Back
Anonymous
Hey I am on Medial • 1y
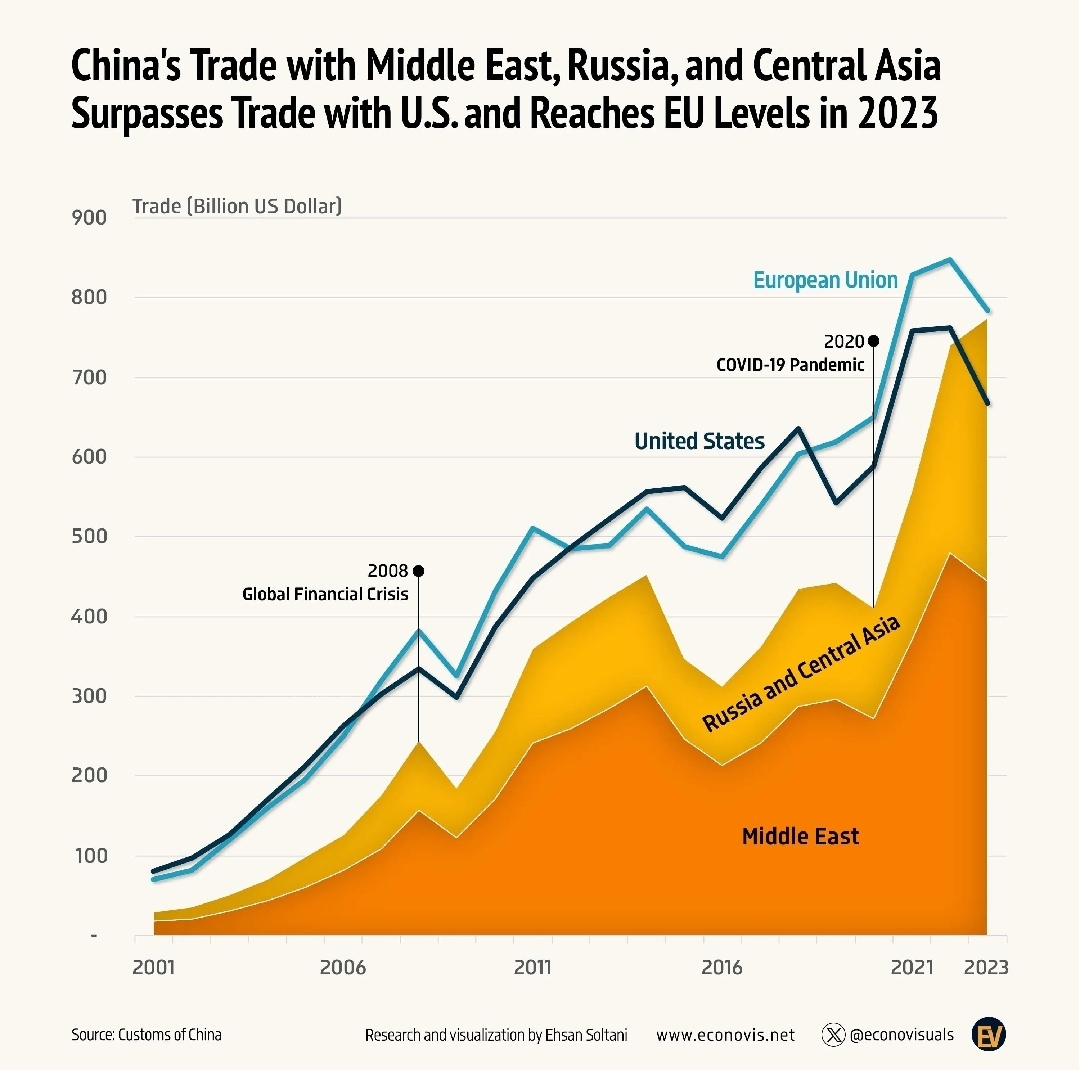
7. The Data of Macroeconomics GDP (Gross Domestic Product): Definition and components (consumption, investment, government purchases, net exports). Unemployment: The different types (frictional, structural, cyclical) and how they are measured. Inflation: Consumer Price Index (CPI) as a measure of inflation, and the effects of inflation on purchasing power. 8. The Real Economy in the Long Run Economic Growth: Focus on factors that drive long-term growth, such as capital accumulation, technology, and human capital. Savings and Investment: Role of savings in the economy and the trade-off between consumption and investment. 9. Money and Prices in the Long Run Money Supply and Inflation: The relationship between the money supply and price levels. Over time, inflation erodes money's value. The Quantity Theory of Money: Explains how inflation is linked to an increase in the money supply. 10. Short-Run Economic Fluctuations Business Cycles: Causes of short-term fluctuations in GDP and employment. Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply: How these curves interact to determine overall economic output and price levels. Monetary and Fiscal Policy: Tools the government and central banks use to influence the economy (taxes, government spending, interest rates). 11. The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy The Federal Reserve (Central Banking): How central banks manage the money supply to control inflation and influence interest rates. Fiscal Policy Tools: Government spending and taxation used to stabilize the economy during recessions or booms. 