Back
SHIV DIXIT
CHAIRMAN - BITEX IND... • 1y
📖 DAILY BOOK SUMMARIES 📖 🔗 FREE DIRECT E-BOOK DOWNLOAD LINK AVAILABLE — https://drive.google.com/file/d/1xXFTDwr-9pN3iZTIPKTPF9UU3WQVCiBY/view?usp=drivesdk 🔥 The Intelligent Investor 🔥 🚀 20 Lessons By 👉 ✨ Benjamin Graham ✨ 1. Core Premise: • The book teaches value investing, focusing on long-term wealth creation by investing in undervalued stocks with a margin of safety. It emphasizes patience, discipline, and avoiding speculative behaviors. 2. Investment vs. Speculation: • Investment: Involves thorough analysis, seeking safety of principal, and aiming for an adequate return. • Speculation: Taking on risk without adequate research, often driven by market fluctuations or emotions. 3. Mr. Market Metaphor: • Graham introduces Mr. Market, a metaphorical character who offers to buy or sell stocks daily at fluctuating prices. The key lesson is not to follow Mr. Market’s emotional ups and downs but to take advantage of his irrationality when it benefits you. 4. Margin of Safety: • Investors should always buy stocks when they are priced below their intrinsic value to create a "margin of safety." This provides a cushion against errors in judgment or unforeseen market conditions. 