Back
Rahul Agarwal
Founder | Agentic AI... • 2m
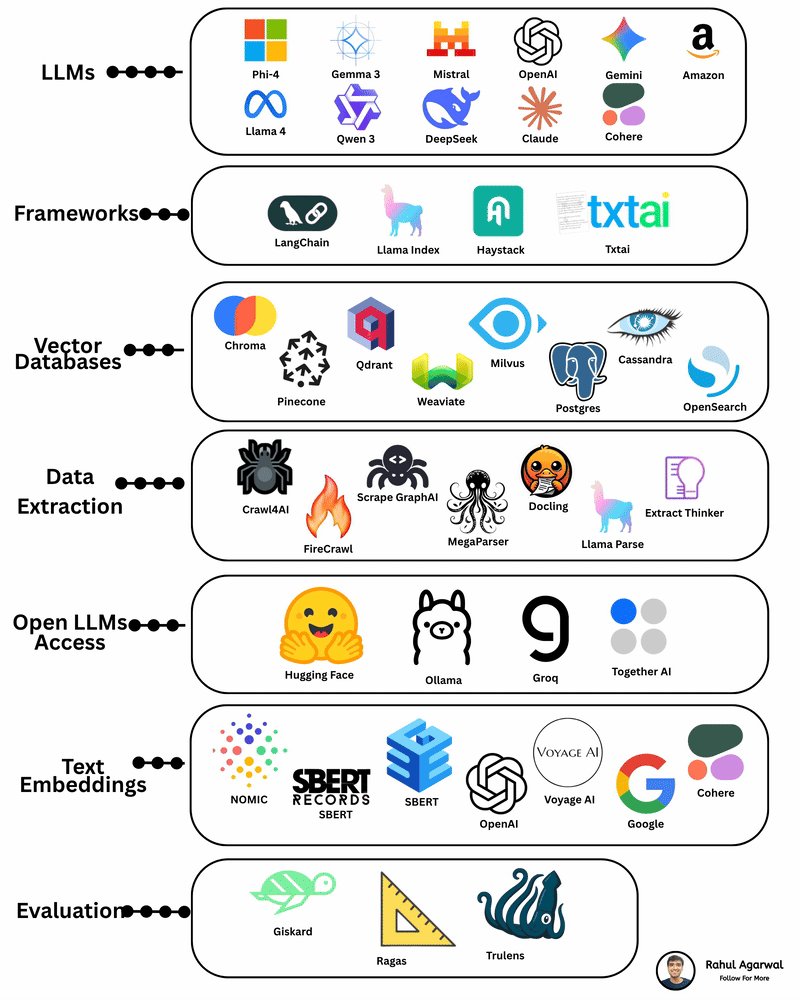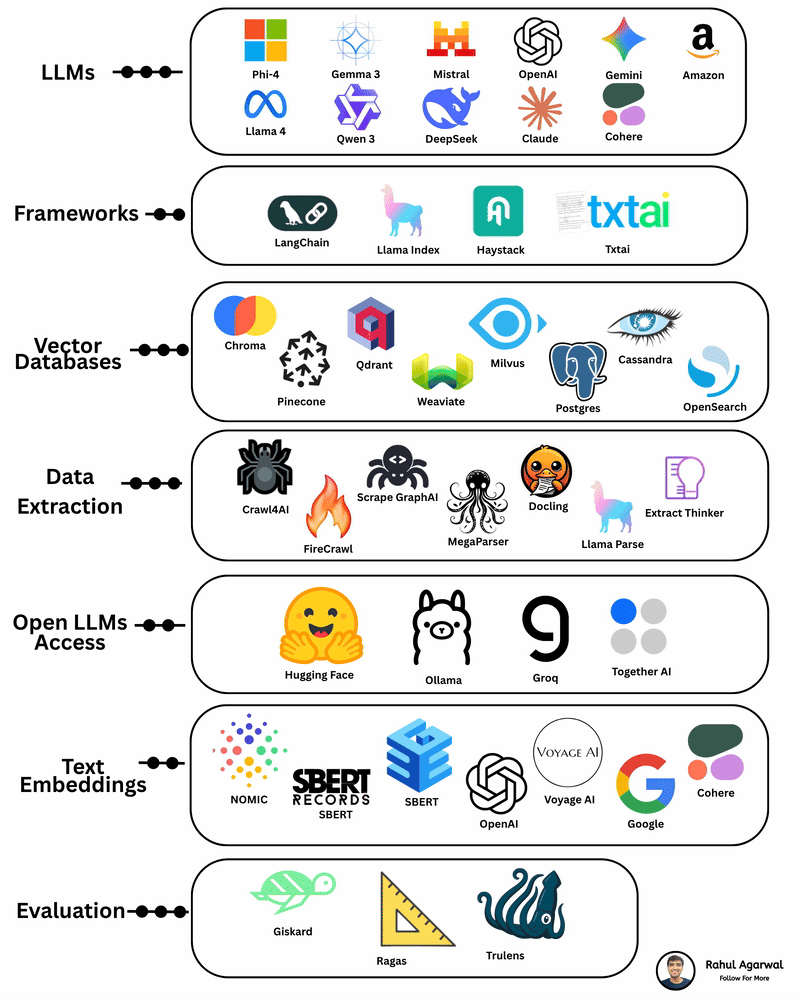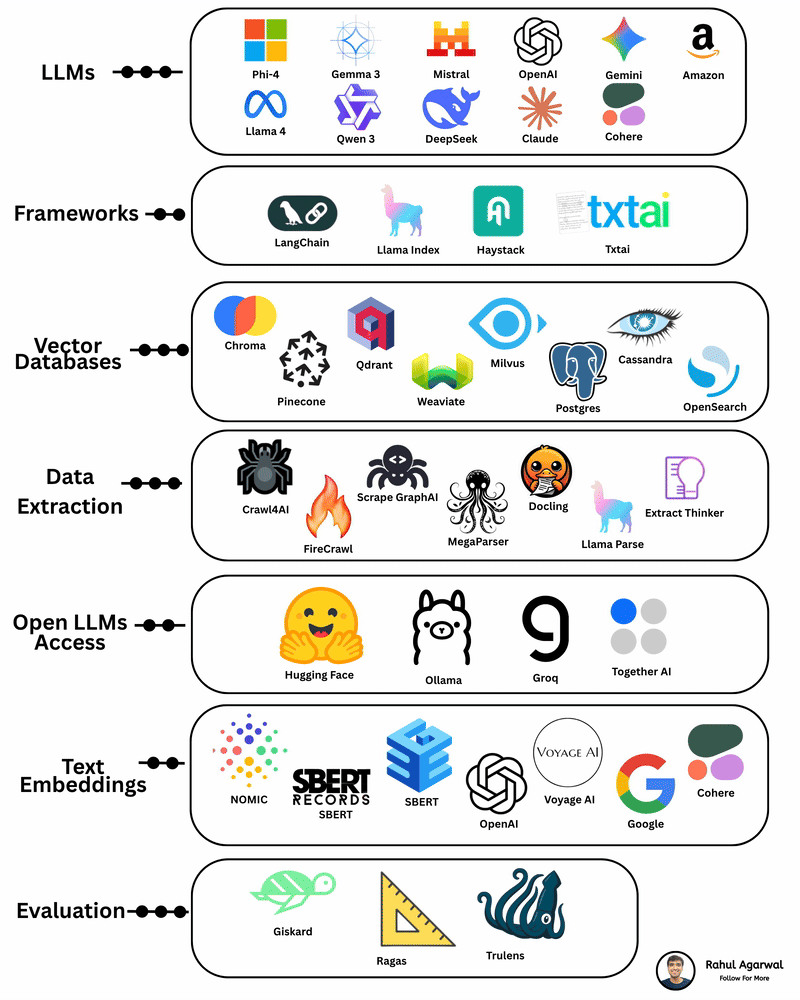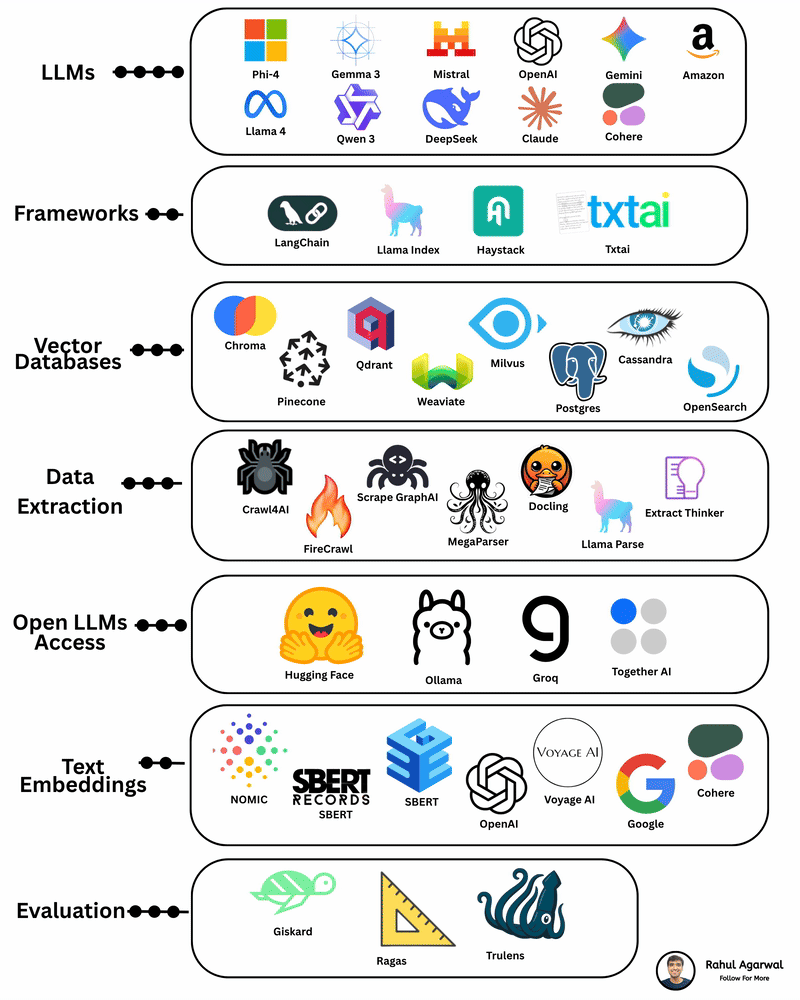
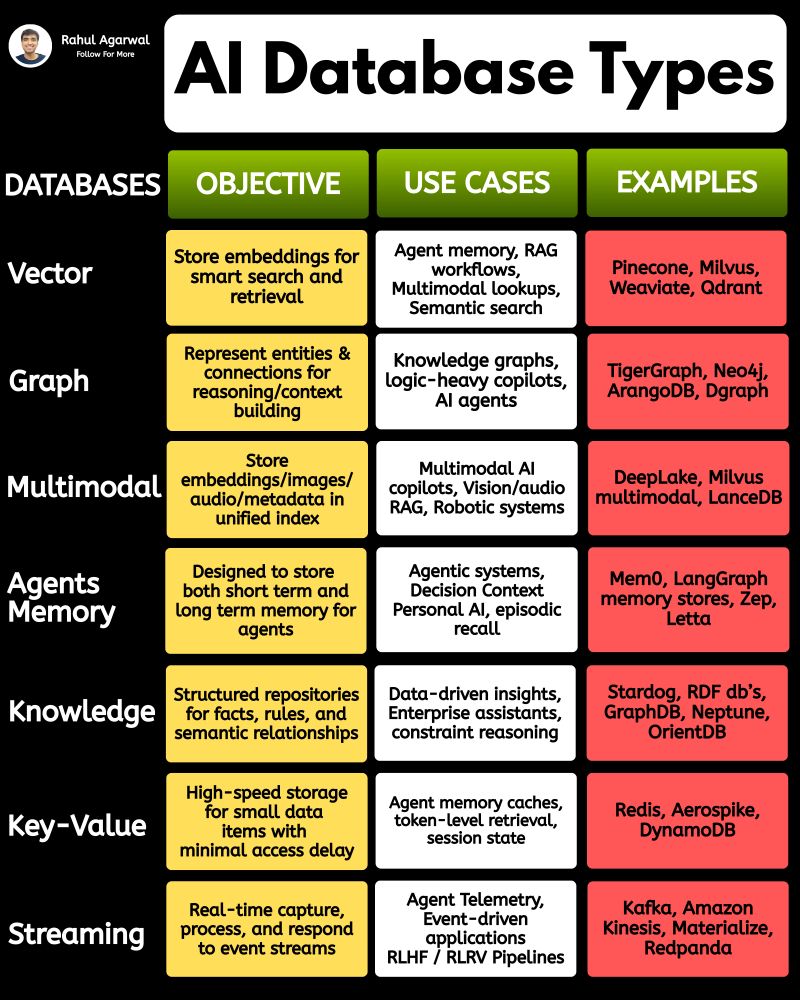
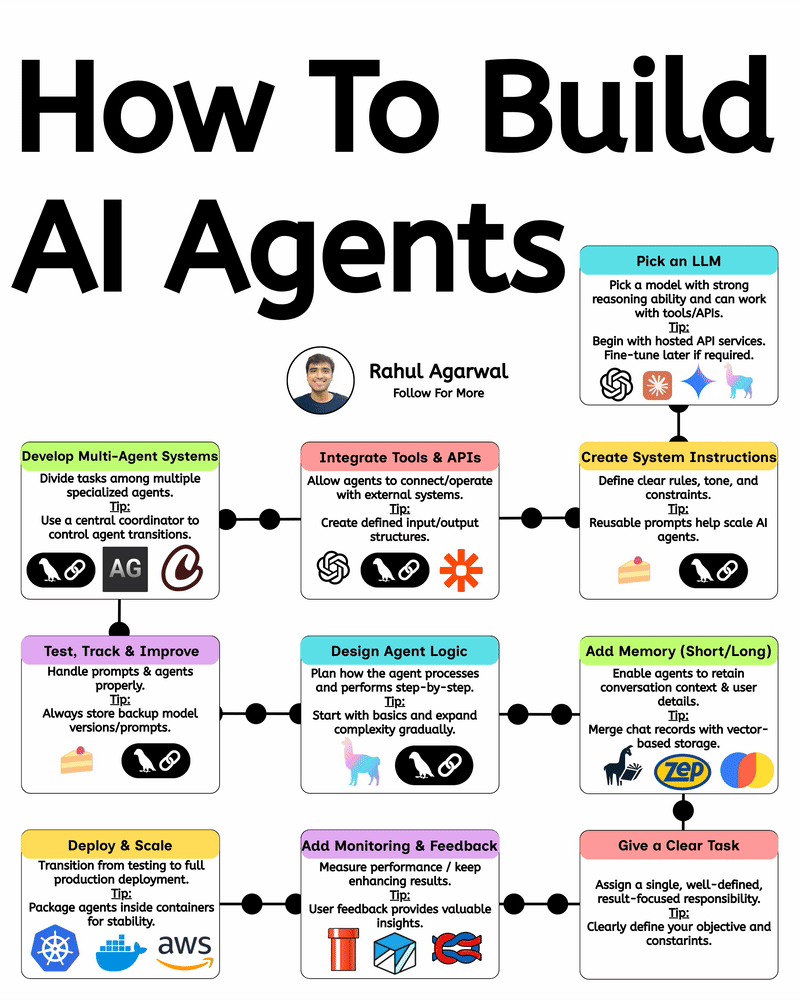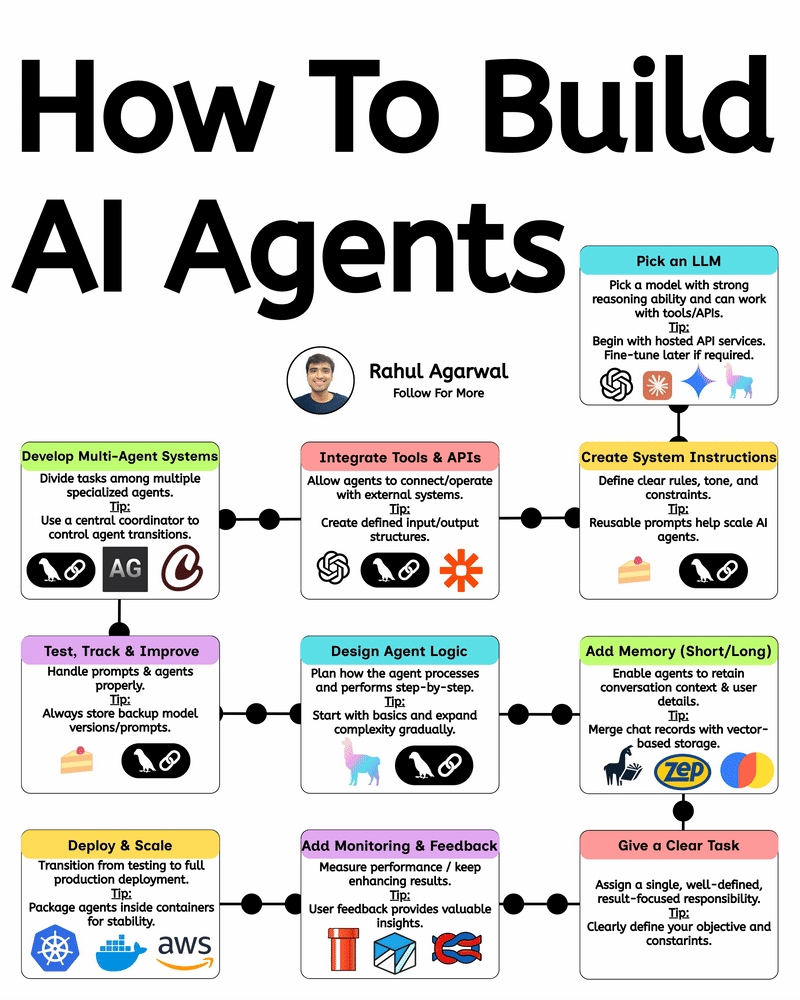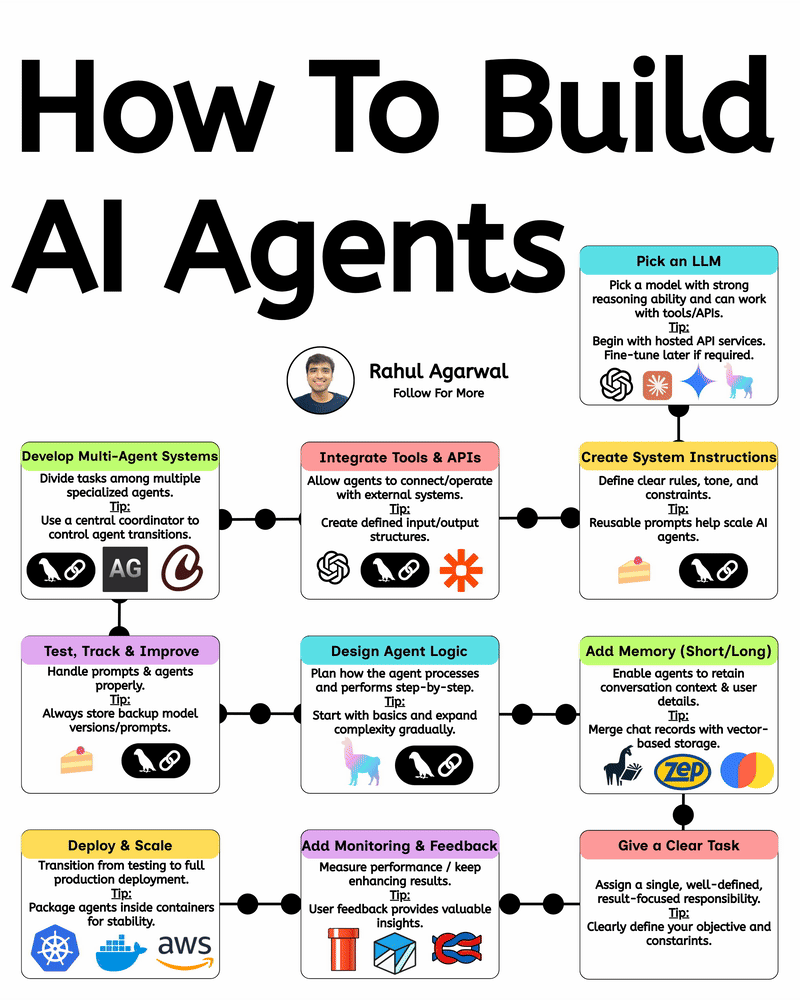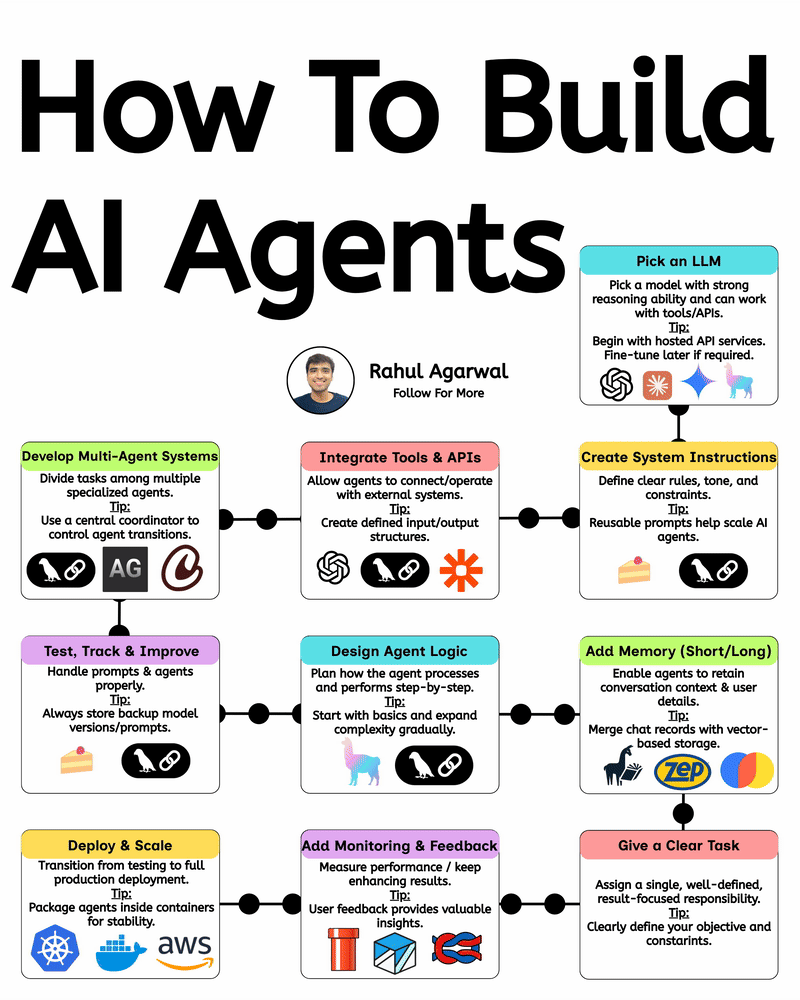
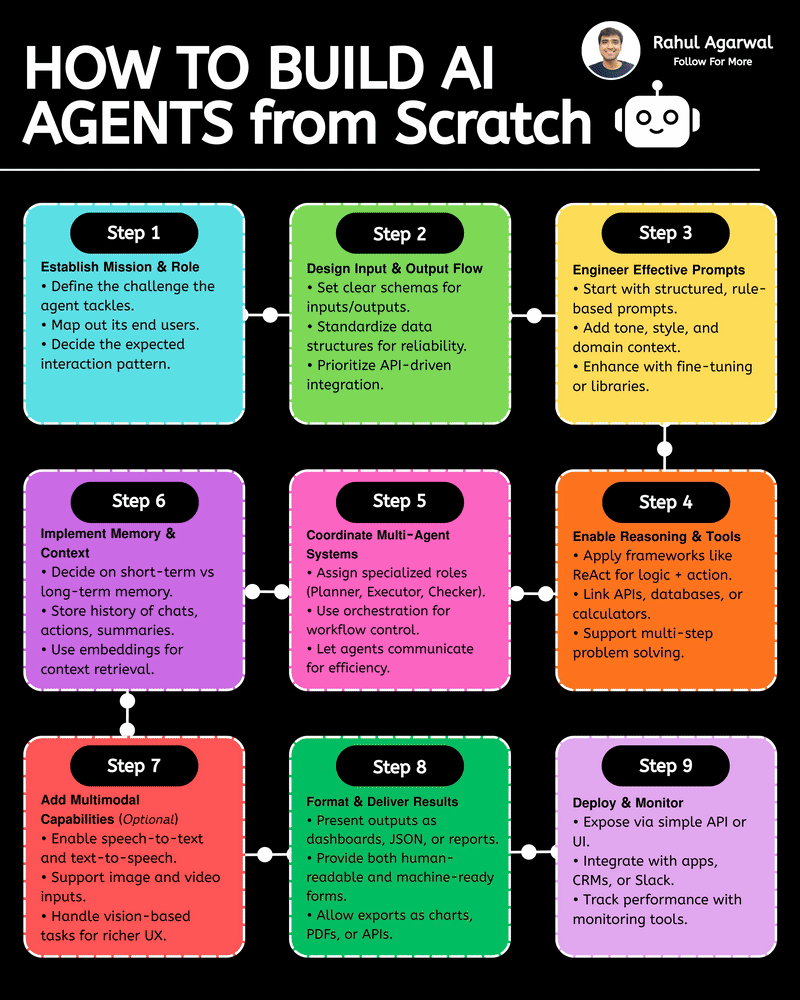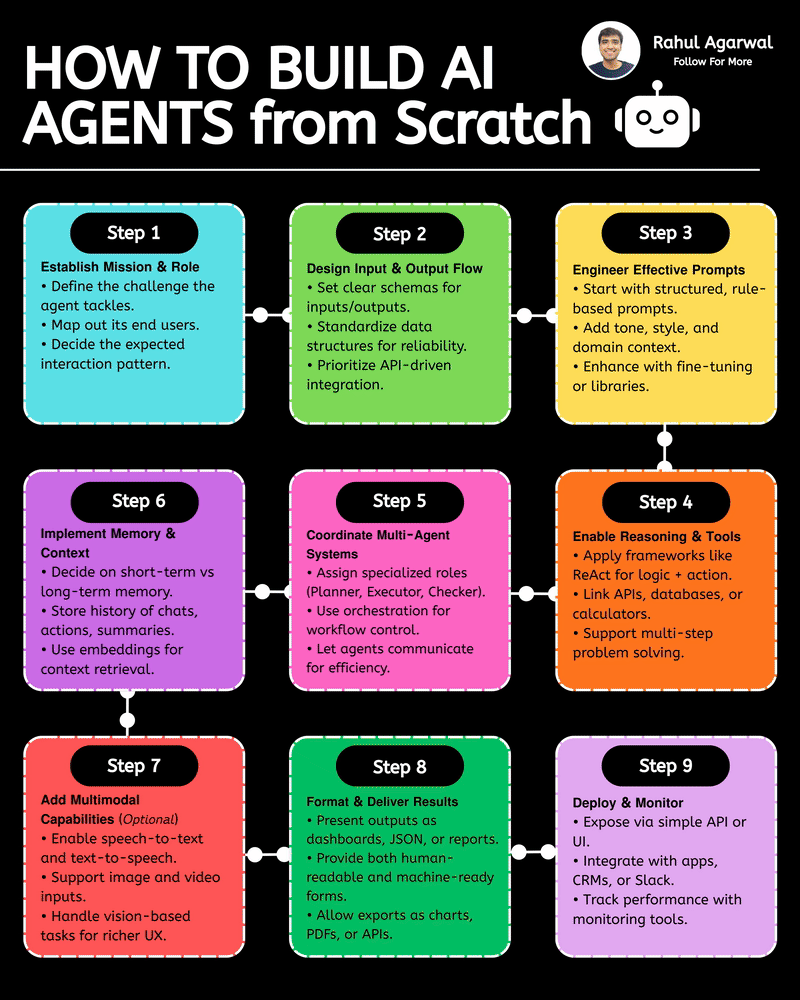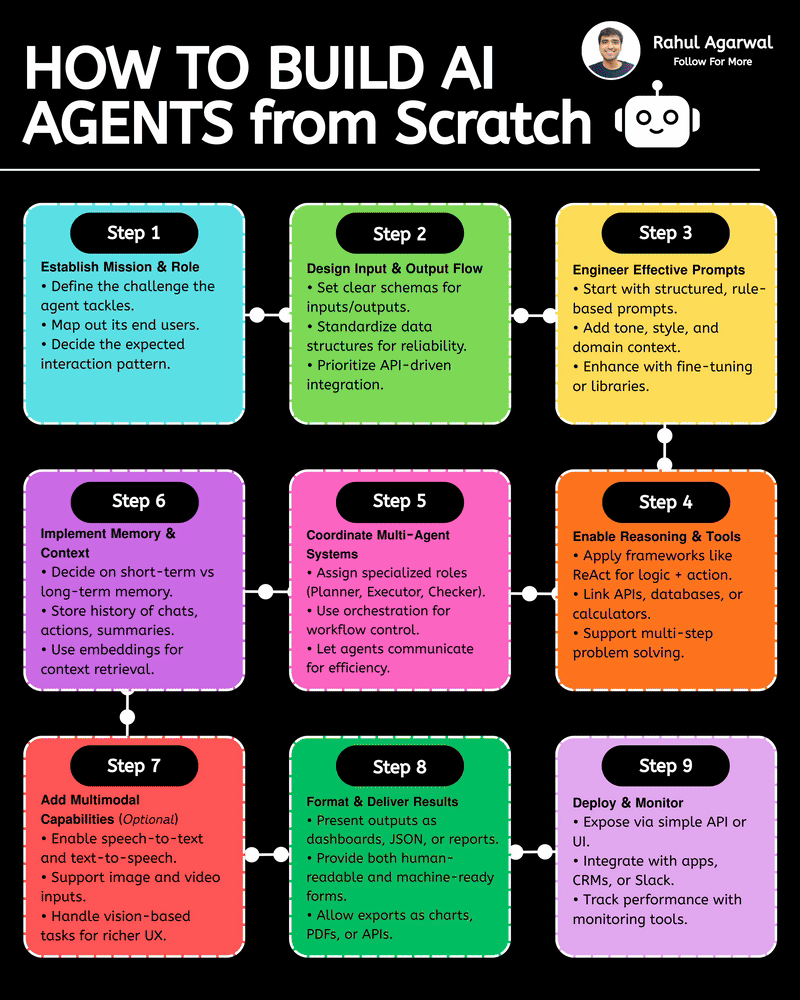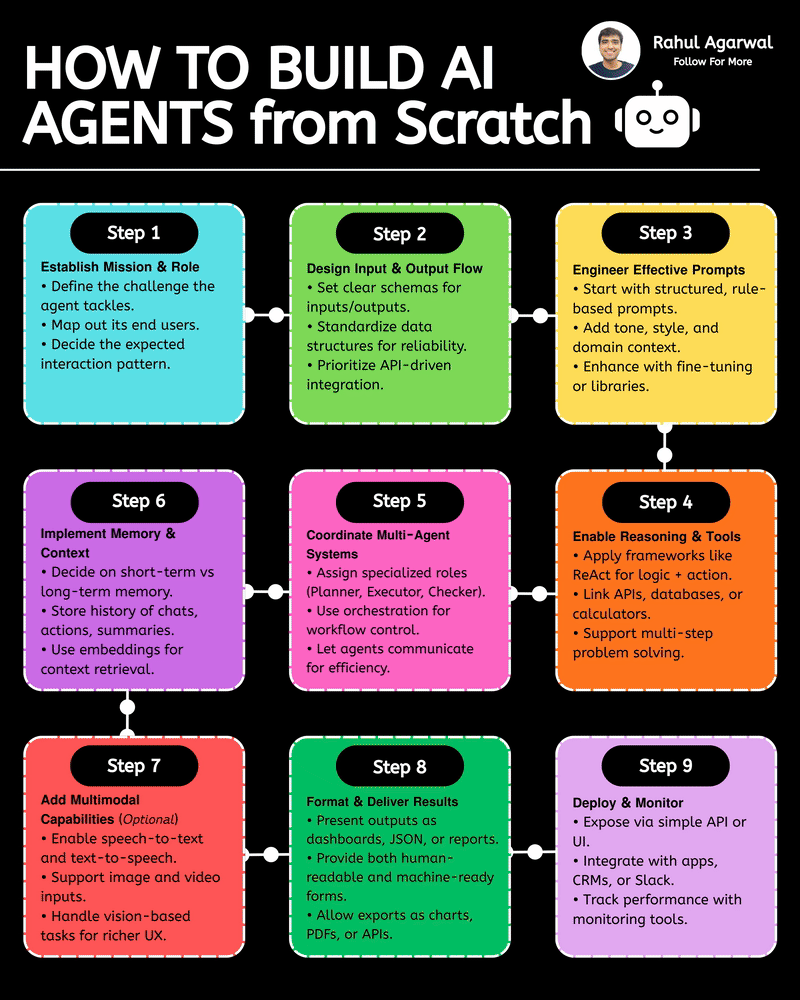
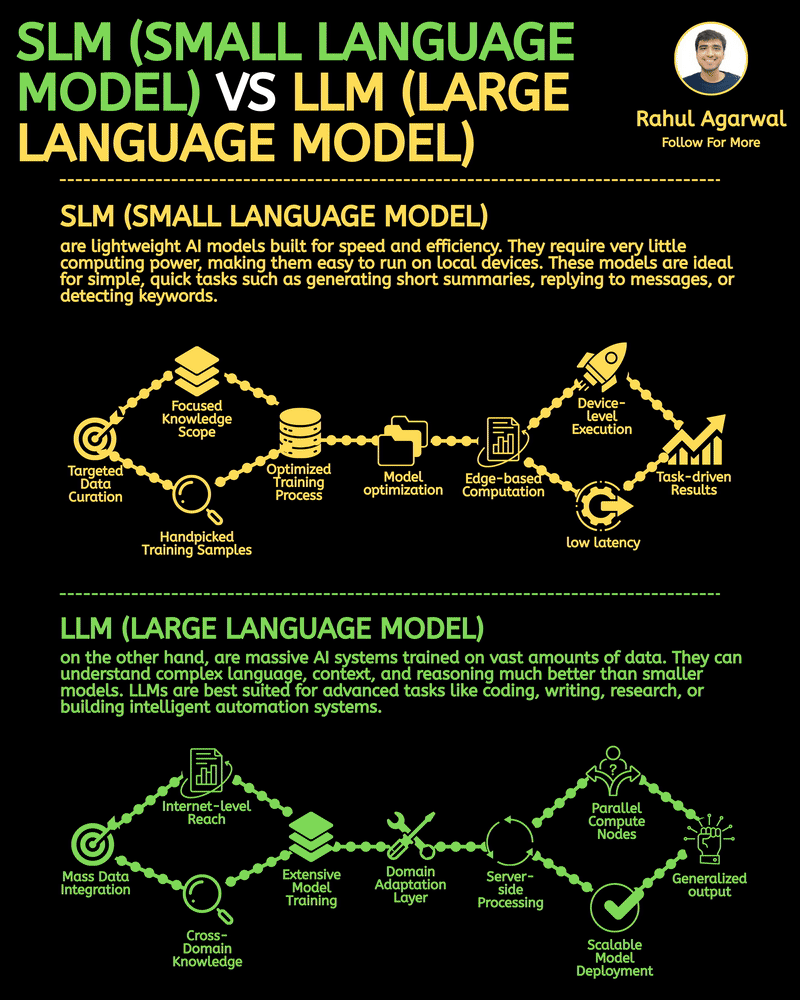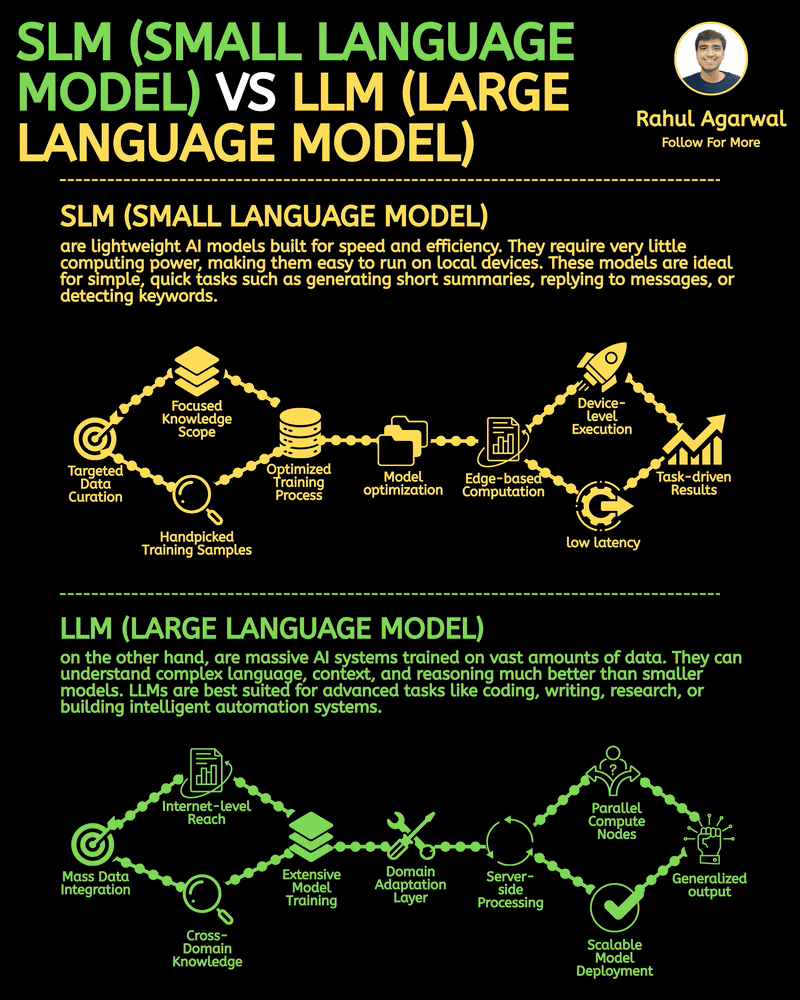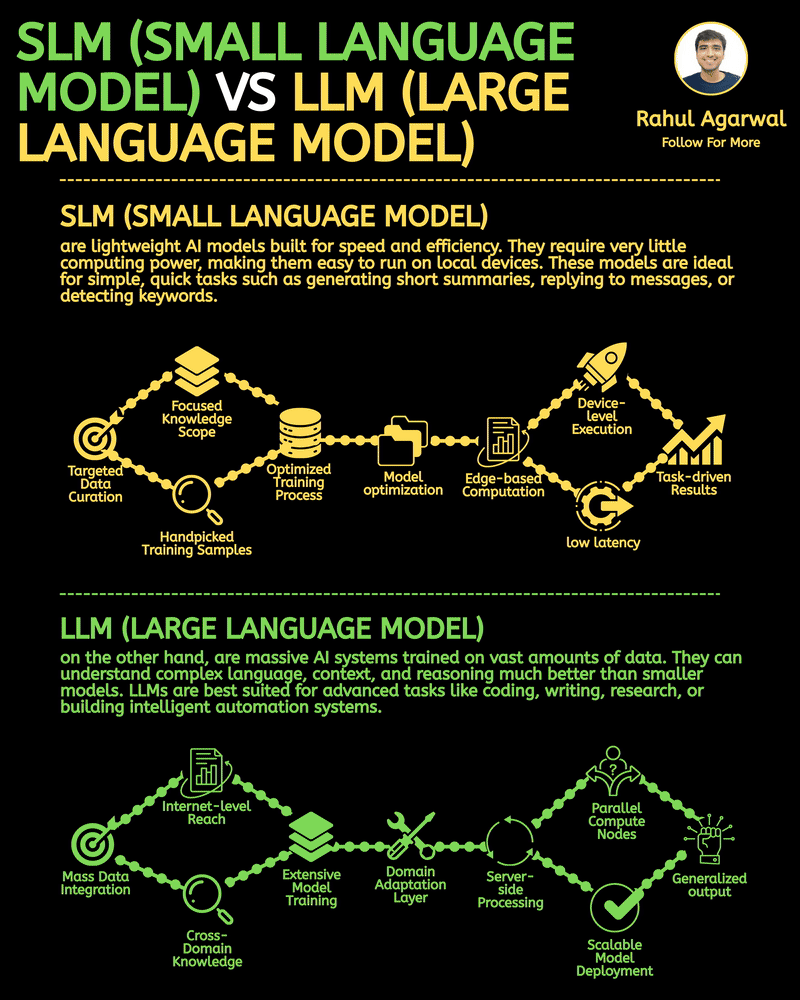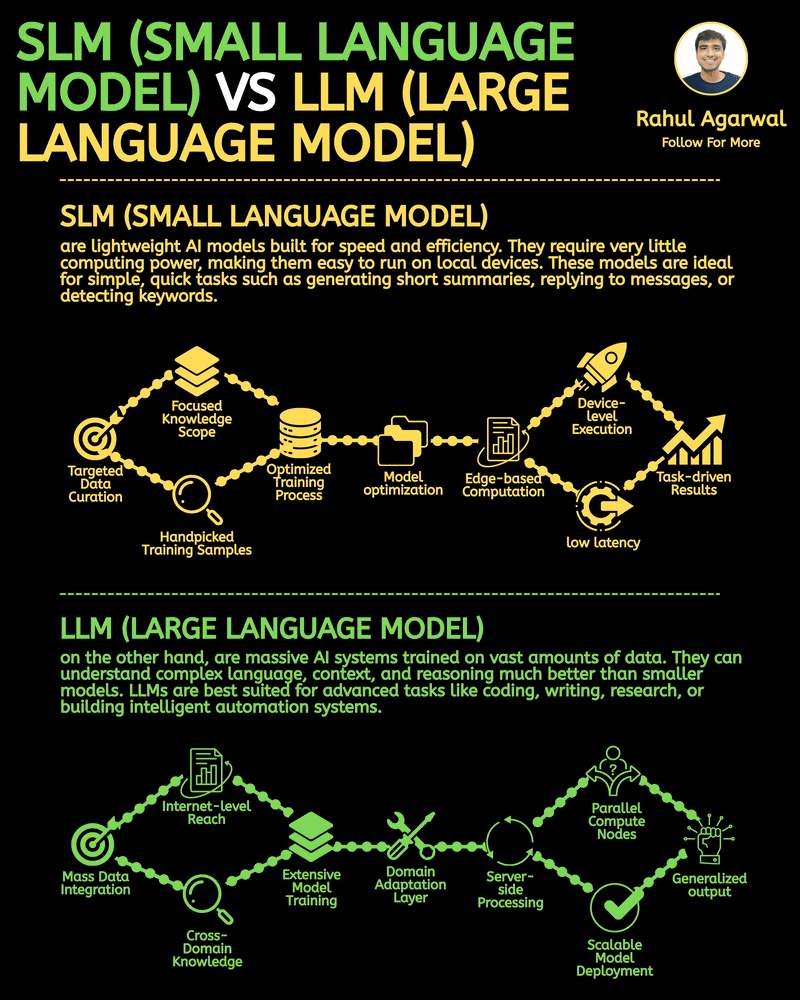