12. Trade and Global Economics Benefits of Trade: How trade allows countries to specialize and increase overall efficiency and production. Trade Barriers: Tariffs, quotas, and their impact on international trade and economies. Exchange Rates: How currency values fluctuate and affect imports/exports. Summary Takeaways: Efficiency vs. Equity: Markets are often efficient but may not always be equitable, prompting government intervention. Rational Decision-Making: Most economic decisions involve weighing marginal costs and marginal benefits. Market Dynamics: Supply and demand, trade-offs, and incentives shape the economy. Macroeconomic Stabilization: Governments and central banks play key roles in managing inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Atharva Deshmukh
Daily Learnings... • 1y
Have studied about Monetary Policy in short and it's effect. The monetary policy is a tool through which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) controls the money supply by controlling the interest rates. RBI is India’s central bank. While setting the int
See MoreKimiko
Startups | AI | info... • 8m
According to the International Monetary Fund's April 2025 World Economic Outlook, India is projected to become the world's fourth-largest economy in 2025. The IMF anticipates India's nominal GDP for the fiscal year 2026 to reach $4.187 trillion, sl
See More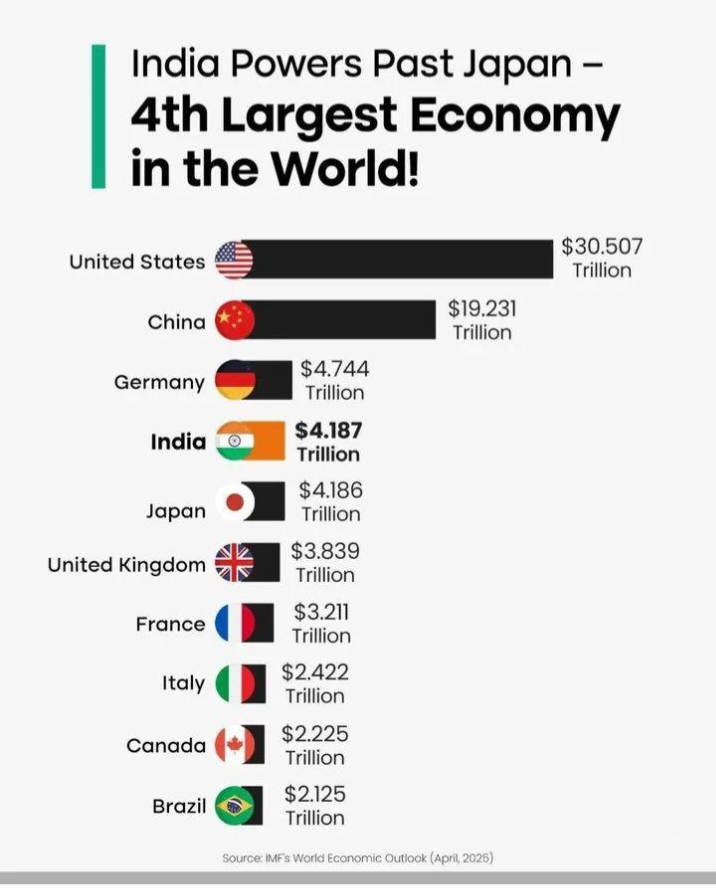
Tushar Aher Patil
Trying to do better • 8m
Exploring Negative Interest Rate Policy (NIRP) Have you ever wondered about central banks setting interest rates below zero? This is known as Negative Interest Rate Policy (NIRP). Here's a quick look at this unconventional monetary tool: ✍️ What is i
See More
Download the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.