Back
Snehangshu Roy
Polymath • 6m
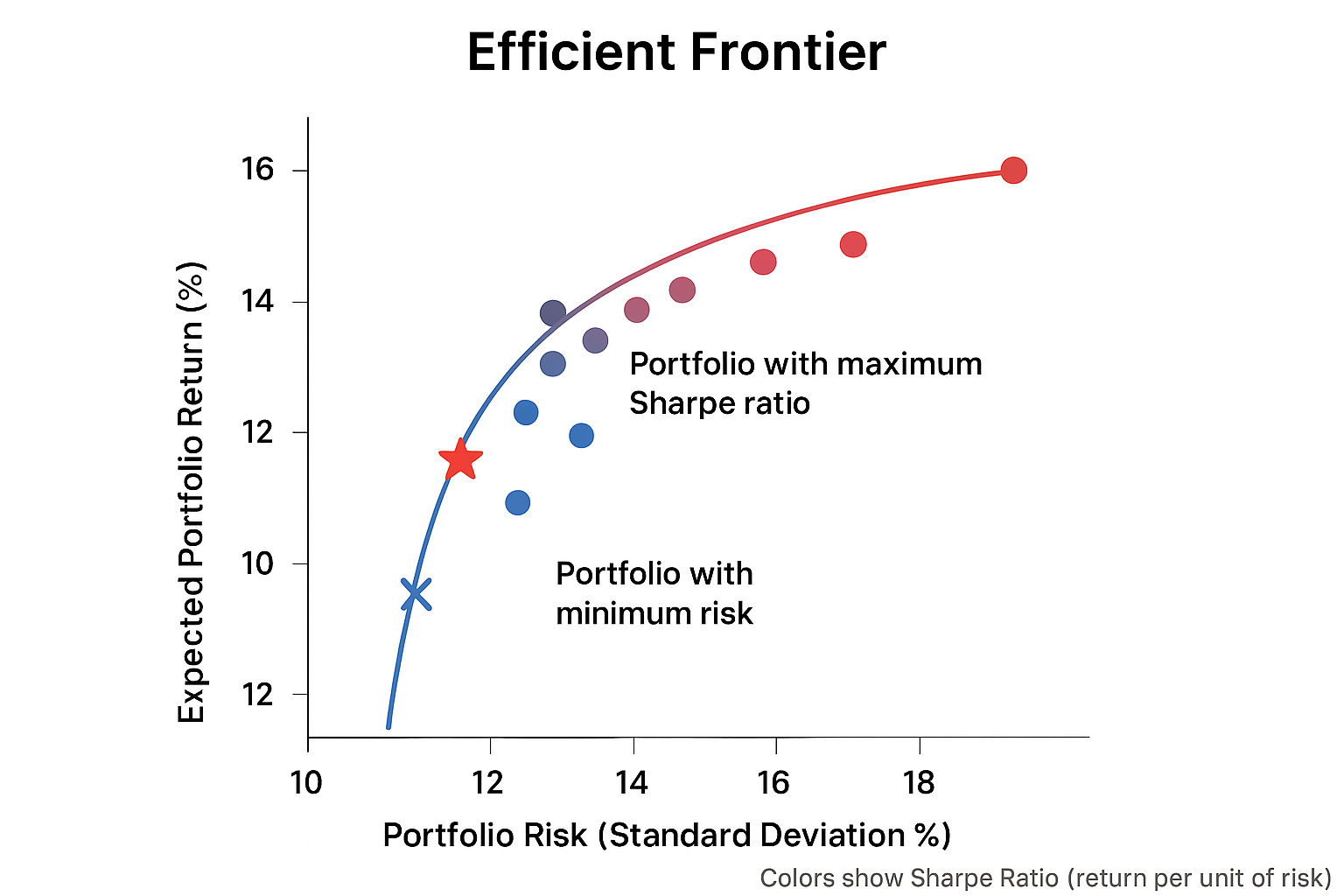
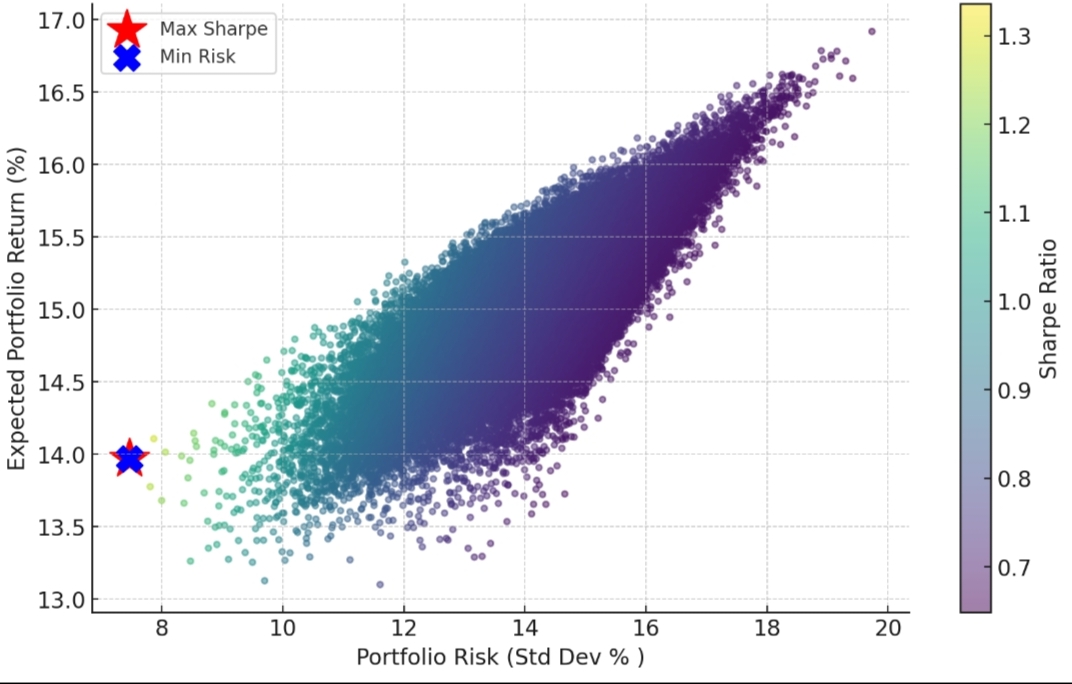
🚨Are you doing the Sip the right way? Have you engaged yourself with multiple funds and doubt whether is it the perfect allocation? The most important part is to understand portfolio allocation and there multiple theories for it but those are according to one's risk appetite and goals 1)Modern portfolio theory: For any target risk, there is a portfolio that gives the maximum return (efficient frontier). The math solves an optimization: pick weights w to maximize (µᵀw − λ wᵀΣw) or equivalently maximize Sharpe. Also the efficient frontier curve to find whether your portfolio sits well on the curve neither too low below or may be above if you are open to take more volatility 2)Core-satellite method:Core (large, cheap, stable) ~ 60–80% Satellite (active, high-conviction) ~ 20–40% Why it works (math intuition): Core lowers volatility (low σ), gives you market beta. Satellite raises expected return µ (but with higher σ). Since portfolio return is weighted average, satellites can lift µ while core keeps σ from exploding. 3)Risk parity Idea: allocate so each asset contributes equally to portfolio risk (variance), not equal cash amounts. Core formula for risk contribution of asset i: Marginal risk = (Σ w)_i (where Σ is cov matrix) Risk contribution RC_i = w_i × (Σw)_i Normalize RC_i so they sum to portfolio variance. Unlevered approximation (retail): weights ∝ 1 / σ (inverse-vol weighting). That equalizes volatility contribution roughly, but needs covariance for exact equal-risk. Numeric results: For Nifty50 (σ=18%), Midcap (σ= 24%), Debt (σ=3%): 4) Barbell (Taleb) — safe + aggressive extremes Idea: split between safe assets (debt/gold) and aggressive assets (smallcaps, options, venture). Avoid the "average" middle. Numeric example I ran: 40% short-term debt + 60% smallcap Result: µ ≈ 13.0%, σ ≈ 16.7%, Sharpe ≈ 0.42 (illustrative). 5) Global Hedge / Diversification (India + US example) Principle: Correlation matters. India & US have correlation ~0.3–0.4 in the example. Adding US reduces portfolio volatility without proportionally reducing return. Numbers I computed: 100% India (Nifty) → µ 12.0%, σ 18.0% 80/20 India/US → µ ~12.2%, σ ~16.7% (Sharpe improves) Why: diversification benefits via low correlation. Parag Parikh Flexi already helps here (it holds global stocks Takeaway: You get downside protection via the safe half and large upside from the aggressive half. Works when you want exposure to black-swan upside but not full risk. 6) Factor investing You remain 55% in the market and remaining allocate in stocks/funds which show the following and historical premia returns that add up to your portfolio But yes this is A total volatile game High sharpe Momentum premium (+3% in your example): Stocks that have been going up in the past 6–12 months tend to continue rising, so historically they earned more than average. Size premium (+2%): Smaller companies often grow faster than large ones, historically giving slightly higher returns. Quality premium (+2%): Companies with strong profits, low debt, and stable earnings tend to outperform over time. Value premium: Cheap stocks relative to earnings or book value tend to outperform over long periods. How it’s calculated: Analysts look at historical returns of stocks that have that factor versus stocks that don’t. The average extra return over the market is called the factor premium.