Your AI sucks because it’s stuck at Level 1. You can easily take it to Level 3. I've explained below. 𝗦𝘁𝗲𝗽 1 – 𝗕𝗮𝘀𝗶𝗰 𝗟𝗟𝗠 (𝗗𝗼𝗰𝘂𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝗰𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗶𝗻𝗴) • This is the simplest level of AI systems. • You give input text or a document → the LLM reads it and produces an output. • It relies only on its built-in knowledge and what you provide in the prompt. • No external data, no tools, just pure text-in/text-out generation. • Useful for summaries, rewrites, explanations, question-answering, etc. 𝗦𝘁𝗲𝗽 2 – 𝗟𝗟𝗠 + 𝗥𝗔𝗚𝘀 (𝗥𝗲𝘁𝗿𝗶𝗲𝘃𝗮𝗹) & 𝗧𝗼𝗼𝗹 𝗨𝘀𝗲 • Here the LLM becomes more powerful by fetching information before answering. • Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) lets the model search documents, PDFs, websites, or databases. • The system pulls relevant facts → sends them to the LLM → the LLM uses these facts to give accurate answers. • The LLM can also use tools (APIs, calculators, search engines, functions). • This reduces hallucinations and allows real-world data access. 𝗦𝘁𝗲𝗽 3 – 𝗔𝗱𝘃𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗲𝗱 𝗔𝗴𝗲𝗻𝘁 𝗔𝗿𝗰𝗵𝗶𝘁𝗲𝗰𝘁𝘂𝗿𝗲 (The stage where LLMs become true agents) 𝗗𝗲𝗰𝗶𝘀𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗠𝗮𝗸𝗶𝗻𝗴 • Instead of simply responding, the AI decides 𝘸𝘩𝘢𝘵 𝘴𝘵𝘦𝘱𝘴 to take. • It can plan tasks, select tools, evaluate results, and revise its strategy. • This is what turns the model into a problem-solving agent. 𝗧𝗼𝗼𝗹 𝗨𝘀𝗲 • Agents can run multiple tools in sequence: search, databases, APIs, code execution, dashboards, etc. • Tool outputs feed back into the agent’s reasoning loop. 