Back
SHIV DIXIT
CHAIRMAN - BITEX IND... • 1y
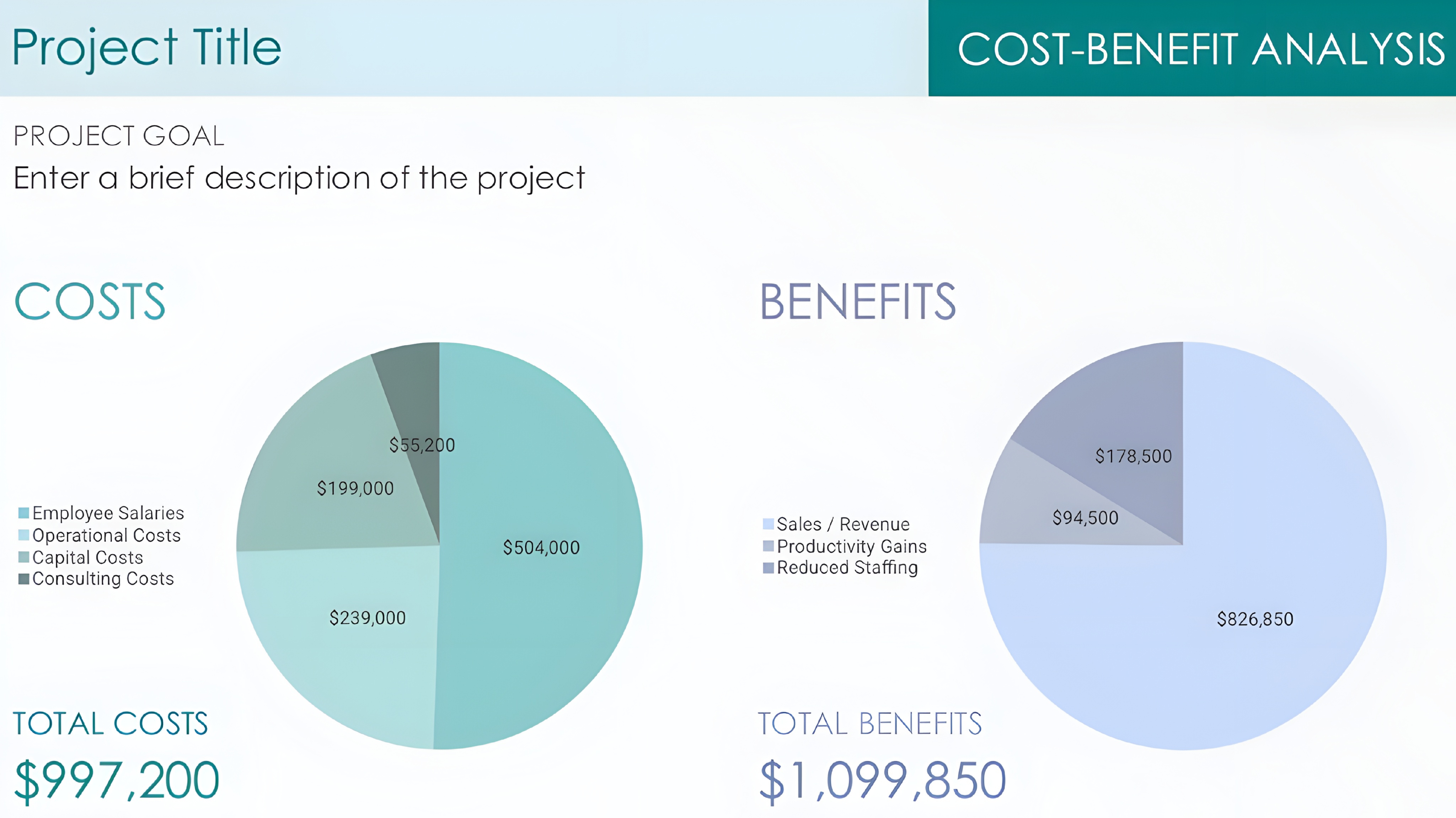
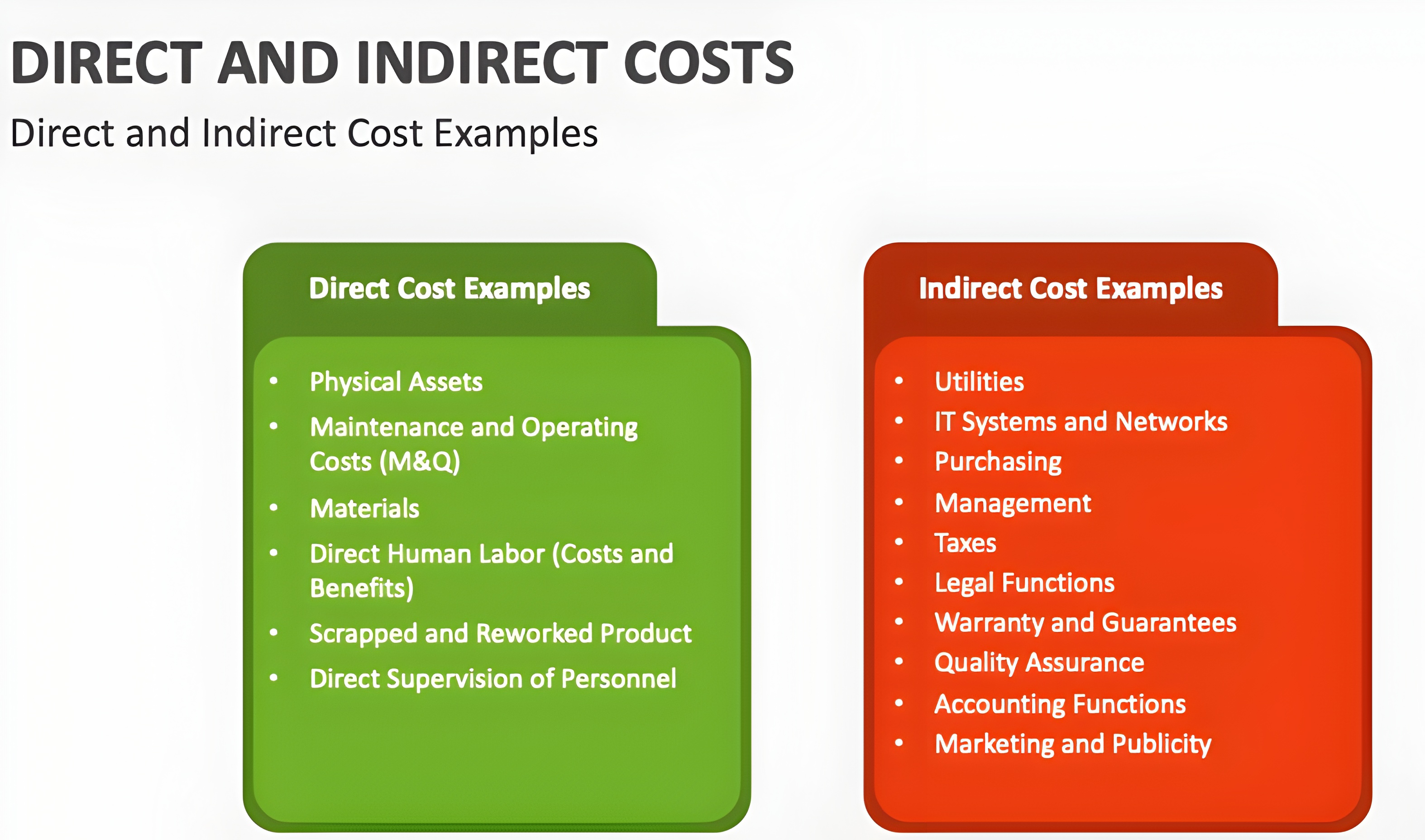
💰Learn Start-up Maths —( Concept - 2 )📊 💱 All details about “ COST ” Whenever someone asks you about the cost just tell him that “ Cost the amount of money that a business spends on the creation of something ” • There are many types of cost # Based on Behavior — 1=} Fixed Costs: Do not change with the level of production or sales like ( rent, salaries ) • Do not change regardless of output 2=} Variable Costs: Change directly with the level of production or sales ( like raw materials, commission ) • Proportional to production volume. 3=} Semi-Variable Costs: Partially fixed and partially variable ( like electricity bill with a fixed charge plus usage-based costs ) • Contain both fixed and variable components. # Based on Nature 1=} Direct Costs: Can be traced directly to a specific product or service ( like raw materials, labor for production ) 2=} Indirect Costs: Cannot be traced directly and support overall operations ( like administrative expenses, factory maintenance ) # Based on Function 1=} Production Costs: Related to manufacturing goods like machinery maintenance) 2=} Administrative Costs: Related to the management of the business like office salaries) 3=} Selling and Distribution Costs: Related to marketing, sales, and delivering goods like advertising, transportation). 4=} Research and Development Costs: Expenses for innovation and development of new products # Based on Controllability 1=} Controllable Costs: Can be influenced or controlled by a specific manager like raw material usage) 2=} Uncontrollable Costs: Cannot be controlled by a specific manager like depreciation) # Based on Time 1=} Historical Costs: Costs that have already been incurred like past material purchases). 2=} Future Costs: Costs expected to be incurred in the future like planned investments) # Based on Decision-Making 1=} Opportunity Costs: The cost of the next best alternative foregone ( like potential income from renting a building instead of using it) • The potential benefit lost when choosing one option over another 2=} Sunk Costs: Costs already incurred and cannot be recovered (like money spent on a failed project) • Costs