Back
SHIV DIXIT
CHAIRMAN - BITEX IND... • 1y
📖 DAILY BOOK SUMMARIES 📖 🔗 DIRECT FREE E-BOOK DOWNLOAD LINK AVAILABLE — https://drive.google.com/file/d/1KWjZOnkhyE4rVlTATN9CQkpLIiIoIhaN/view?usp=drivesdk 🔥 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 🔥 🚀 20 Lessons 👉 ✨ Peter Drucker ✨ 1. The Importance of Innovation • Innovation is the key to driving business growth, enhancing productivity, and maintaining a competitive edge in the market. 2. Types of Innovation • There are two main types: Entrepreneurial Innovation (new ideas or practices) and Managerial Innovation (process improvements). 3. The Entrepreneurial Process • Entrepreneurship is a process of identifying opportunities, developing ideas, and bringing them to life in the form of new products or services. 4. The Role of the Entrepreneur • Entrepreneurs are the driving force behind innovation, taking risks to create new products, services, or solutions that fulfill market needs. 5. Innovative Opportunities • Successful innovation often comes from identifying gaps in the market or unmet needs, thus creating value for customers. 6. Creative Destruction • Innovation often disrupts existing market leaders, a concept known as creative destruction, leading to the replacement of outdated business models with new ones. 7. Invention vs. Innovation • Invention is the creation of new ideas or technologies, while innovation involves transforming these ideas into products or services that bring value to the market. 8. The Role of Risk and Failure • Risk is inherent in entrepreneurship, and failure is often a step toward learning and refining ideas, ultimately leading to success. 9. The Importance of Knowledge • Innovation relies heavily on knowledge — both the technical expertise and market understanding necessary to develop and refine new ideas. 10. The Need for Systematic Innovation • Innovation should be systematic, involving structured processes, goal-setting, and continuous learning. 11. Innovation and Corporate Culture • Companies need to foster a culture that supports risk-taking, creativity, and the acceptance of failure as a learning experience to encourage innovation. 12. The Innovator’s Dilemma • Established companies often struggle with innovation because they are entrenched in their existing practices, making it harder to adapt to new market demands. 