𝗠𝗲𝗺𝗼𝗿𝘆 𝗦𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺 Agents store information across different memory types: • 𝗦𝗵𝗼𝗿𝘁-𝘁𝗲𝗿𝗺 𝗺𝗲𝗺𝗼𝗿𝘆: Current conversation or session context. • 𝗟𝗼𝗻𝗴-𝘁𝗲𝗿𝗺 𝗺𝗲𝗺𝗼𝗿𝘆: Persistent facts, user preferences, profiles, past knowledge. • 𝗘𝗽𝗶𝘀𝗼𝗱𝗶𝗰 𝗺𝗲𝗺𝗼𝗿𝘆: Logs of past tasks, experiences, and decisions. 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗮𝗯𝗮𝘀𝗲𝘀 𝗨𝘀𝗲𝗱 • 𝗩𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗼𝗿 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗮𝗯𝗮𝘀𝗲𝘀: Store embeddings for semantic search (meaning-based retrieval). • 𝗦𝗲𝗺𝗮𝗻𝘁𝗶𝗰 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗮𝗯𝗮𝘀𝗲𝘀: Store structured knowledge to support reasoning and long-term memory. 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗢𝘂𝘁𝗽𝘂𝘁 • After reasoning, retrieving, planning, and tool execution, the agent generates a polished output or performs an action. • This architecture creates AI that can autonomously handle workflows, not just answer questions. ✅ 𝗙𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗙𝗹𝗼𝘄 (𝗙𝗿𝗼𝗺 𝗦𝗶𝗺𝗽𝗹𝗲 𝗟𝗟𝗠 → 𝗙𝘂𝗹𝗹 𝗔𝗜 𝗔𝗴𝗲𝗻𝘁) 1. LLM processes text/documents. 2. LLM retrieves facts & uses tools to improve accuracy. 3. Full agent architecture adds decisions, planning, memory, and databases. 4. The system becomes capable of multi-step autonomous reasoning. ✅ Repost this so others can upgrade their AI from basic to powerful.

More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Download the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.