already incurred that cannot be recovered (like R&D for failed projects) 3=} Incremental Costs: Additional costs incurred by choosing a particular option 4=} Marginal Costs: The cost of producing one additional unit • The additional cost of producing one extra unit 5=} Imputed Costs: Costs not involving direct cash outlay but considered for decision-making like owner’s time) # Based on Accounting Treatment 1=} Capital Costs: Incurred for acquiring fixed assets like machinery, buildings). 2=} Revenue Costs: Incurred for day-to-day operations ( like repairs, fuel). # Based on Association with Units 1=} Unit Costs: Costs per unit of production (like cost per sandwich) 2=} Batch Costs: Costs associated with producing a batch of goods (like setting up a machine for a production run) # Based on Industry or Specific Use 1=} Prime Costs: Direct material, labor, and expenses directly related to production. 2=} Conversion Costs: Costs incurred to convert raw materials into finished products ( labor + overhead). # Other cost 1=} Operating Costs Includes all costs necessary for day-to-day business activities. Types: Fixed + Variable operating costs 2=} Non-Operating Costs Costs unrelated to core operations (like loan interest, penalties 3=} Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) • Direct costs tied to goods or services sold 4=} Overhead Costs • Indirect costs required for business operations ( like utilities, admin salaries). • Cost Formulas and Calculations 1=} Cost of Goods Sold COGS = Opening Inventory + Purchases - Closing Inventory 2=} Total Cost TC = Fixed Costs + Variable Costs 3=} Marginal Cost MC = Change in Total Cost ÷ Change in Quantity 4=} Break-Even Point BEP (units) = Fixed Costs ÷ (Selling Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Un 5=} Profit Margin Profit Margin = (Revenue - Total Cost) ÷ Revenue × 100 6=} Contribution Margin Contribution Margin = Selling Price - Variable Cost 7=} Cost Per Unit Total Cost ÷ Total Units Produced 8=} Return on Investment (ROI) ROI = (Net Profit - Total Cost) ÷ Total Cost × 100 • Cost Management Methodologies 1. Activity-Based Costing Allocates indirect costs based on activities driving them Example: Assigning machine maintenance costs to products that use