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Tushar Aher Patil
Trying to do better • 1y
Day 3 About Basic Finance Concepts Here's Some New Concepts 4. Investment Stocks: Shares in a company that give investors ownership rights and potential dividends. Bonds: Debt securities where investors loan money to companies or governments in re
See More
VIJAY PANJWANI
Learning is a key to... • 5m
Debt-Free Penny Stocks to Watch in 2025 When it comes to penny stocks, financial health matters the most. One strong indicator is the Debt-to-Equity Ratio – and a zero debt ratio signals a company with no debt burden. Here are a few debt-free penn
See More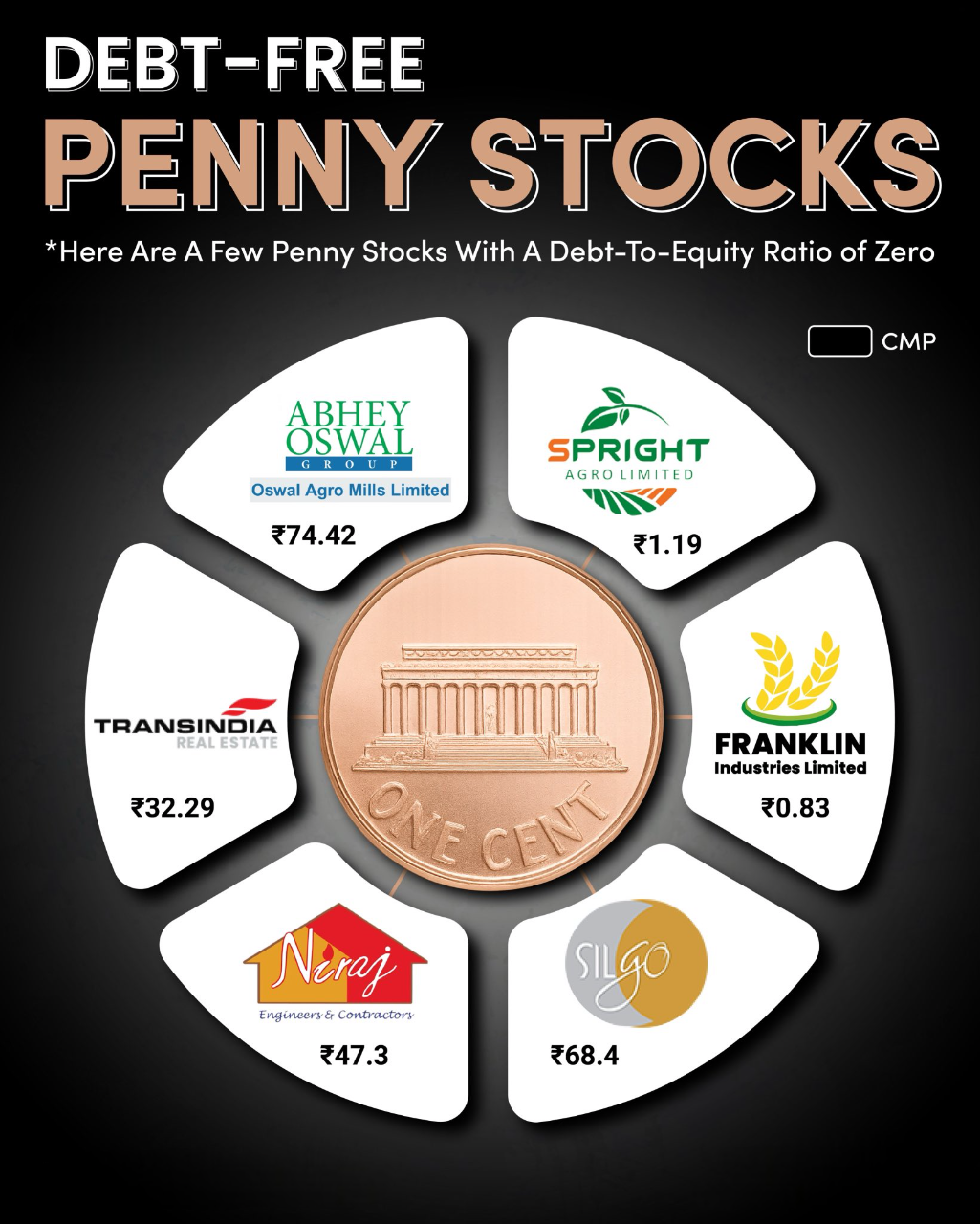
Soumya Ranjan Dash
Hit & Trial • 1y