5. Defensive vs. Enterprising Investor: • Defensive Investor: Prioritizes safety and stability, often choosing diversified, low-risk investments such as blue-chip stocks and bonds. • Enterprising Investor: Willing to put in extra time and effort to research undervalued opportunities and make more aggressive stock picks. 6. Stock Market Volatility: • The stock market is inherently volatile, but intelligent investors should not be swayed by short-term price movements. Instead, they should focus on the long-term value of their investments. 7. Intrinsic Value: • The intrinsic value of a stock is its actual worth based on the company’s assets, earnings, and future growth prospects. Graham advises calculating this to determine whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued. 8. Risk Management: • Successful investors manage risk by diversifying their portfolios and avoiding speculative bubbles. Diversification spreads risk, ensuring that no single investment significantly harms the portfolio. 9. Importance of Emotional Discipline: • Investors must control their emotions, especially during market booms and busts. Emotional investing—driven by fear or greed—leads to poor decisions. Rationality and discipline are key. 10. Dividend Policy: • Companies with a strong, consistent dividend policy often represent solid investment opportunities. Dividends provide steady income and indicate financial health 11. Avoiding Market Timing: • Graham warns against trying to time the market, as predicting short-term movements is extremely difficult. Instead, focus on long-term fundamentals and value

Replies (3)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Soumya Ranjan Dash
Hit & Trial • 1y
When I started investing in stock markets, I cared about: 100x returns Multibagger stocks Sharing profit screenshots What peers thought about me After getting grilled in the Market, I care about: Risk per investment Overall consistent annual retur
See MoreAtharva Deshmukh
Daily Learnings... • 1y
Commonly used Jargons 1)Bull Market:-If you expect the stock prices to go up,you are bullish on the stock price. 2)Bear Market:-If you expect the stock prices to go down,you are bearish on the stock price. 3)Trend:-The term ‘trend’ usually refers
See MoreAccount Deleted
Hey I am on Medial • 11m
The stock market is a marketplace where investors buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. It enables companies to raise capital by issuing stocks, while investors can profit through price appreciation and dividends. Stock exchanges, like th
See MoreVIJAY PANJWANI
Learning is a key to... • 1m
Is That Stock Really Cheap… or Just Hype? Most people buy stocks because: “Price is going up 🚀” But smart investors ask only ONE question: 👉 Is the market cap justified by CASH FLOW? Legendary investor logic: Fair Value = Annual Cash Flow × 30 t
See More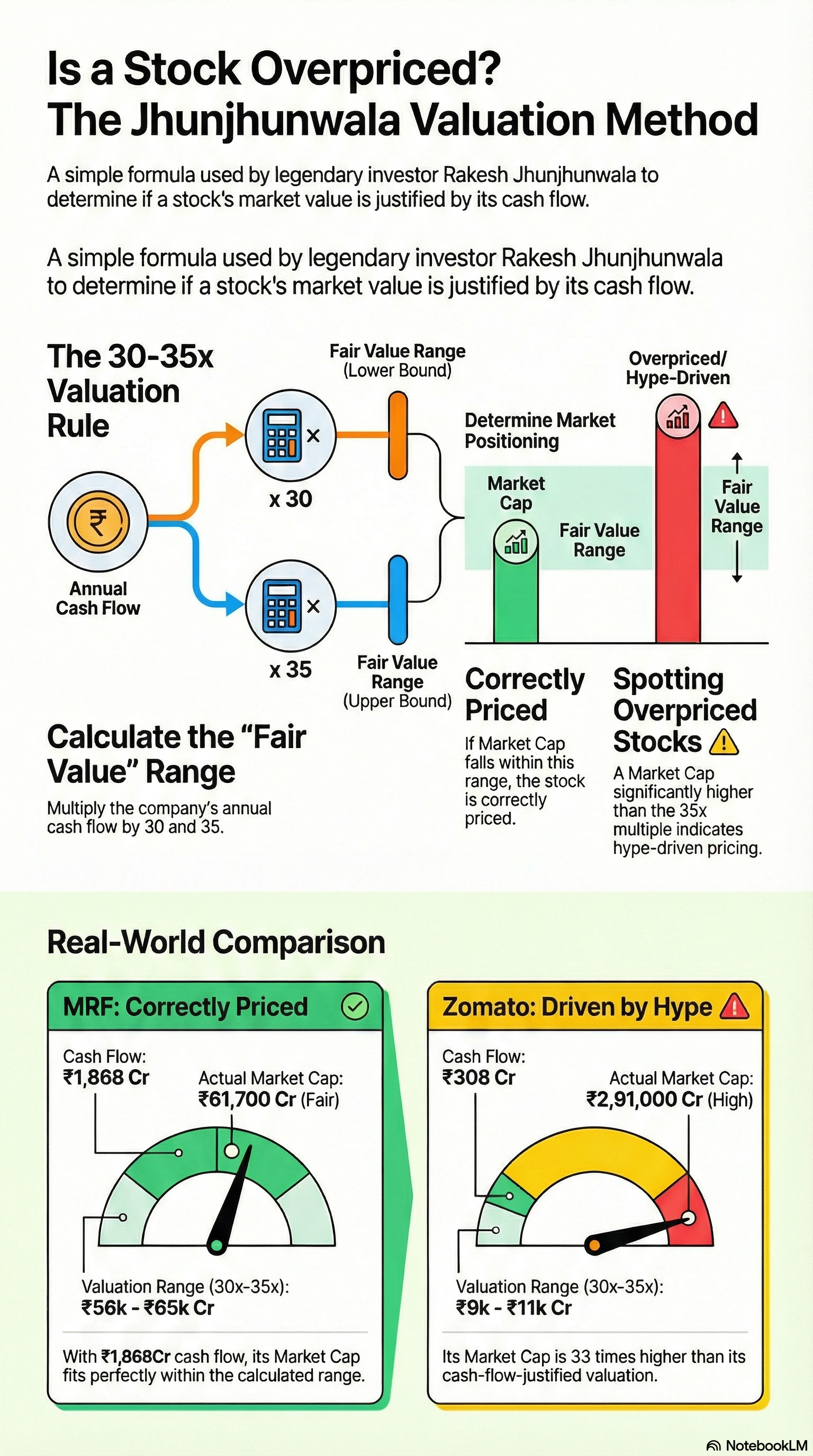
VIJAY PANJWANI
Learning is a key to... • 5m
