Back
Sairaj Kadam
Student & Financial ... • 1y
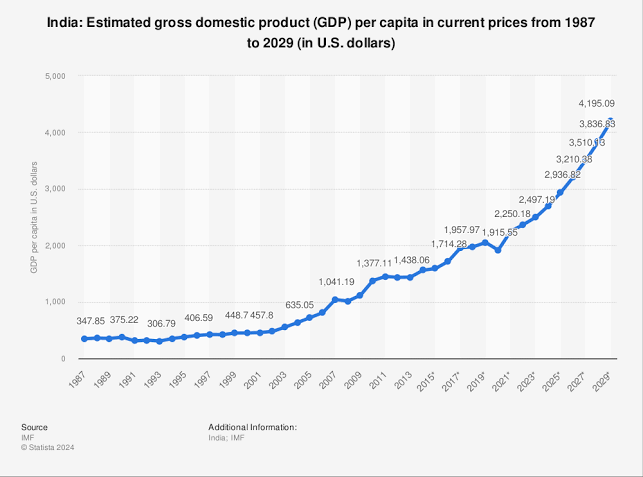
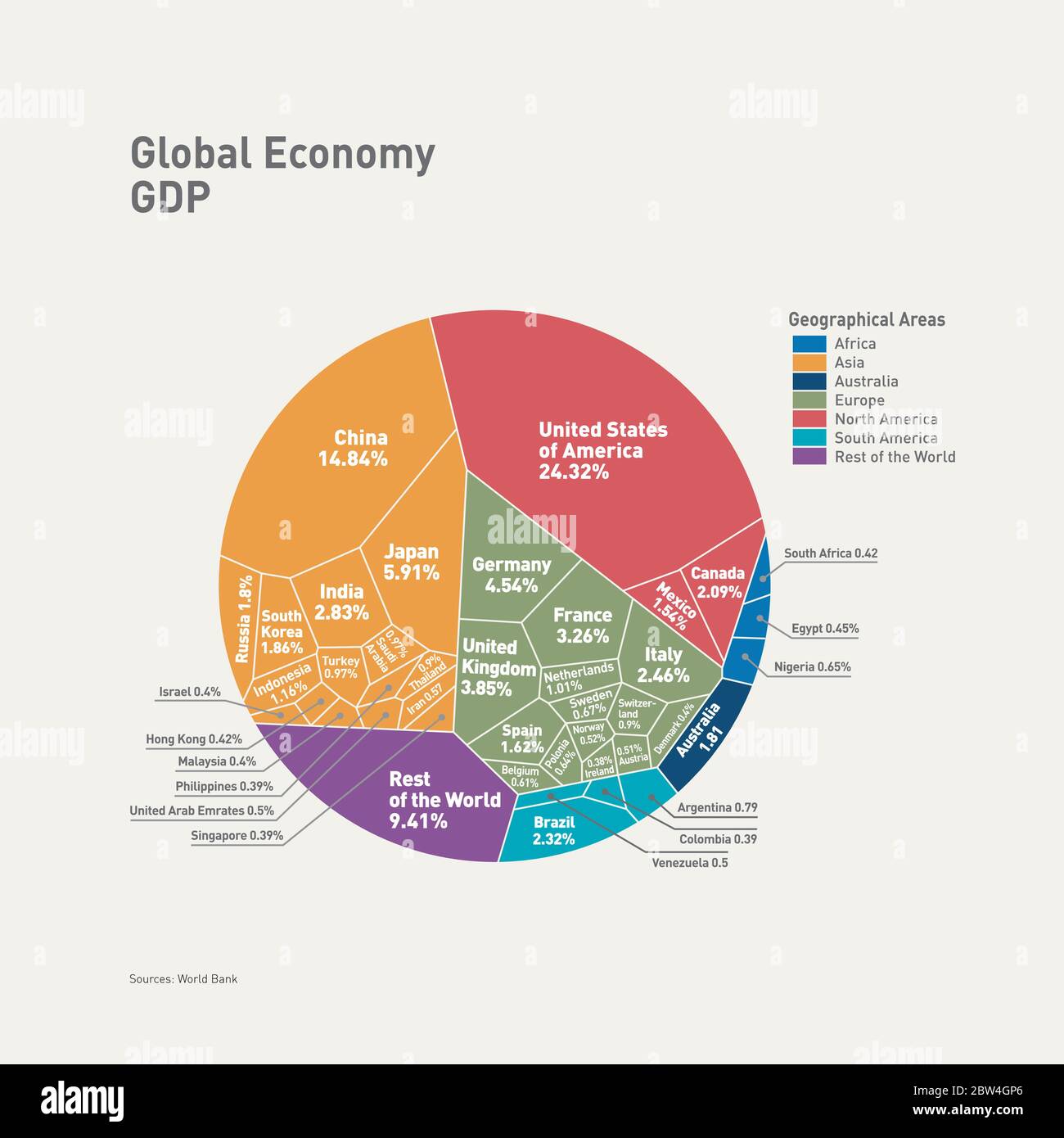
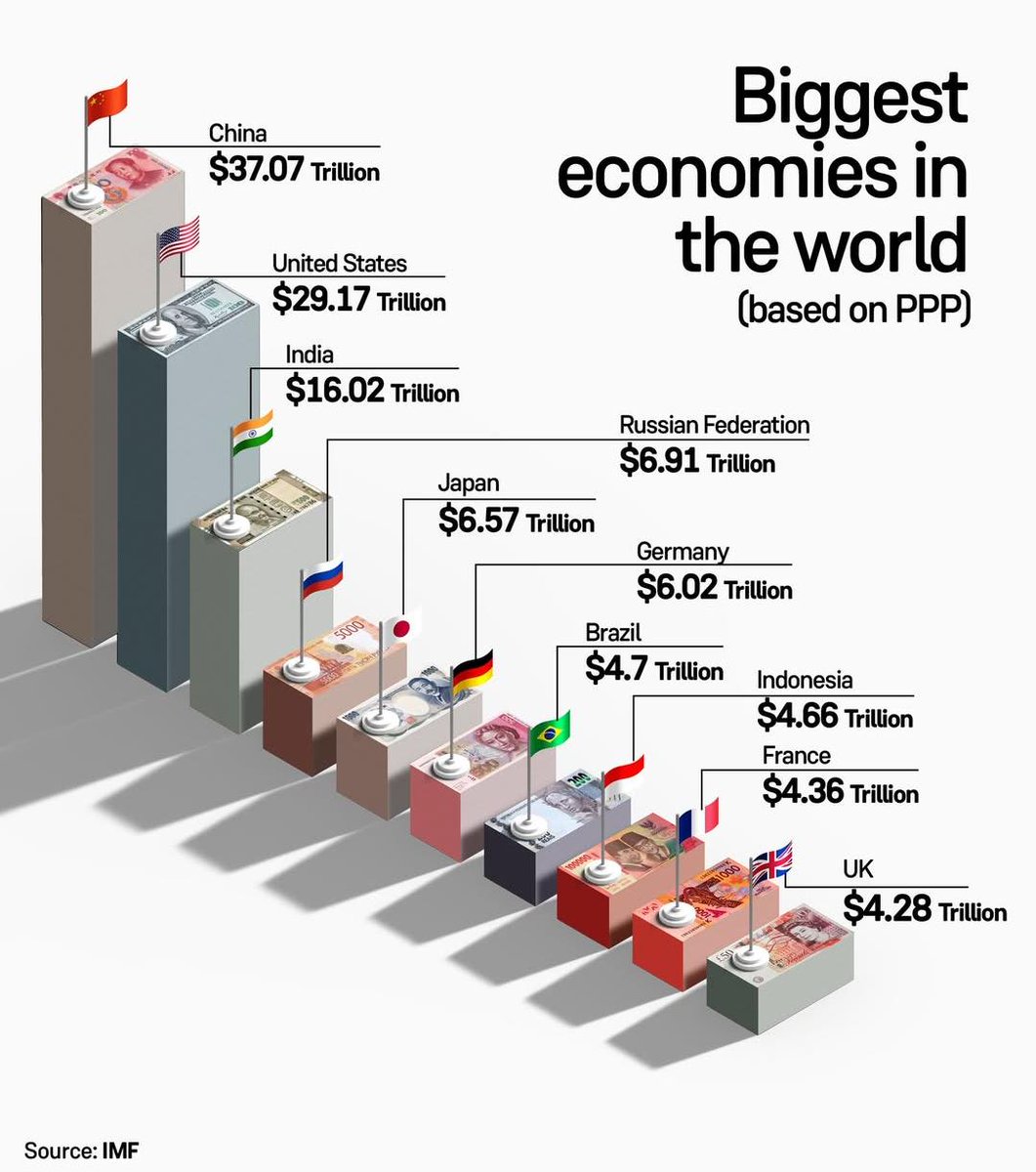
Does India Have the Capability? Does India Have a Market as Strong as the USA or Other Countries? Probably Not. This is where Price Power Parity (PPP) comes in. PPP compares the purchasing power of currencies by analyzing how much a basket of goods costs in different countries. For instance, if a basket costs $10 in the U.S. but ₹800 in India, PPP evaluates whether ₹800 holds the same value as $10. Where Does India Stand? India’s market is large but faces challenges: 1. Income Disparity: A significant portion of the population has limited purchasing power. 2. Currency Value: The rupee’s lower value impacts competitiveness globally. 