Back
SHIV DIXIT
CHAIRMAN - BITEX IND... • 1y
📖 DAILY BOOK SUMMARIES 📖 🚀 20 Lessons from 👉 🔥 Competitive Advantage 🔥 ✨ By Michael E. Porter ✨ 1. Definition: Competitive advantage is achieved when a company can create more value for its customers than its competitors. 2. Types of Competitive Advantage: • Cost Leadership: Achieving the lowest cost in the industry while maintaining acceptable quality. • Differentiation: Offering unique products or services that provide value to customers, allowing for premium pricing. 3. Value Chain Analysis: • Breaks down a company’s activities into primary (inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, service) and support activities (firm infrastructure, human resource management, technology development, procurement). • Identifies areas where a company can create a competitive advantage. 4. Industry Structure: • The competitive environment is shaped by five forces: • Threat of New Entrants: New competitors can increase competition and reduce profitability. • Bargaining Power of Suppliers: Powerful suppliers can influence costs and profitability. • Bargaining Power of Buyers: Strong buyers can demand lower prices or higher quality, affecting margins. • Threat of Substitute Products: Alternatives can reduce demand for a product. • Rivalry Among Existing Competitors: Intense competition can erode profits. 5. Strategic Positioning: • Companies must choose a strategy that aligns with their strengths and the industry dynamics. • Focus on segments where they can create the most value. 6. Sustainable Competitive Advantage: • Achieved through unique resources, capabilities, or market position that cannot easily be replicated by competitors. • Importance of continuous improvement and innovation. 7. Implementing Strategy: • Effective execution requires aligning the organization’s structure, culture, and systems with the chosen competitive strategy. 8. Role of Technology: • Technology can enhance competitive advantage by improving processes, products, or customer experiences. 