Debt-Free Penny Stocks to Watch in 2025 When it comes to penny stocks, financial health matters the most. One strong indicator is the Debt-to-Equity Ratio – and a zero debt ratio signals a company with no debt burden. Here are a few debt-free penn
See More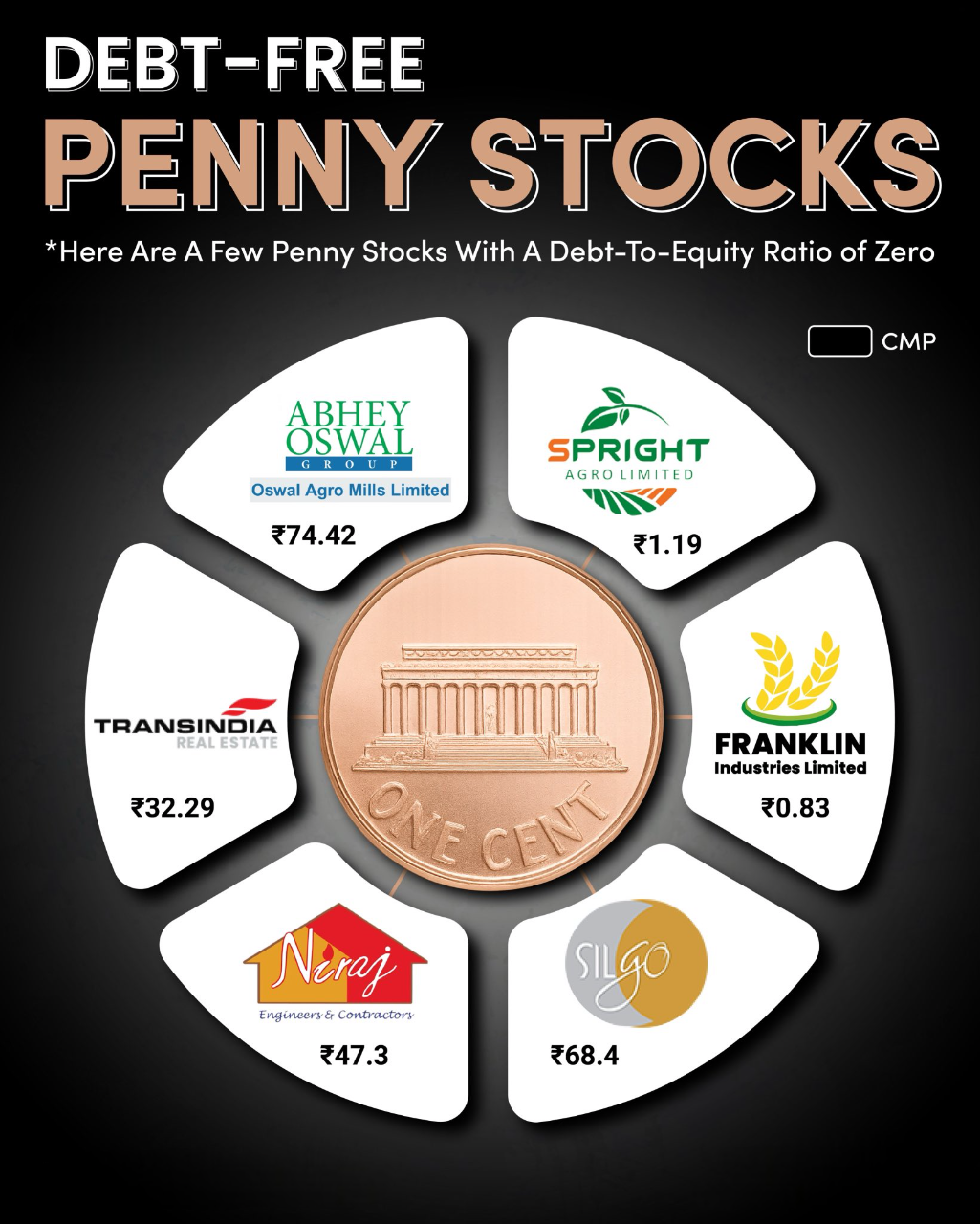
Rohan Saha
Founder - Burn Inves... • 1y
Okay, I was just checking the valuation of our Indian stock market and I noticed something interesting. Despite the heavy sell-off in October, FMCG, IT, and small-cap stocks are still overvalued. I understand why IT stocks are overvalued because the
See MoreVIJAY PANJWANI
Learning is a key to... • 3m
PEG Ratio Explained in 30 Seconds! Want to know if a stock is undervalued or overvalued? Use the PEG Ratio one of the smartest tools used by pro investors! 🧮 Formula: PEG = P/E Ratio ÷ Earnings Growth Rate ✅ PEG < 1 = Undervalued ⚖️ PEG = 1 = Fai
See More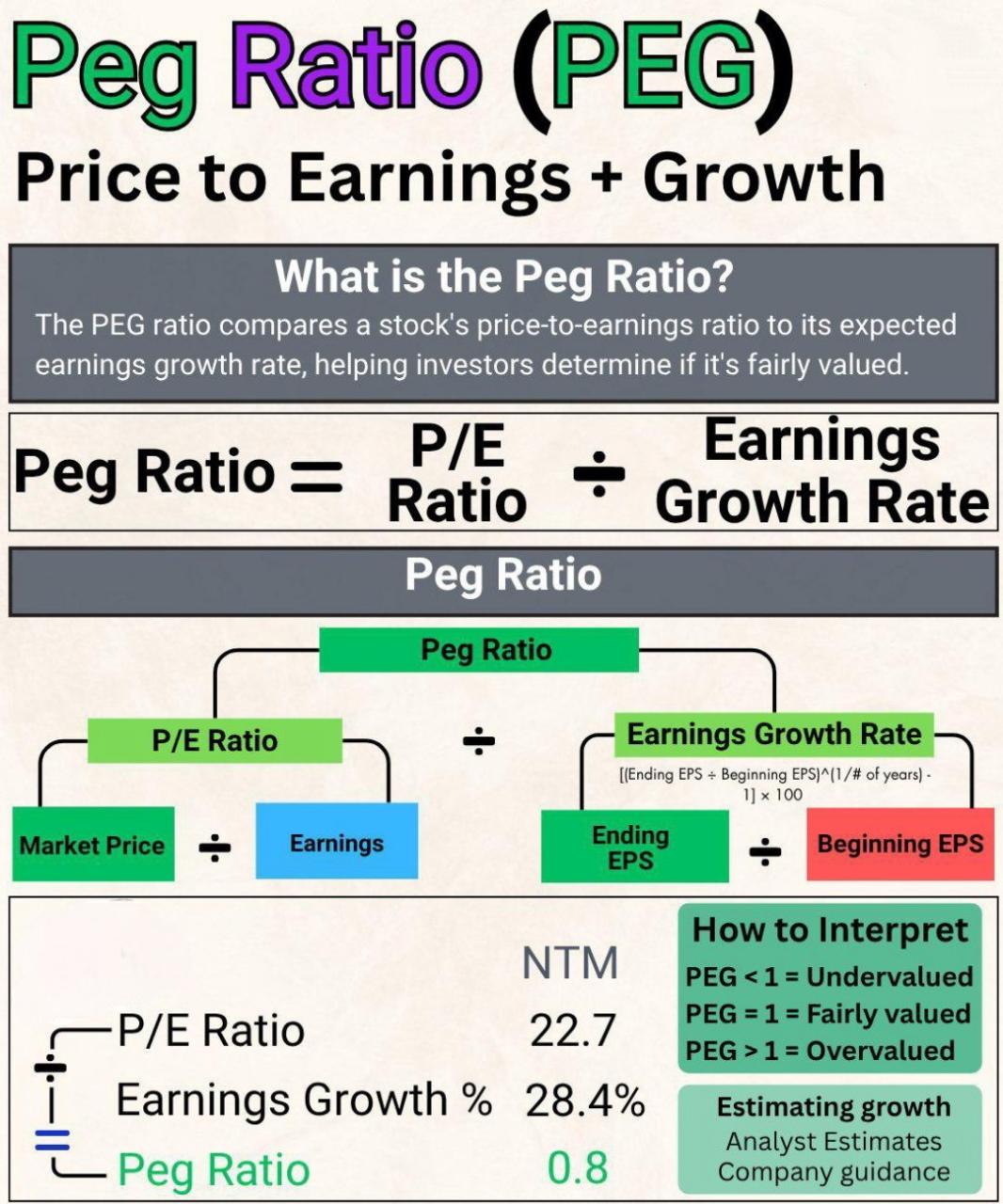
Mahendra Lochhab
Content creator • 1y
Indian stock market has reached a 7-month low. Along with this, the total value of the stock market has also come below $5 tn for the first time in 7 months. The total value of the Indian stock market was $5.7 tn on September 27, 2024, which came d
See More
Download the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.
















/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)

















