Back
SHIV DIXIT
CHAIRMAN - BITEX IND... • 1y
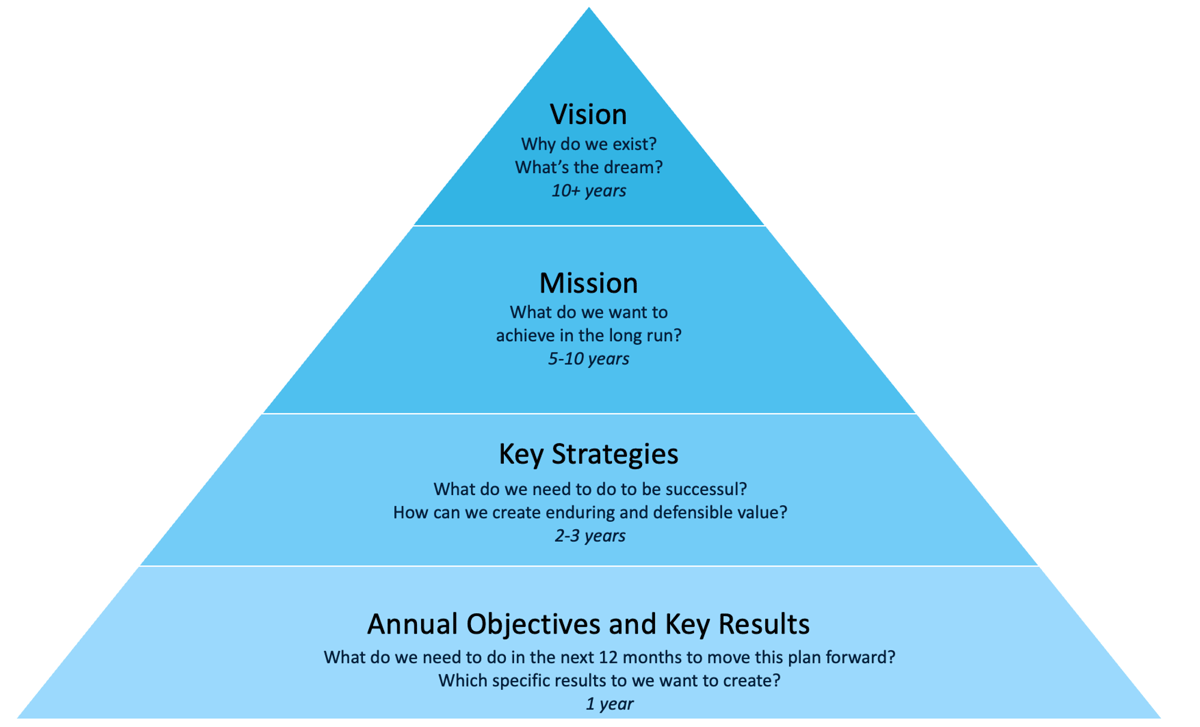
📖 DAILY BOOK SUMMARIES 📖 🚀 20 Lessons from 👉 🔥 Measure what matters : OKRs 🔥 ✨ By John doerr ✨ 1. Definition of OKRs: • OKR stands for Objectives and Key Results. It is a goal-setting framework used to define and track objectives and their outcomes. 2. Objectives: • Objectives are qualitative, inspirational, and time-bound goals that provide direction and motivation. • Should be ambitious and align with the organization’s mission. 3. Key Results: • Key Results are specific, measurable outcomes that indicate progress toward achieving the objective. • They should be quantifiable and provide clear evidence of success. 4. Benefits of OKRs: • Focus: Helps prioritize and align efforts on the most important goals. • Transparency: Encourages open communication about objectives across the organization. • Engagement: Involves teams in goal-setting, enhancing commitment and motivation. 5. Cascading OKRs: • OKRs can be set at various levels (company, team, and individual) to ensure alignment throughout the organization. • Each level should support the higher-level OKRs. 6. Regular Check-ins: • Frequent reviews (quarterly or monthly) are essential for tracking progress and making adjustments. • Encourages accountability and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. 7. Scoring and Assessment: • Key Results are typically scored on a scale (e.g., 0.0 to 1.0) to measure progress. • A score of 0.7 to 1.0 indicates success, while scores below may require reevaluation. 8. Stretch Goals: • OKRs should encourage teams to set challenging goals that push them to achieve more. • Aiming for ambitious targets fosters innovation and growth. 9. Cultural Impact • Implementing OKRs can transform an organization’s culture by promoting accountability, transparency, and alignment • Encourages a mindset focused on results and continuous learning 10. Case Studies • The book includes examples from successful companies (e.g., Google, Intel) that have effectively used OKRs to drive performance and growth • Highlights the adaptability of the OKR framework across different industries 11. Origins of OKRs • The OKR framework was popularized by Intel in the 1970s and later adopted by Google in the early 2000s, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness in various organizational contexts 12. Distinction from Traditional Goal Setting: • OKRs differ from traditional goal-setting methods by emphasizing outcomes rather than outputs • Encourages teams to focus on the impact of their work rather than just completing tasks 13. Role of Leadership • Leadership commitment is critical for successful OKR implementation • Leaders should model transparency and accountability to inspire teams 14. Flexibility: • The OKR framework is adaptable to different team sizes and organizational structures, making it suitable for startups, large enterprises, and non-profits 🔗 You can download whole book freely from comment 🔗

Replies (3)
More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Last AdmiraL
Level up in producti... • 1y
Day 5 of giving actionable insights to founders Goal Setting Made Simple: SMART Goals and OKRs Setting goals can feel overwhelming without a clear structure. SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) help break down big am
See MoreHemant Prajapati
•
Techsaga Corporations • 1y
Pehle toh follow 👋 kare aur 📑 bookmark kare . . Key terms every startup founder must know: 🔍 Product-Market Fit - Ensuring your product meets real customer needs in a large market. 📈 Traction - Signs that show user growth and engagement. ⏳ Ru
See More
Pranjal Majumdar
Hey I am on Medial • 1y
Tell yourself every day: "I am where I am because of my decisions! If I want better results: I must take better actions. I will learn the lessons. I will see the blessings. I will not stop until my goals are realized. When I reach that goal, I will
See MoreCHINMAYEE SAMAL
Digital Marketing St... • 4m
🎯 Master the Steps of Digital Marketing! 🚀 From research to results — every step counts! ✅ Market Research ✅ Competitive Analysis ✅ Identify Target Audiences ✅ Set Goals & Objectives ✅ Define Strategies ✅ Evaluate & Improve Build your digital s
See More
Download the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.













/entrackr/media/post_attachments/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Accel-1.jpg)



















