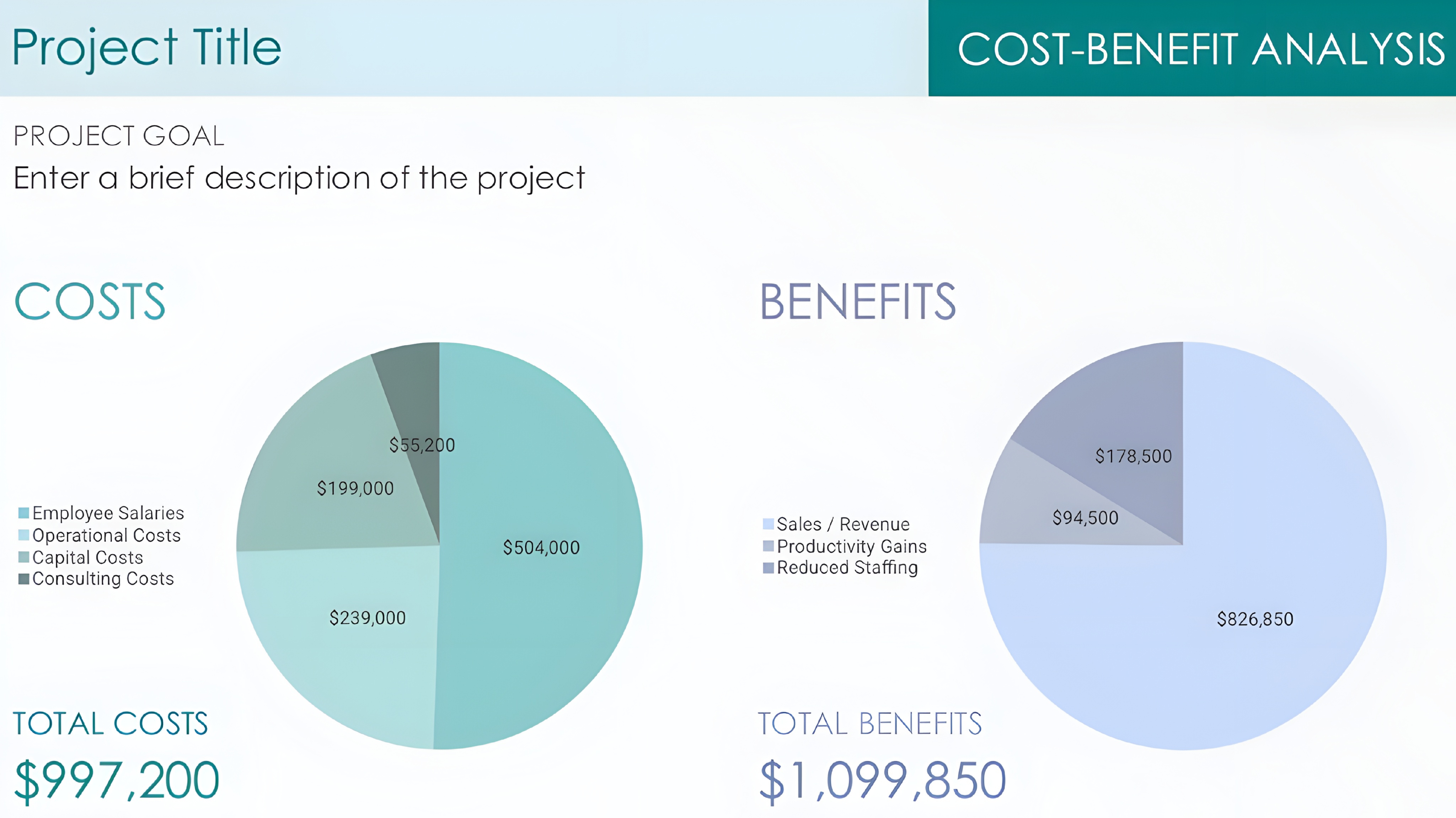
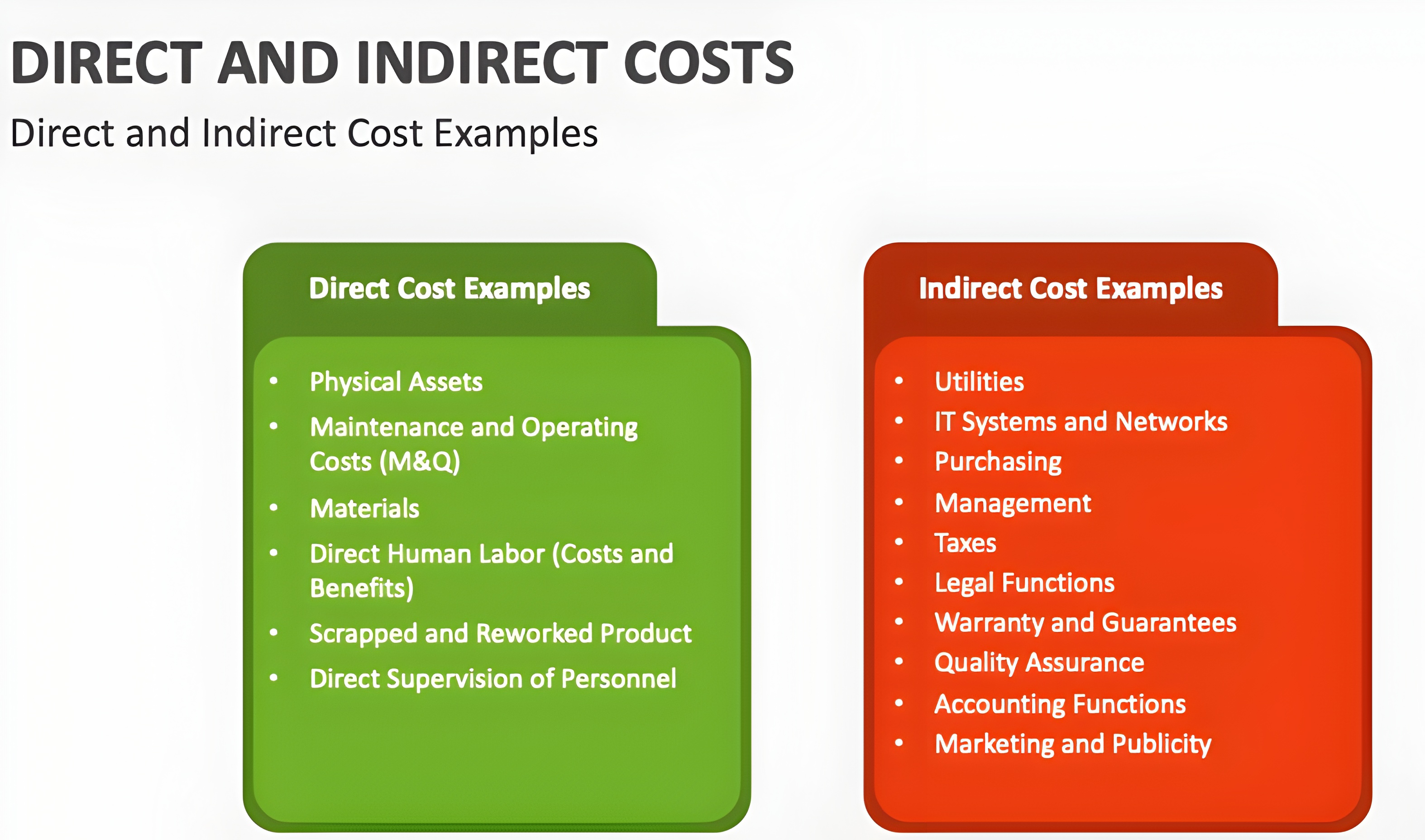
💰Learn Start-up Maths —( Concept - 2 )📊 💱 All details about “ COST ” Whenever someone asks you about the cost just tell him that “ Cost the amount of money that a business spends on the creation of something ” • There are many types of cost #
See More

Vivek Joshi
Director & CEO @ Exc... • 9m
Mastering Unit Economics Unit economics isn’t just a metric—it’s your startup’s financial DNA. It reveals whether each customer adds value or drains cash. Here’s how to build your unit economics from scratch: 1. Define Your Economic Unit What drives
See More
Medial User
Hey I am on Medial • 11m
Ek company ban ka liya 1. *Company ka type*: Private Limited, Partnership, Sole Proprietorship, etc. 2. *Industry*: Kya company kya business karegi? 3. *Location*: Company kahan registered hogi? 4. *Initial investment*: Company ko kitna initial inv
See MoreSwapnil gupta
Founder startupsunio... • 9m
✅ Must for Business Students 🥇10 Most Important metrics that are asked by investors. 1. Revenue Growth Rate 2. Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) 3. Burn Rate 4. Cash Runway 5. Gross Margin 6. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) 7. Customer Lifetime Val
See MoreDownload the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.
















/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)




















