Back
Hemant Prajapati
•
Techsaga Corporations • 1y
Firstly, bookmark 📑 this post:------- . . The Rise and Fall of BlackBerry: A Case Study . . 📱 Introduction -> Former leader in the smartphone industry, known for its QWERTY keyboard and secure email services. -> Popular among professionals for business communication and security features. 📈 Peak Success -> Dominated the market in the mid-2000s with a significant share in the enterprise segment. -> Iconic models like BlackBerry Bold and Curve were widely adopted globally. 🔒 Key Strengths -> Secure communication: End-to-end encryption was a major selling point for businesses and governments. -> Email and messaging: BlackBerry Messenger (BBM) was a pioneer in instant messaging. -> Physical keyboard: Differentiated itself with a tactile keyboard, appealing to professional users. 🔄 Market Shifts -> Apple’s iPhone launch in 2007 introduced a touch screen interface and App Store, revolutionizing the smartphone industry. -> Android emerged as a strong competitor with its open-source platform and wide range of devices. ❌ Strategic Missteps -> Overconfidence in physical keyboards: Underestimated the consumer preference shift towards touch screens. -> Delayed transition to touchscreen devices: Lagged behind competitors in adopting new technology. -> Limited app ecosystem: Focused on enterprise users but failed to attract developers, leading to a sparse app marketplace. 📉 Decline -> Loss of market share: Rapid decline in sales as consumers preferred iOS and Android devices. -> Failed product launches: BlackBerry 10 OS and devices like Z10 and Q10 did not resonate with the market. -> Leadership challenges: Frequent changes in leadership created strategic inconsistency. 🔧 Attempted Recovery -> Shift to software: Transitioned focus from hardware to enterprise software and security solutions. -> Licensing strategy: Licensed BlackBerry brand to third-party manufacturers, exiting the smartphone hardware business. 💻 Current Status -> Focused on cybersecurity, IoT, and enterprise solutions with offerings like BlackBerry Spark. -> No longer a smartphone manufacturer but retains brand recognition in software services. 📚 Lessons Learned -> Importance of adaptability: Failure to quickly adapt to market changes can lead to rapid decline. -> Consumer-centric innovation: Ignoring consumer trends and focusing solely on niche markets can limit growth. -> Leadership and vision: Consistent leadership and clear vision are crucial in navigating market transitions. 🔚 Conclusion -> BlackBerry's journey serves as a reminder of the fast-paced nature of the tech industry. -> Reinvention and focusing on core strengths have allowed BlackBerry to remain relevant in the enterprise sector despite its exit from the smartphone market. . . 🔗 Like | 🔄 Repost | 💬 Comment | ⭐ Bookmark | 👥 Follow
Replies (1)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Mohammad Asaad Sayed
My mind to me a king... • 1y
BlackBerry vs. iPhone: A Market Survey 📱 1. User Base : -BlackBerry: Corporate professionals, security-focused users. -iPhone: Mass-market appeal, from Gen Z to executives. 2. Key Strengths : -BlackBerry: Enterprise-grade security, physical keyboa
See MoreSameer Patel
Work and keep learni... • 1y
Business Incidents BlackBerry a pioneer in the smartphone industry. Despite initially dominating the market with its secure email and messaging services, BlackBerry failed to innovate and adapt to the rapidly changing smartphone landscape. The compa
See MoreJaswanth Jegan
Founder-Hexpertify.c... • 1y
How Apple and Android Killed Blackberry Billions to bankruptcy #6 The first BlackBerry device was released in 1999.They gained popularity by their unique physical keyboard design.They reached peak with the BB Curve and BB Bold series known for thei
See More
Ashish Singh
Finding my self 😶�... • 1y
🤯This is how Blackberry killed itself. Back in 2010, Blackberry had a 43% market share in smartphones. However, by 2016, it was down to 0%. So, why did people abandon Blackberry? 🧐 See, in the 2000s, Blackberry was the ultimate status symbol, us
See More


Anonymous
Hey I am on Medial • 1y
☹️ In the era of AI and technology, our pursuit of development and advancement has inadvertently led to the decline of bird populations. Each smartphone user contributes to this phenomenon. In recent times have you noticed a decrease in bird sighting
See More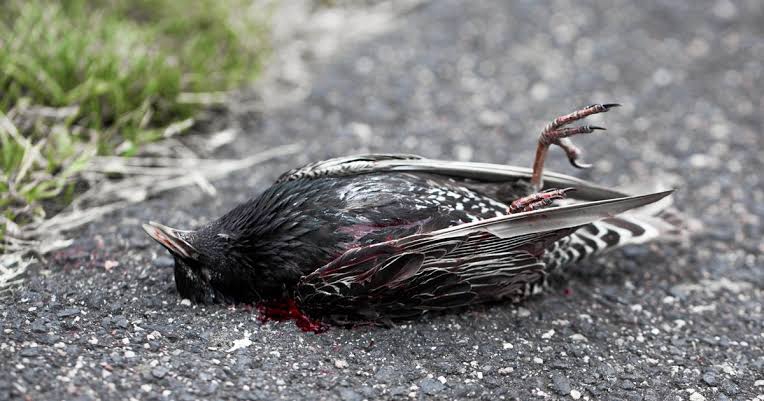
Download the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.

















/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)




