the machine 2. Standard Costing Pre-determined cost estimates for budgeting and performance evaluation 3. Target Costing Setting a product cost target based on desired profit margin and competitive price 4. Lifecycle Costing Analyzing costs across a product’s lifecycle (development, production, marketing, etc.) 5. Lean Costing Eliminating waste to reduce costs and increase efficiency 6. Kaizen Costing Continuous cost reduction through small, incremental improvements 🚀 Check Comment Section For More 🤍


Replies (14)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Dipesh Pimpale
Data Analytics | 𝐀�... • 1y
Imporant metric for Start-ups - Break Even Units Suppose we are a shoe brand and we want to calculate our units to be sold for break even (No profit No Loss) Fixed Cost - 4,00,000 Selling Price per Unit - 1200 Variable Cost per Unit - 800 Contributi
See More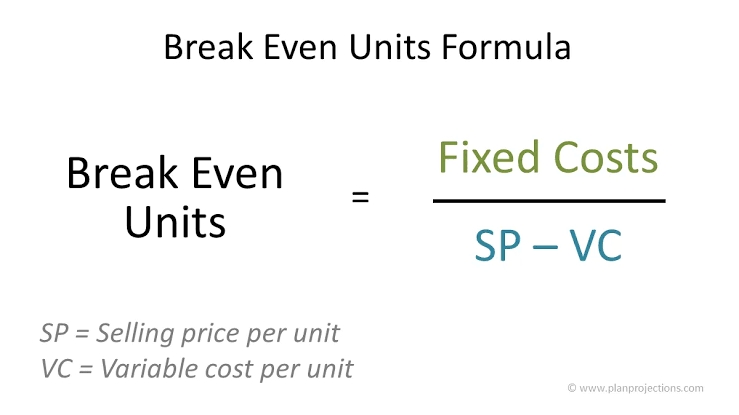
Vivek Joshi
Director & CEO @ Exc... • 9m
Mastering Unit Economics Unit economics isn’t just a metric—it’s your startup’s financial DNA. It reveals whether each customer adds value or drains cash. Here’s how to build your unit economics from scratch: 1. Define Your Economic Unit What drives
See More
Medial User
Hey I am on Medial • 11m
Ek company ban ka liya 1. *Company ka type*: Private Limited, Partnership, Sole Proprietorship, etc. 2. *Industry*: Kya company kya business karegi? 3. *Location*: Company kahan registered hogi? 4. *Initial investment*: Company ko kitna initial inv
See MoreRajan Paswan
Building for idea gu... • 1y
[Business Resource] A 40-minute session by LLA on how to build and sell products, based on their real experience with the product Jagruk Journal. They covered the following topics: R&D: 1. Ideation 2. Market Research 3. Documentation 4. Waterfall
See MoreAbdul Alim
Building Duolingo fo... • 1y
Whataboyut free water marketing in india..? Cost of plastic bottle - 2 re (500ml) label cost - 2 re labour cost - 1 re water - .5 re total - 5.5 re if I charge 4 re from company and do advertisement of 2 company 1 on front other on back will it wor
See MoreDownload the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.


















/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)




















