Back
Dr Saurav singh
Doctor by profession... • 1y
In India, the rapid rise of restaurants, street food stalls (thelas), and tea shops (chai tapris) is driven by several key factors: 1. Easy Licensing & Low Entry Barriers – Compared to other businesses, setting up a small food venture often requires minimal regulatory approvals, making it an attractive option for entrepreneurs. 2. Limited Employment Opportunities – With formal job markets struggling to absorb the growing workforce, many individuals turn to the food business as a means of self-employment. 3. Profitability Depends on Cost Management – A food business can be profitable if: The owner or family members manage operations themselves, reducing labor costs. Ingredients and resources are sourced efficiently to keep expenses low.
Replies (3)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Kamlesh Gurjar
ll प्रत्येकं त्रुटिः... • 11m
Cloud Kitchens: India’s 2025 Food Revolution 🍳 What’s Cooking? A delivery-only kitchen model—low overheads, high profits. 💰 Starting Investment: ₹5L-₹20L₹2L-₹5L: Basic equipment & setup₹1L-₹3L: Licensing & marketing₹2L-₹10L: Scaling (location-depe
See MoreKetan Sojitra SMEDOST
•
Gujarathi Empire Group • 4m
💡 Street Food: India’s Fastest-Growing Micro Startup Movement” -Solopreneurs 👉 India’s new startup wave isn’t happening only in co-working spaces —it’s brewing on the streets According to recent reports, small food ventures have grown over 35%
See More
Sanskar
Keen Learner and Exp... • 1y
Fabindia was founded in 1960, by the initiative of John Bissell, initially Fabindia started by exporting home furnishings, championing rural artisans. Fast-forwarding to today, Fabindia boasts over 341 stores (as of July 2020) across India and abroad
See MoreHitanshu Jha
Sugar Free Flavorful... • 4m
Amazon and flipkart are joining blinkit in the quick commerce race. That means more jobs, but it also means something else, more young people working as delivery riders At one level I respect the hustle, these jobs put food on the table and keep fa
See MoreVIJAY PANJWANI
Learning is a key to... • 1y
Reliance is bringing back a BANNED Chinese company to India! Here’s how they did it: Reliance has tried launching its own fast fashion chains—Azorte, Yousta, and Reliance Trends. But none really took off.So this time, they pulled a different move. I
See More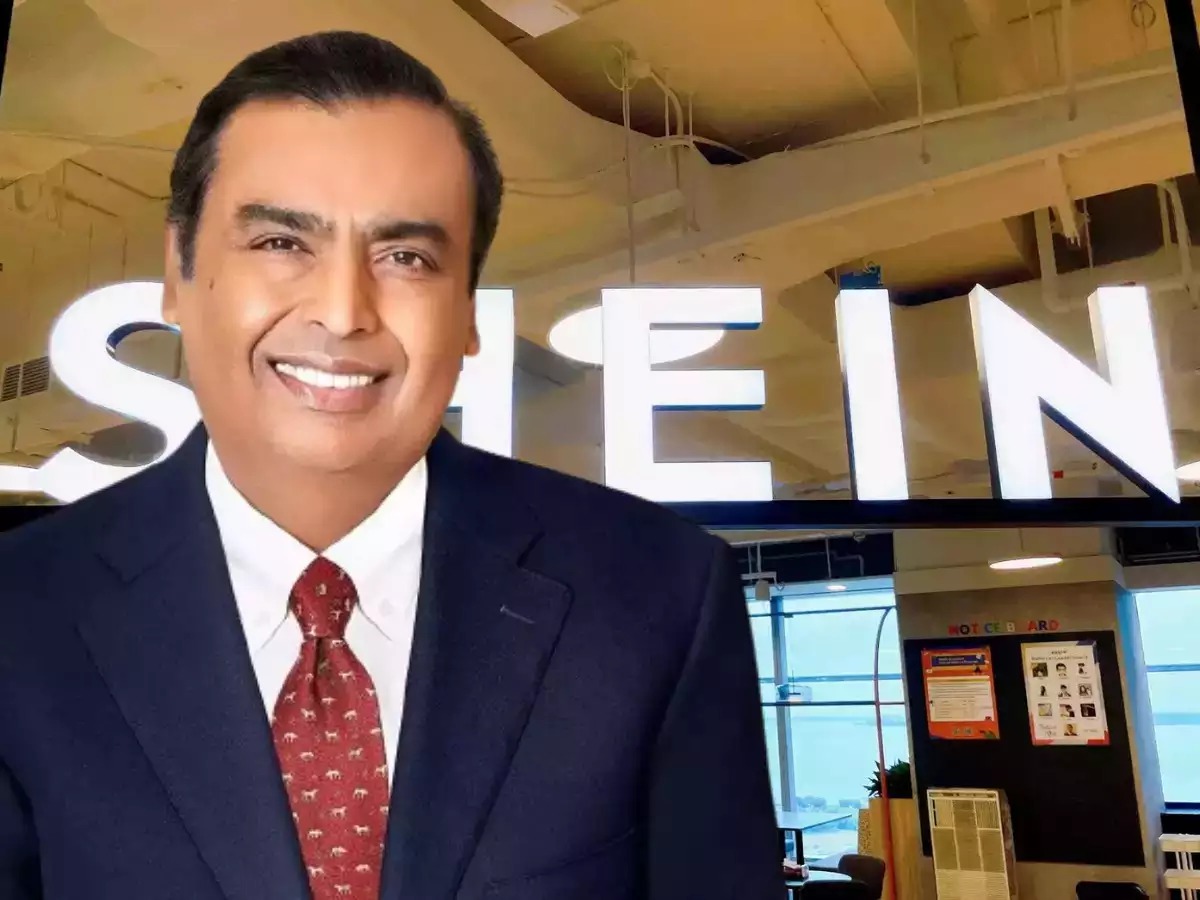
CA Jasmeet Singh
In God We Trust, The... • 9m
CureBay – Bridging Healthcare Gaps in Rural India Industry: Health-Tech Founded: 2021 Headquarters: Bhubaneswar, Odisha Founder & CEO: Curie Panda --- 🩹 The Challenge India's rural population often faces significant barriers to accessing quali
See More
Ansh Kadam
Founder & CEO at Bui... • 10m
Here’s why Flipkart actually needs Amazon to survive and vice versa Duopolies are not just a coincidence; they’re a kind of market law. Think about it: Coke and Pepsi. Swiggy and Zomato. Amazon and Flipkart. Why are there always two players domin
See More
Poosarla Sai Karthik
Tech guy with a busi... • 3m
India’s (Fake vs Original) Economy: Counterfeits aren’t just cheap copies. They shift pricing, distort consumer trust, and undercut brands that actually invest in compliance and safety. Here’s a condensed sector-wise look at how originals and fakes
See MoreDownload the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.



















/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)




