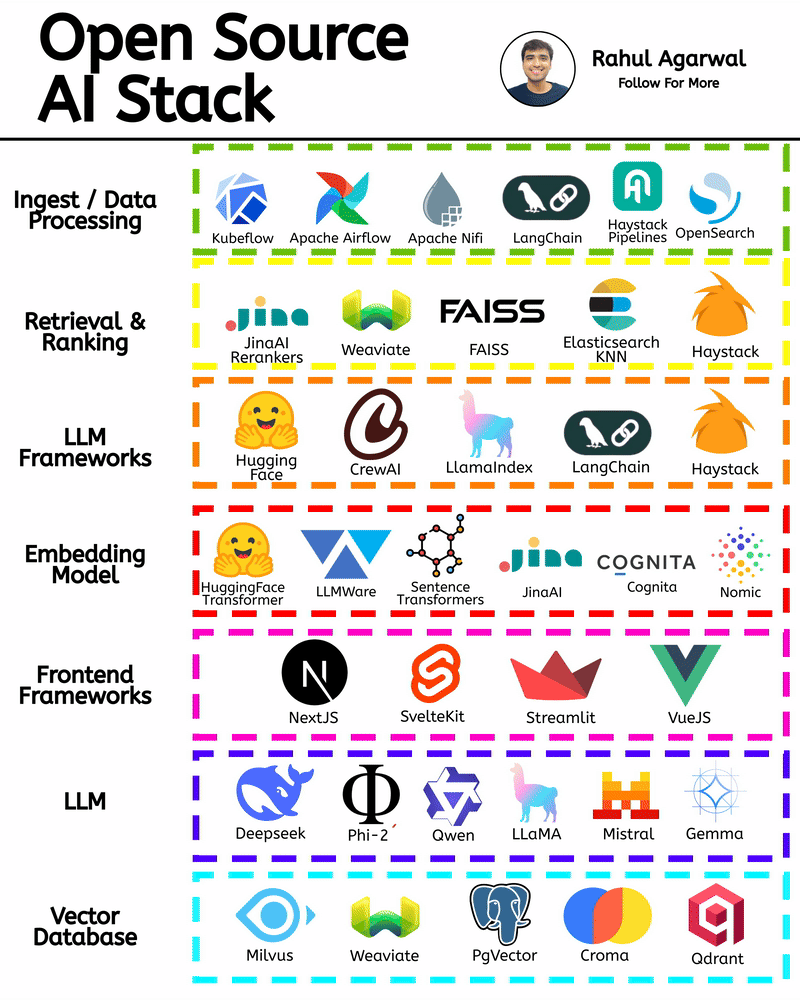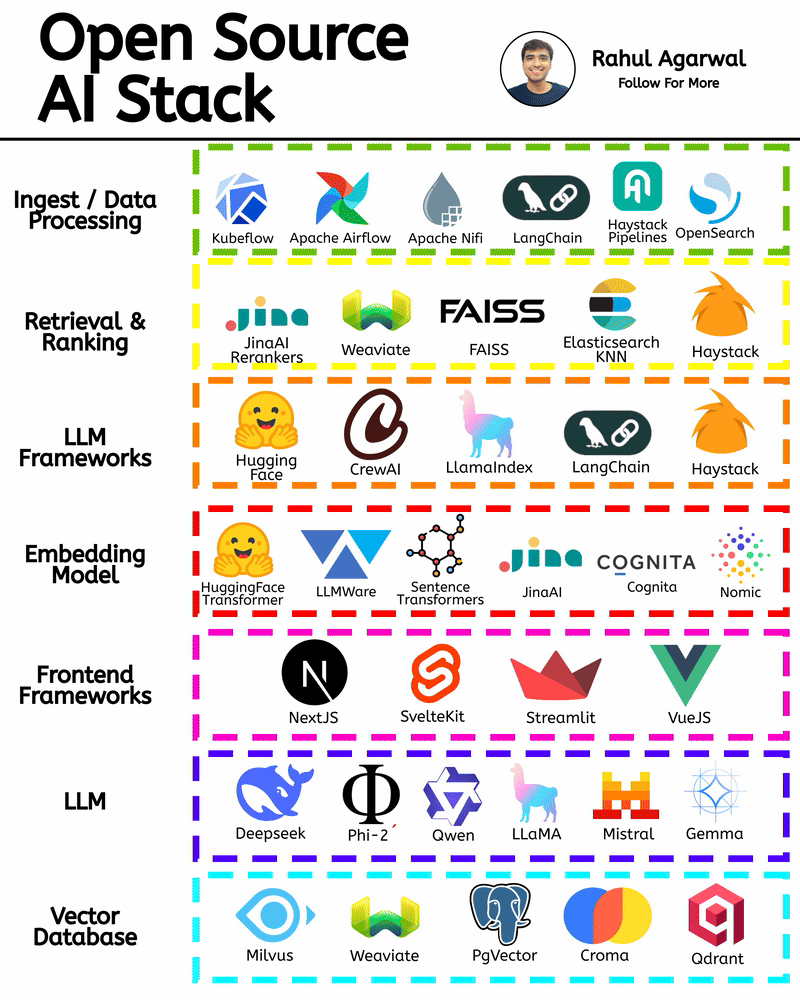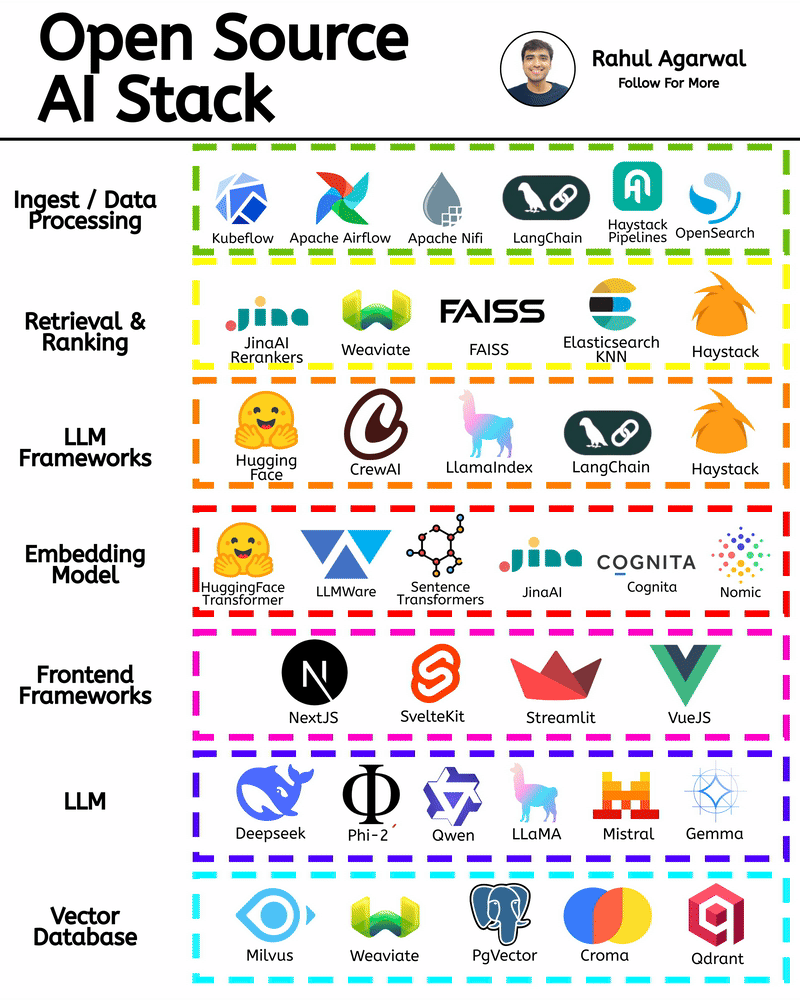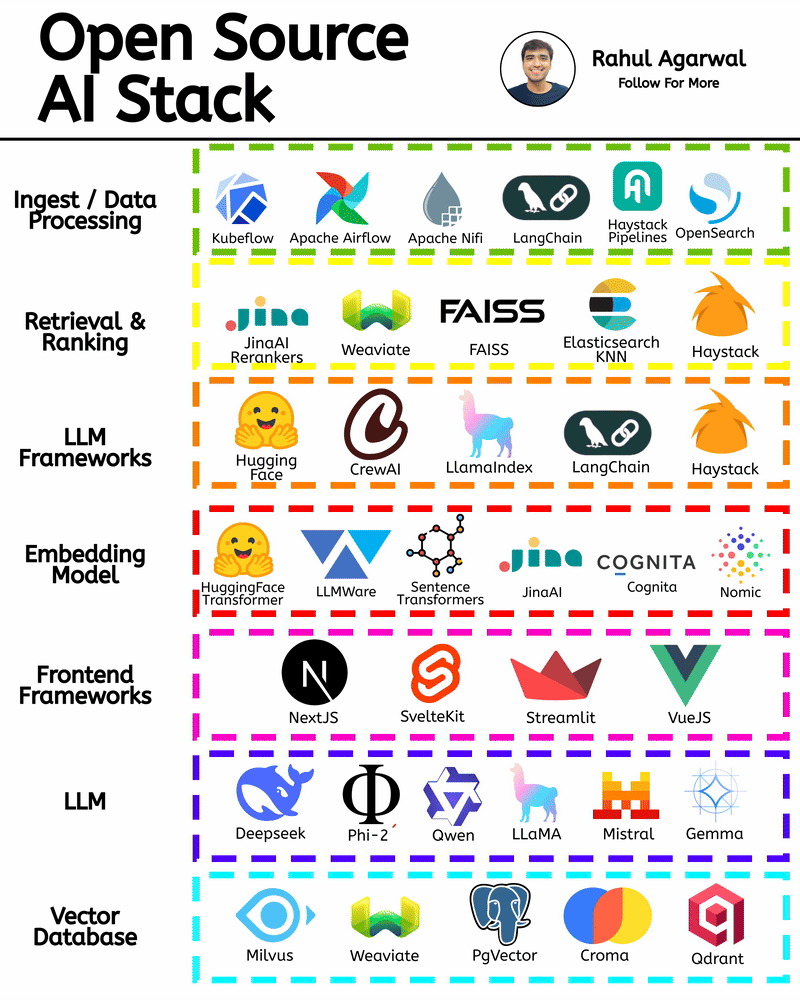