13. Sources of Innovation • Innovation can arise from a variety of sources, including technological advancements, customer needs, new management practices, and even social or environmental changes. 14. Innovative Strategies for Firms • Firms should employ strategies like differentiation, cost leadership, and focus strategies to create and sustain innovation. 15. The Role of Government in Innovation • Governments can promote innovation by creating supportive policies, providing incentives, and investing in research and development.

Replies (2)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Thakur Ambuj Singh
Entrepreneur & Creat... • 11m
🚀 Competitive Life Cycle 🔬 Innovation – The stage where new ideas, products, or services are developed. Teams brainstorm, experiment and bring something unique to the market. 📈 Growth – Demand increases and businesses expand. Scaling up operatio
See More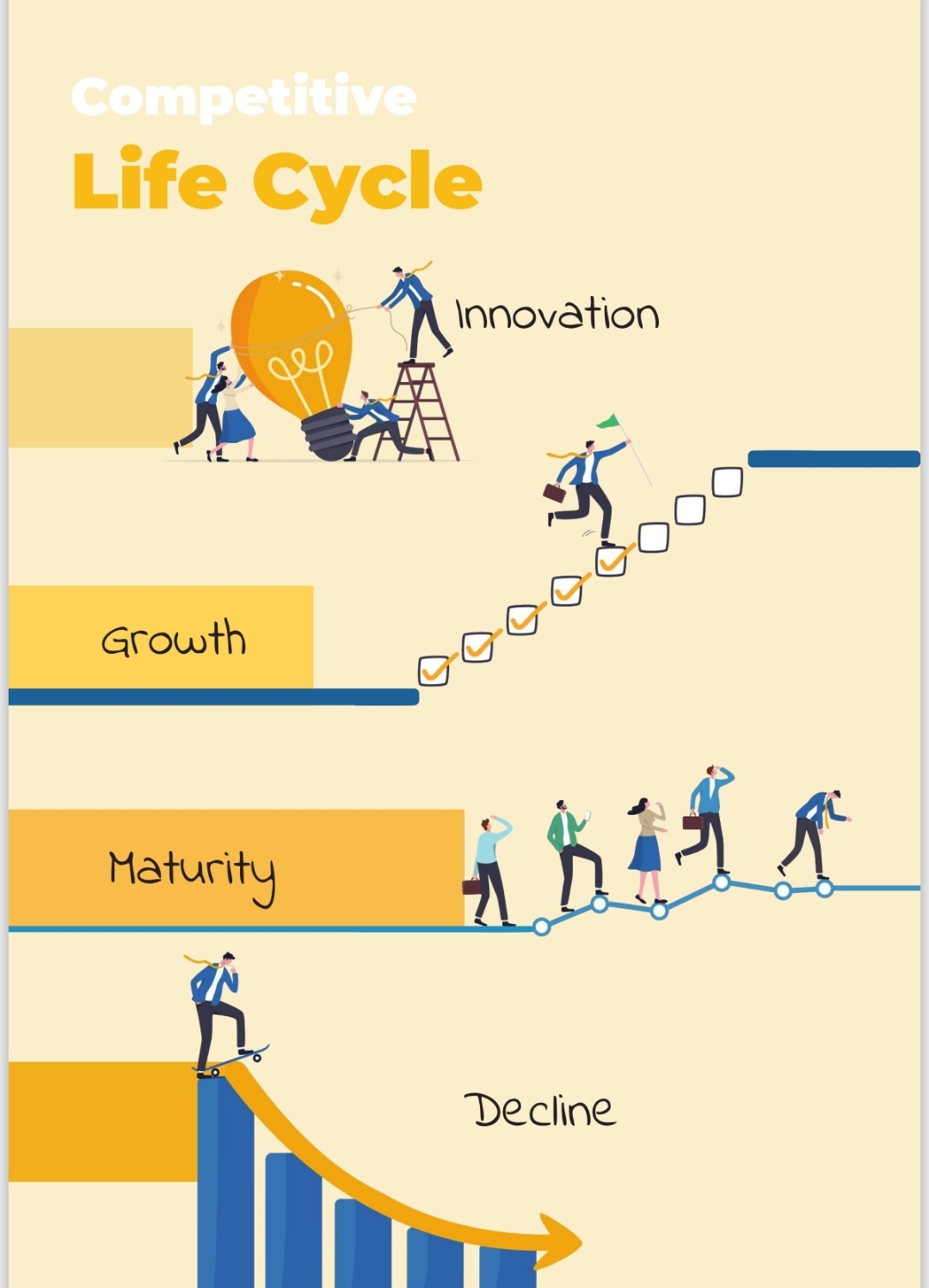
Its Me Pratik
Your business and my... • 8m
I shared my mindset or thoughts for all failure & future founders.... If a startup or business fails, it's not necessarily the business idea that failed — it's often the mindset and execution of the founder and their team. The market has room for man
See MoreSandip Kaur
Hey I am on Medial • 1y
The Fear of Failure: How It Can Be Your Greatest Asset Failure is often seen as the ultimate fear in the business world, but what if it could be your biggest advantage? Here’s how embracing the fear of failure can lead to success: 1. Learning Opportu
See MoreVikas Acharya
Building Reviv | Ent... • 1y
NITI Aayog invites EoI for preparation of India Innovation Index 2025 Government think tank NITI Aayog has invited expression of interest for the preparation of the India Innovation Index 2025, intending to encourage states to improve their innovati
See More
Prog Kanishk Raj
Programmer, Founder ... • 1y
The Seeds of Success (Story) Failure is a word we often dread, but it’s a universal experience shared by everyone who has ever achieved greatness. From failed relationships to unsuccessful businesses, from poor exam results to rejected ideas—failur
See MoreDownload the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.

















/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)


