When I started investing in stock markets, I cared about: 100x returns Multibagger stocks Sharing profit screenshots What peers thought about me After getting grilled in the Market, I care about: Risk per investment Overall consistent annual retur
See MoreVIJAY PANJWANI
Learning is a key to... • 11d
Before Buying Any Option Premium, Read This! 🚨 Most traders focus only on direction… But professionals focus on Greeks & Volatility. 📊 If you want consistency in option buying, follow these 3 Golden Rules: ✅ 1️⃣ Delta > 0.3 (30) Delta measures the
See More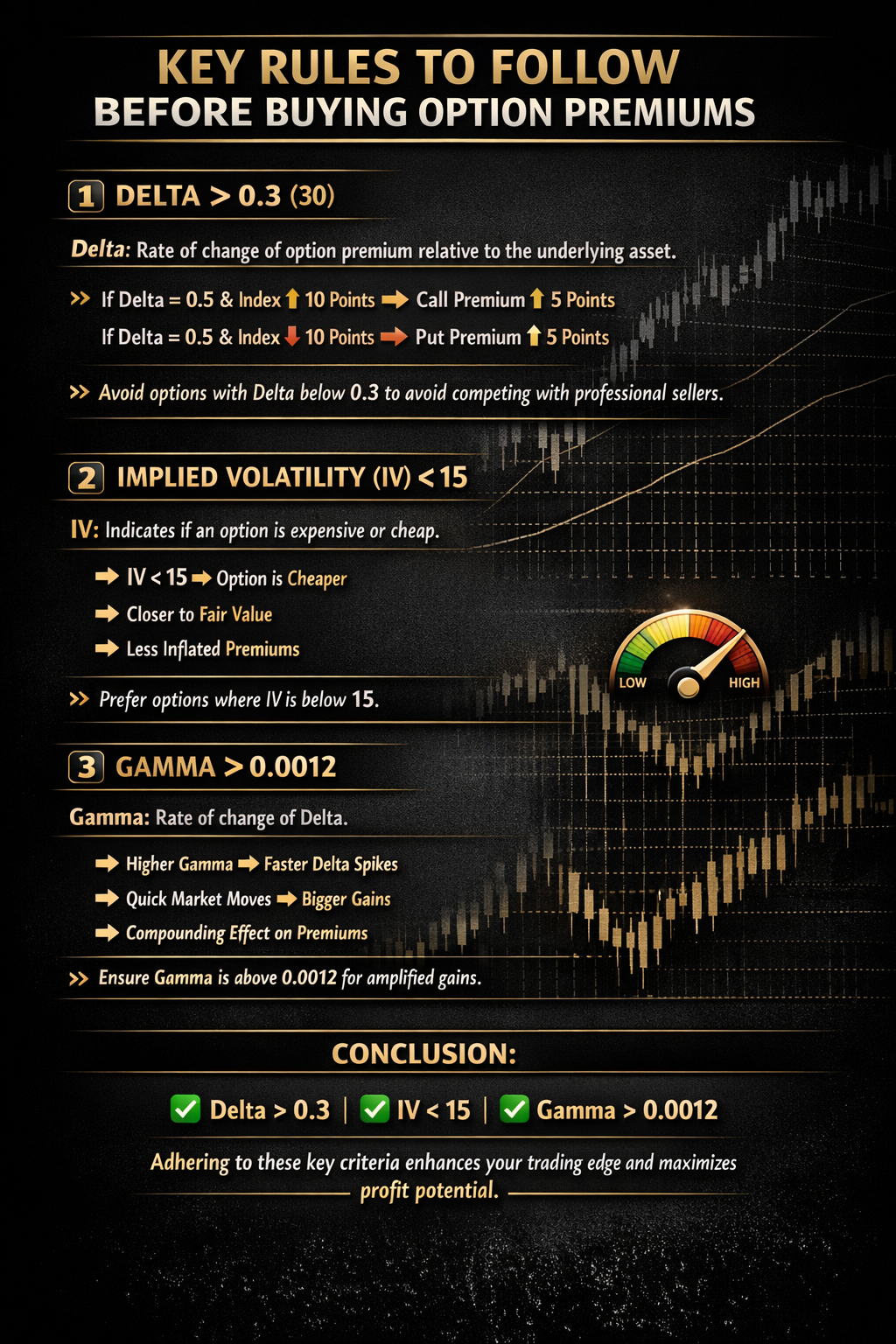
Download the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.
















/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)



