9. Global Competition: • Companies must understand the dynamics of global markets and adapt their strategies accordingly 10. Conclusion • Competitive advantage is not static; companies must continually analyze their position and adapt to changes in the industry and market conditions 11. Cost Advantage: • Achieved by reducing costs below competitors while maintaining quality. • Can stem from economies of scale, experience curves, or access to low-cost inputs 12. Differentiation Advantage: • Unique features, brand image, technology, or customer service can differentiate a product. • Allows firms to charge higher prices due to perceived value 🔗 13. Scope of Competitive Advantage • Competitive advantage can be applied to • Industry-wide: Aimed at the entire industry (e.g., cost leadership) • Focus: Targeting a specific market segment (e.g., niche markets) 🔗 Download whole book freely from comment 🔗


Replies (3)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
SHIV DIXIT
CHAIRMAN - BITEX IND... • 1y
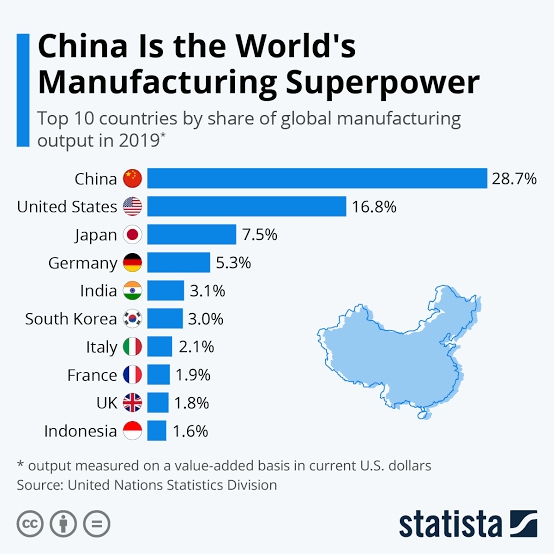
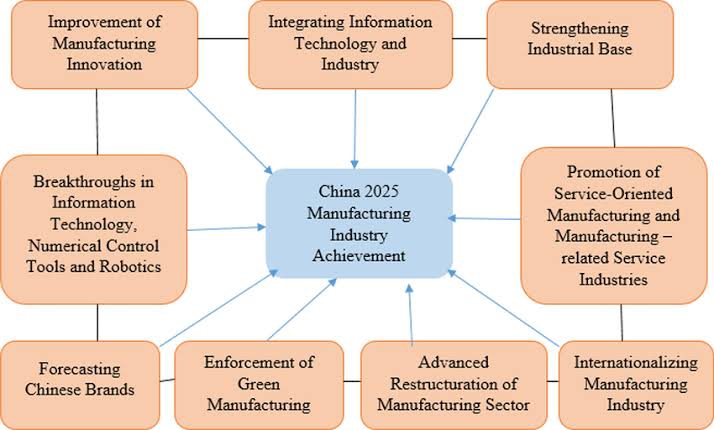
“China Manufacturing strategy breakdown” Do you know China is Earning whole India gdp with the help of manufacturing. Basically China is entrepreneur economy and around 29% global manufacturing belongs to china worth ( 4 Trillion dollars ). Chin
See More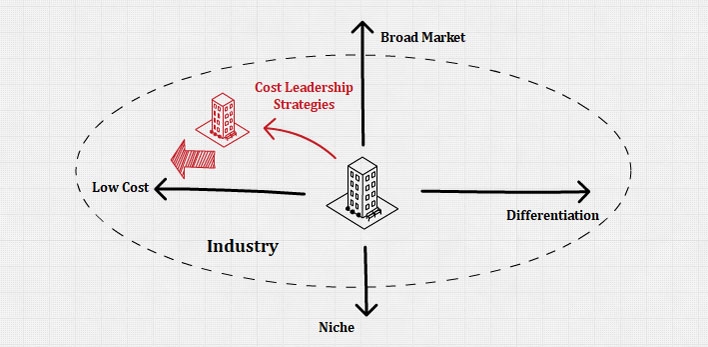
Ritik Barnwal
Server Administrator... • 1y
I am running a web hosting startup that has already achieved impressive sales without any marketing efforts. To take the business to the next level, I am seeking an investor to help scale operations. The investment will be used to implement strategic
See MoreThakur Ambuj Singh
Entrepreneur & Creat... • 11m
The 9 Point Business Circuit is a comprehensive framework for analyzing any business within its industry. It covers key aspects such as value proposition, business model, industry trends, competitive positioning and growth potential, helping entrepr
See More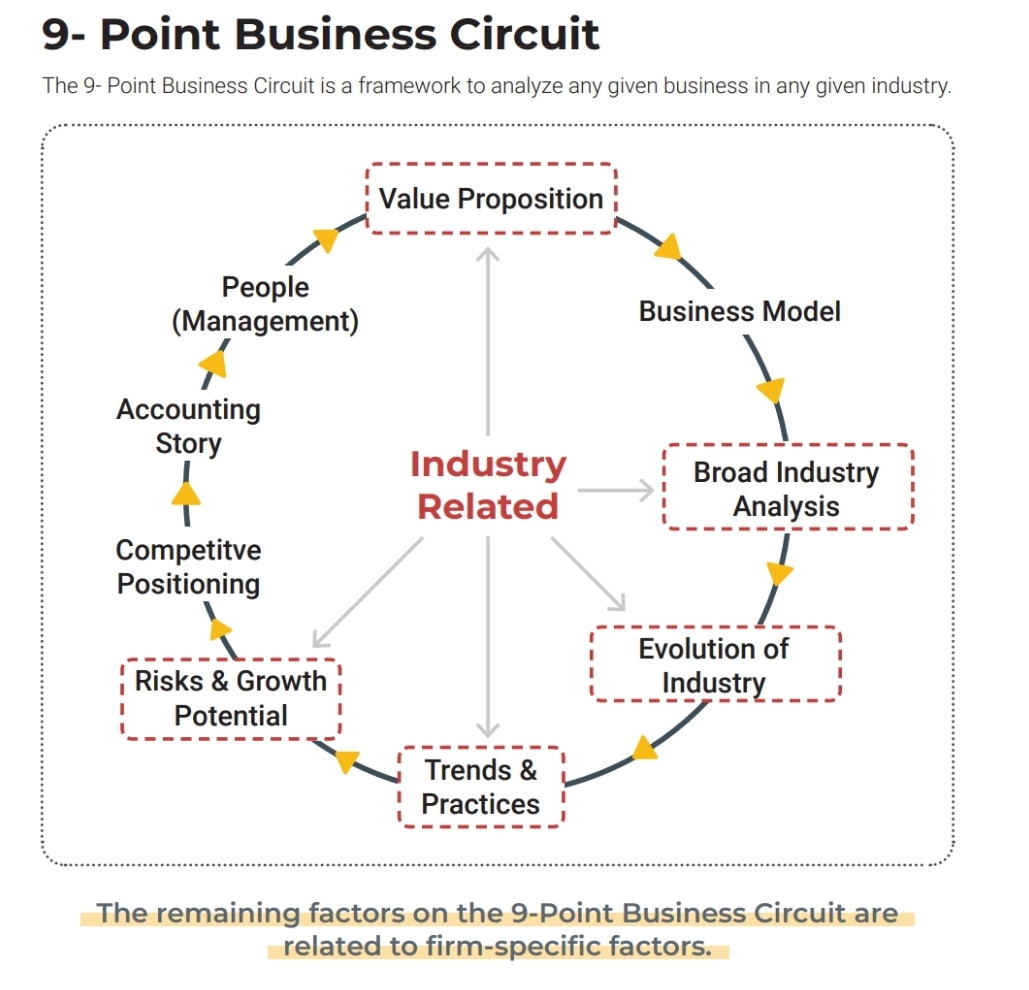
Download the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.













/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)



