3. Infrastructure Gaps: Taxes and transportation costs affect price parity. The Reality Even if we consider a growing India, it could take 10-20 years to bridge the gap. But here’s the catch—the RBI and the Indian government have the ability to address this disparity within months if they truly commit to it in the current conditions. Can India match up? Share your thoughts.
Replies (6)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Yash S
Founder @ Innovzeal ... • 9m
In 2025, India officially became the world’s fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP, overtaking Japan. For those who recall similar headlines from the 2009–2014 period, the distinction lies in what’s being measured. Back then, India rose to third plac
See More
Account Deleted
Hey I am on Medial • 10m
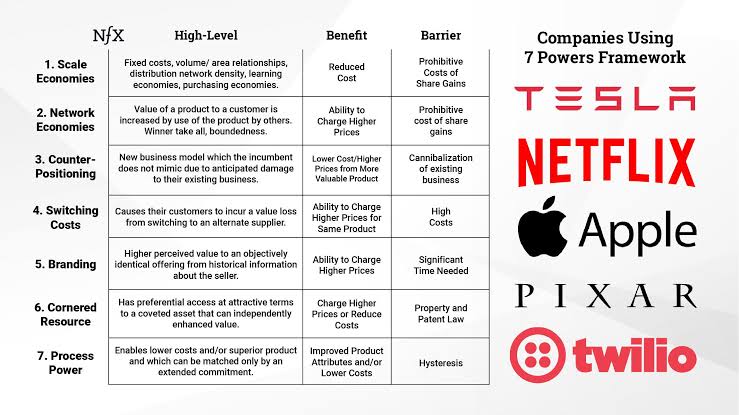
A quick short read one should must explore. Purpose: To build enduring, compounding business value ("Power" = sustainable differential advantage). Few build Power while other chase growth. #Hamilton Helmer breaks it down into 7 defensible advanta
See More
Dhandho Marwadi
Welcome to the possi... • 10m
Flipkart Minutes plans to scale up its dark stores from 300 to 800 by 2025 to dominate the quick commerce race! → Competing with Blinkit, Zepto, Instamart and Big-Basket QC → AI-powered catalog & focus on Tier-1 speed → Over 1 million orders already
See MoreSairaj Kadam
Student & Financial ... • 1y
Do you Know How Important inflation is? Let's test it. If you had to borrow $1,000 from a friend and they agreed not to charge interest, but inflation is 3% annually, are you actually paying them back the full value of what you borrowed after one
See MoreDownload the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.



















/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)





















