Back
Vishu Bheda
•
Medial • 1y
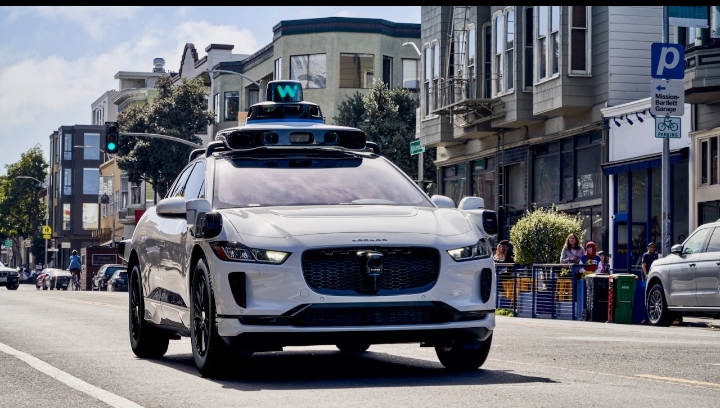
Waymo's market share is now equal to Lyft in SF. In just 15 months, they've captured 22% of the rideshare market. And they did it without a single human driver. Here's how a Google side project became the future of transportation: In 2009, Google started working on self-driving cars. Most people thought it would fail. For years, autonomous cars had always been “five years away.” But Google knew the real problem wasn’t just technology—it was trust. People needed to believe that a computer could drive better than humans. So, instead of rushing to market, they took their time gathering data: 20+ billion miles in virtual tests 20+ million miles on real roads 40,000 different test scenarios They focused on making driving safer, not just matching humans. The results? 84% fewer crashes causing injuries 57% fewer police-reported accidents 76% fewer property damage claims How did they do it? They built smart cars with incredible sensors: LiDAR that sees 300 meters in the dark Cameras that spot objects from 500 meters away Radar that works in rain, fog, and snow The real magic is their AI. It doesn’t just see—it predicts. It watches other cars, bikes, and pedestrians, making quick decisions to avoid danger. In 2016, Google spun off Waymo, focusing on ridesharing instead of selling cars. Why? Each car costs $100,000—too expensive for most people. But in ridesharing, cars can work 24/7 and earn money without needing a driver. By 2023, Waymo was giving 10,000 driverless rides a day in San Francisco, taking 22% of the market. Even Uber partnered with Waymo because competing was too hard. Next, Waymo is expanding to Japan. Self-driving cars are no longer the future—they’re here. And they’re safer, smarter, and changing how we travel.

Replies (16)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Saswata Kumar Dash
Buidling FedUp| AI R... • 10m
Anthropic Launches Claude 3.7 Sonnet: Anthropic unveiled Claude 3.7 Sonnet, a hybrid reasoning AI model offering faster, more nuanced responses. The model features "extended thinking mode" on paid plans, improving performance in mathematics, coding,
See Moreshahnawaz khan
Hey I am on Medial • 12m
Hay everyone i am ceo and founder of ashrafi cars and having used cars dealership in ajmer rajasthan and running it from more then 5 years. any one intrested in to invest in used cars and get 50% of profit in cars. we are raising 50 lakh in exchange
See MorePoosarla Sai Karthik
Tech guy with a busi... • 3m
In the 1900s, only a few thousand cars were built each year, hand made for the wealthy. By the 1920s, Ford’s assembly line scaled production 100x and put cars in the hands of millions. Rockets are now at a similar shift. Engines that once took years
See MoreDownload the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.