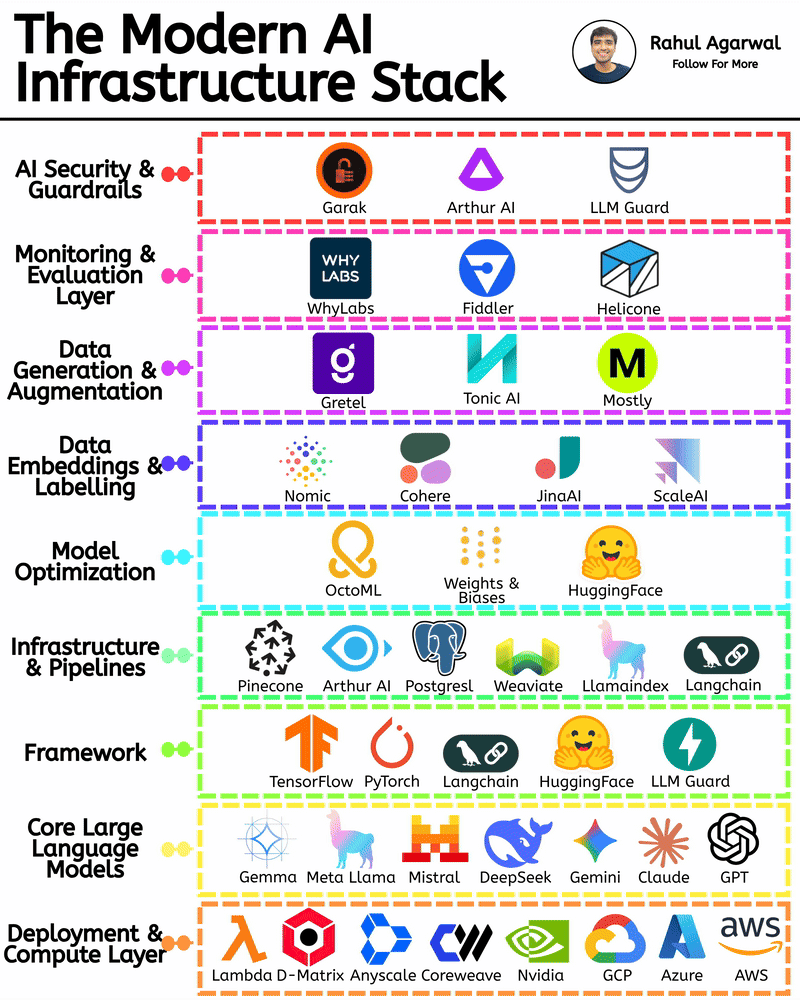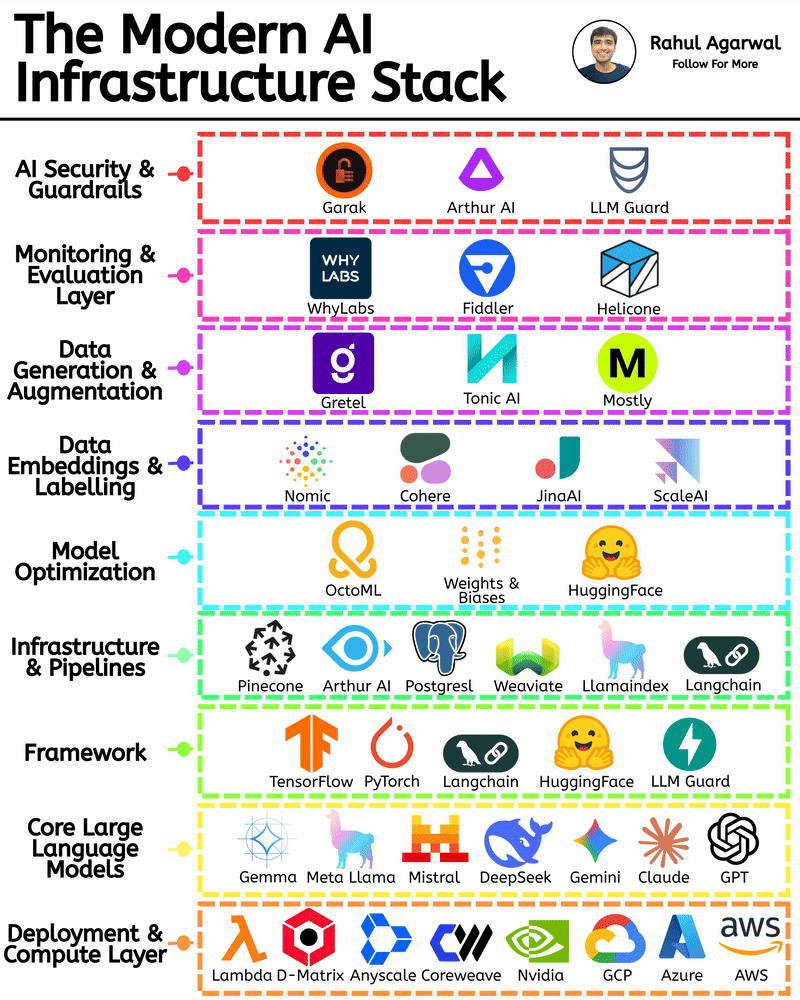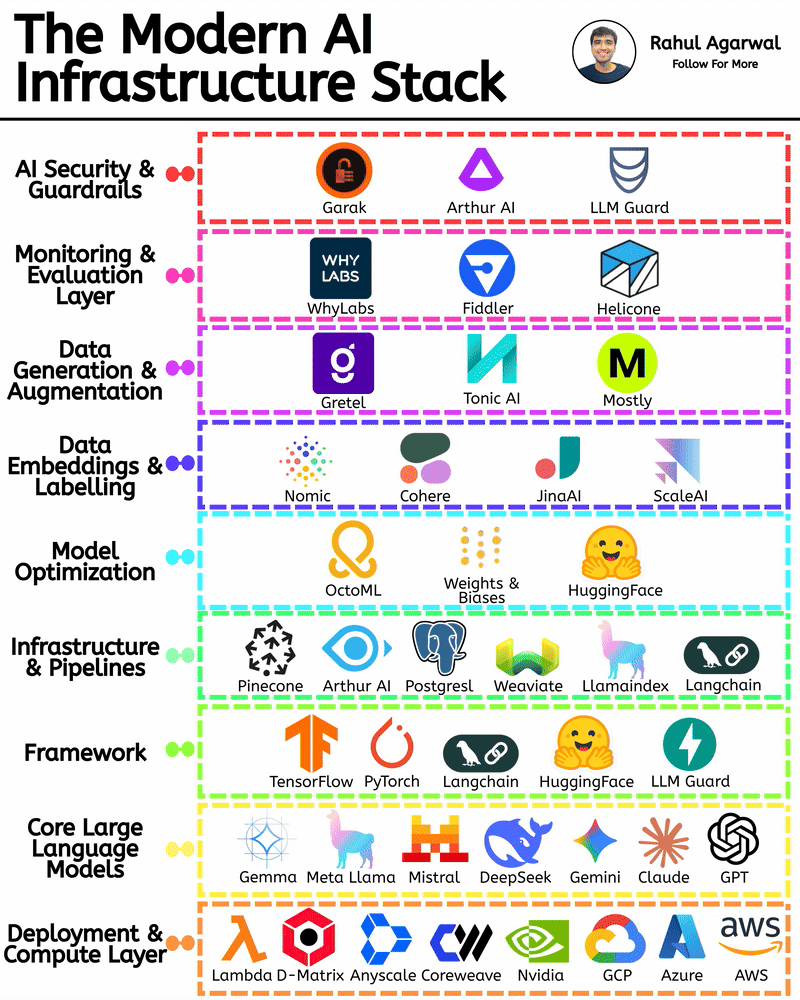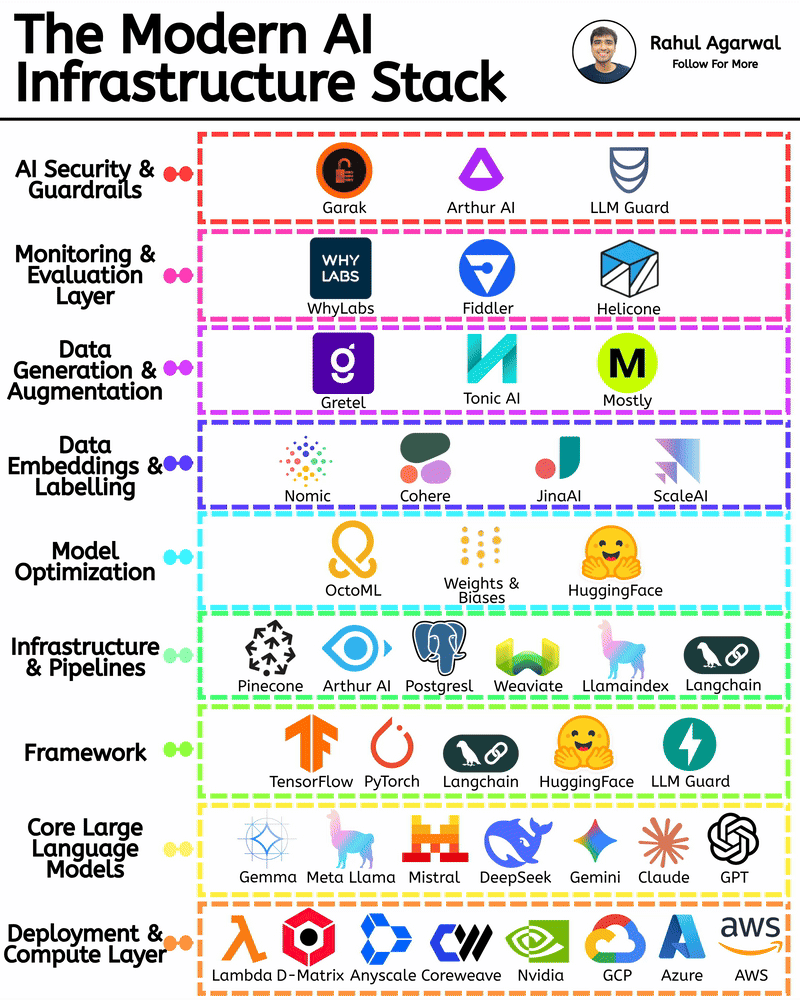
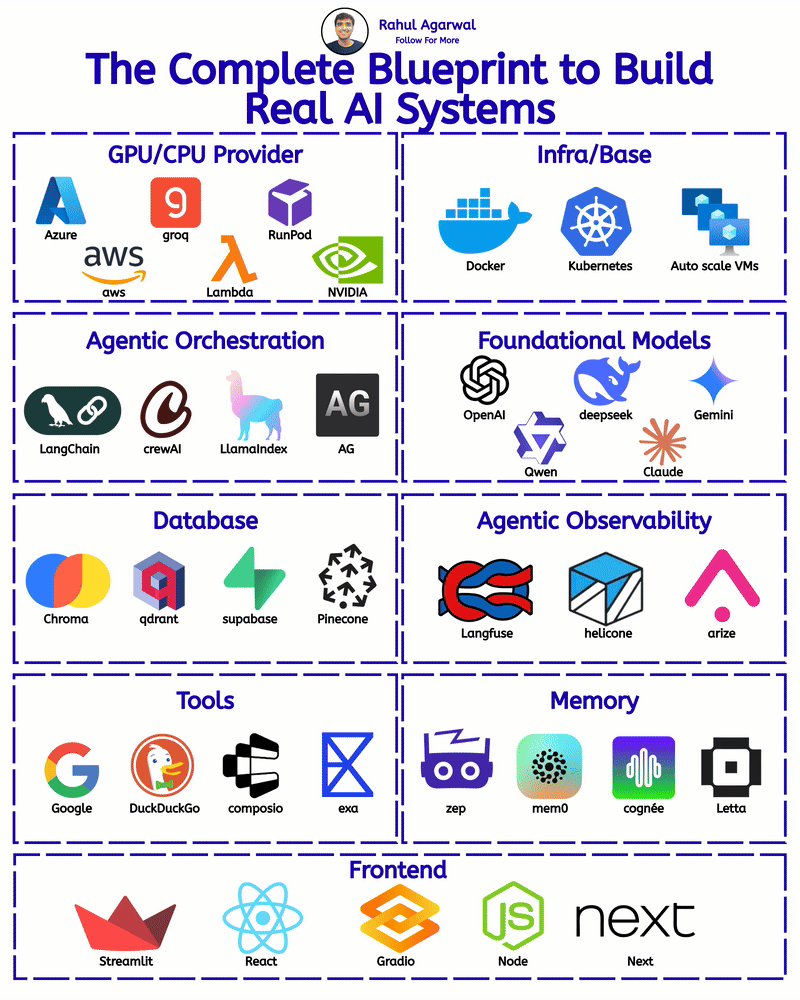