Back
SHIV DIXIT
CHAIRMAN - BITEX IND... • 1y
📖 DAILY BOOK SUMMARIES 📖 🚀 12 Lessons From 👉 🔥 Business Model Generation 🔥 ✨ By Alexander Osterwalder ✨ 1. Customer Segments: • Identifying the different groups of people or organizations a business aims to reach and serve • Importance of understanding each segment’s specific needs, problems, and behaviors to tailor products and services 2. Value Propositions : • Describes the unique value a company offers to its customer segments • It can be innovative or fulfill a need better than competitors. It includes aspects like newness, performance, customization, and price 3. Channels: • The means by which a company delivers its value proposition to customers • Includes communication, distribution, and sales channels, both direct and indirect. Understanding customer preferences in channel interaction is key 4. Customer Relationships: • Outlines how a company interacts with its customer segments to acquire, retain, and grow customers • Relationships can range from personal assistance to automated services, each influencing customer experience and loyalty 5. Revenue Streams: • The ways a company generates income from each customer segment • It covers pricing mechanisms and strategies, including one-time payments, subscriptions, licensing, and brokerage fees 6. Key Resources: • The most important assets required to make a business model work • These resources can be physical, intellectual, human, or financial and are crucial in delivering the value proposition, reaching markets, and maintaining customer relationships 7. Key Activities: • The most important actions a company must take to operate successfully • Includes activities like production, problem-solving, platform/network maintenance, and more, which are critical to delivering the value proposition 8. Key Partnerships: • The network of suppliers, partners, and alliances that help the business model work • Partnerships can reduce risk, optimize resources, or allow a company to acquire necessary resources and activities from outside. 9. Cost Structure: • Describes all the costs incurred to operate a business model • It involves understanding the most significant costs in the business and how they are tied to key activities and resources. The business model can be cost-driven (focused on minimizing costs) or value-driven (focused on creating value) 10. Innovation and Prototyping: • The book encourages using innovation to stay competitive and suggests prototyping business models to test and refine ideas before implementation 11. Storytelling: • It highlights the power of creating a compelling narrative around the business model to engage stakeholders and communicate value effectively 12 Iteration and Adaptability • Emphasizes that business models should evolve based on market feedback and changes, advocating for a willingness to pivot when necessary 🔗 You can download this book for free from comment section 🔗

Replies (1)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Anurag Patel
Calm mind. Precise h... • 4m
The startup owner's manual (Part 4) Business Model Planning: Customer Relationships Hypothesis This describes how you will get, keep, and grow customers. For physical products, there are four “get” stages — Awareness, Interest, Consideration, and P
See MoreVivek Joshi
Director & CEO @ Exc... • 8m
Early-stage startups need engineered business models for hypergrowth, not just great ideas. A "boosted" model ensures rapid validation, capital efficiency, scalability, competitive edge, & attracts investment. The "Accelerated Performance Framework"
See More
Anurag Patel
Calm mind. Precise h... • 4m
The startup owner's manual (Part 2) Business Model Planning: Value Proposition Hypothesis This includes product vision, features and benefits, and a description of the smallest number of features it would take to make a stand-alone product (i.e., t
See MoreThakur Ambuj Singh
Entrepreneur & Creat... • 11m
The 9 Point Business Circuit is a comprehensive framework for analyzing any business within its industry. It covers key aspects such as value proposition, business model, industry trends, competitive positioning and growth potential, helping entrepr
See More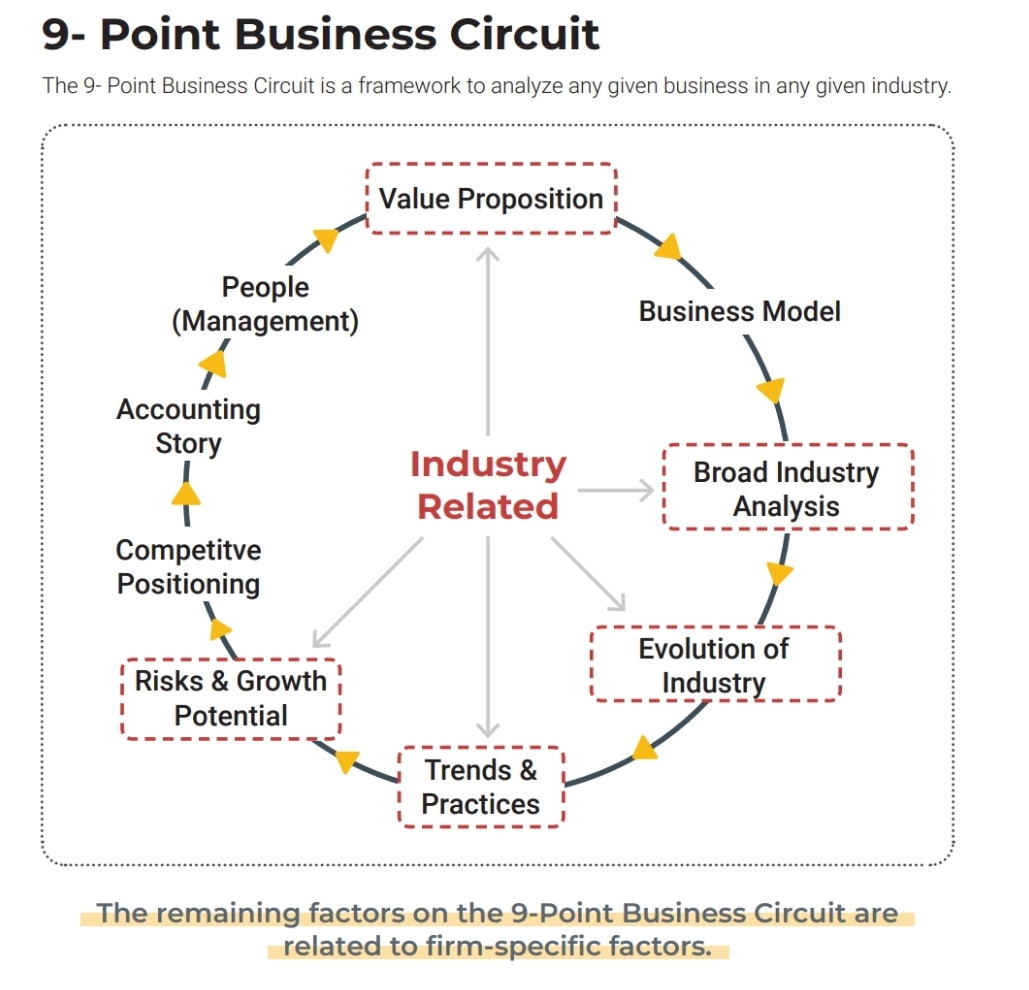
Vansh Khandelwal
Full Stack Web Devel... • 1y
Licious disrupted India's meat industry with its Farm-to-Fork model, ensuring control over the entire value chain for consistent quality and a predictable customer experience. By leveraging General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS), Licious adapted to market
See MoreThakur Ambuj Singh
Entrepreneur & Creat... • 11m
📊💡 Unlocking the Profit Pool: A Roadmap to Smart Business Decisions! 🚀 Want to focus on the most profitable areas of your business? Here’s how: 1️⃣ Define the value chain – Identify key activities to include. 2️⃣ Measure size & profitability – I
See More
Download the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.











/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)




