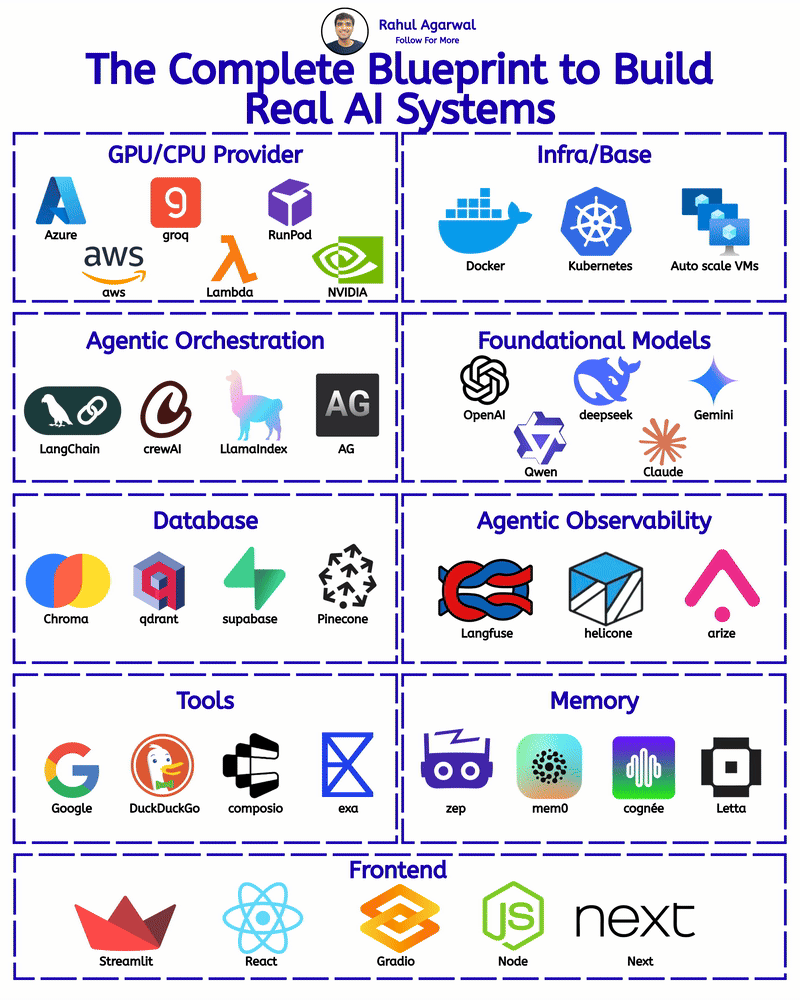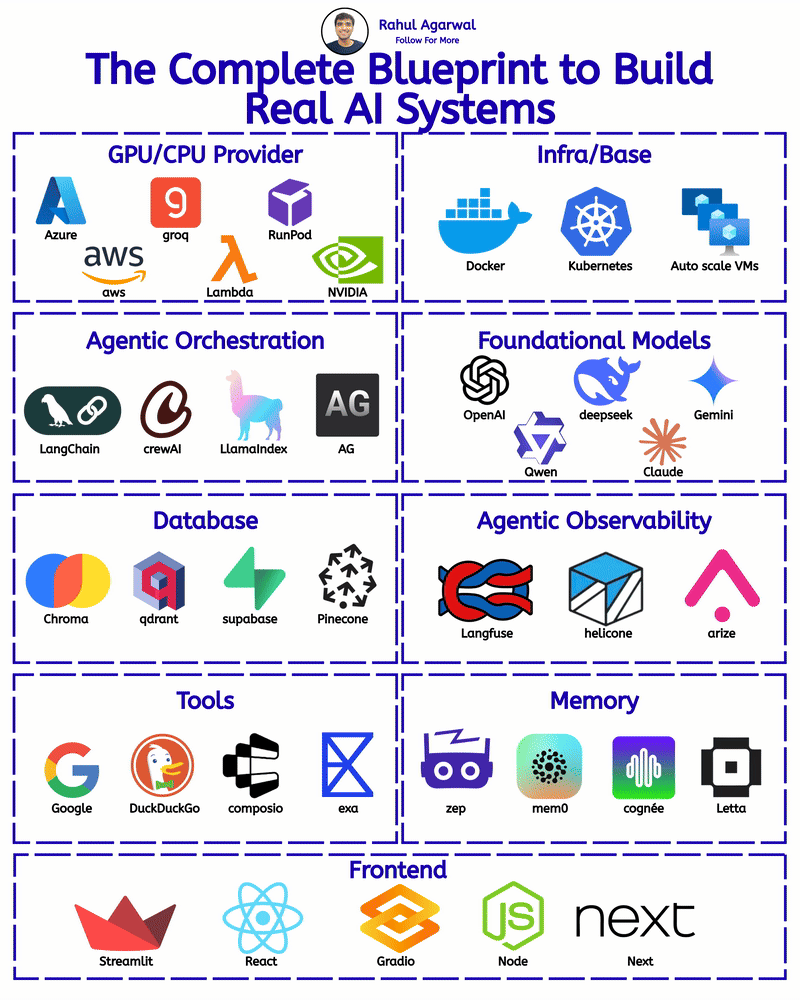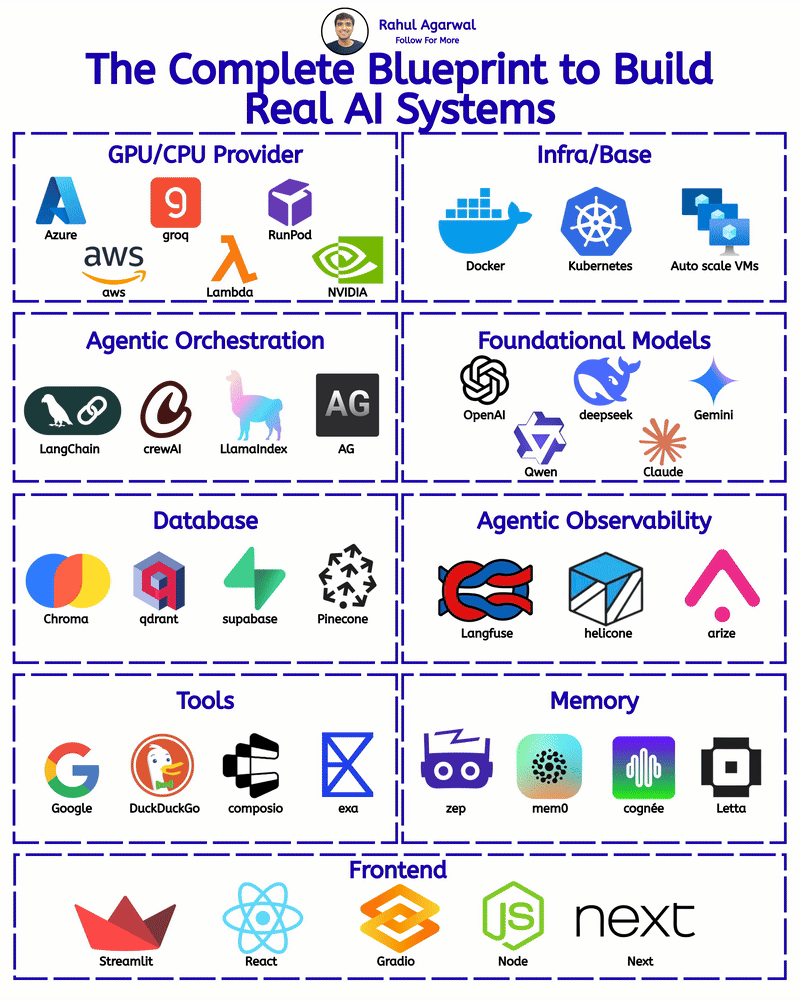


/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)





















