Back
Rahul Agarwal
Founder | Agentic AI... • 1d
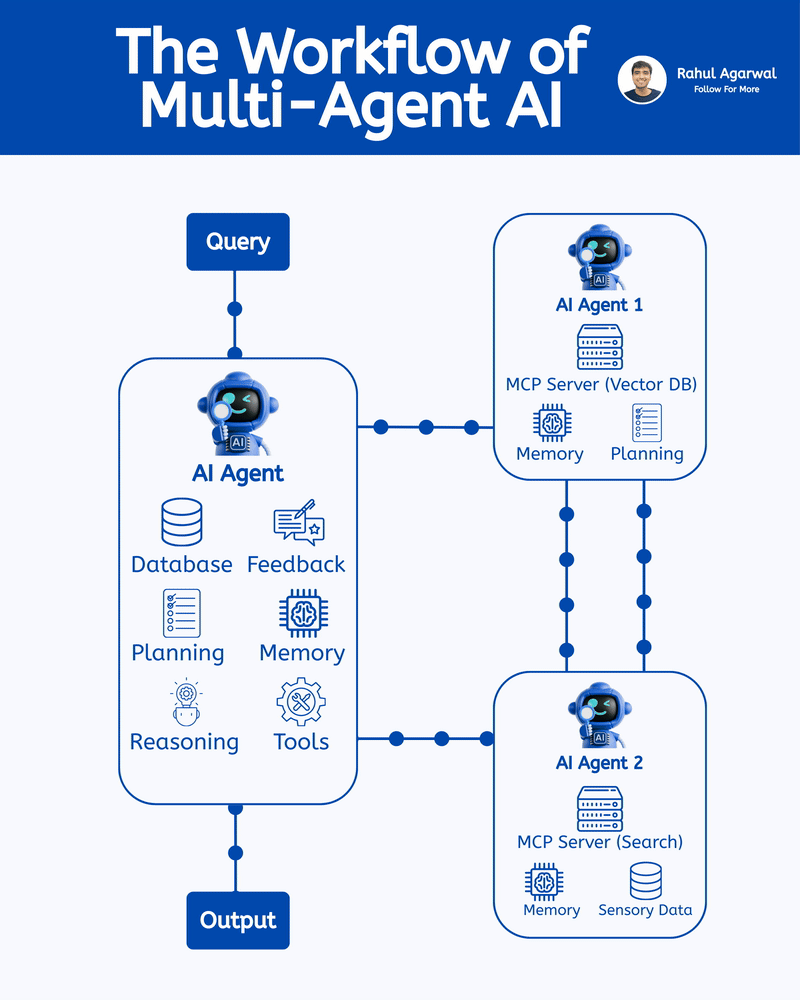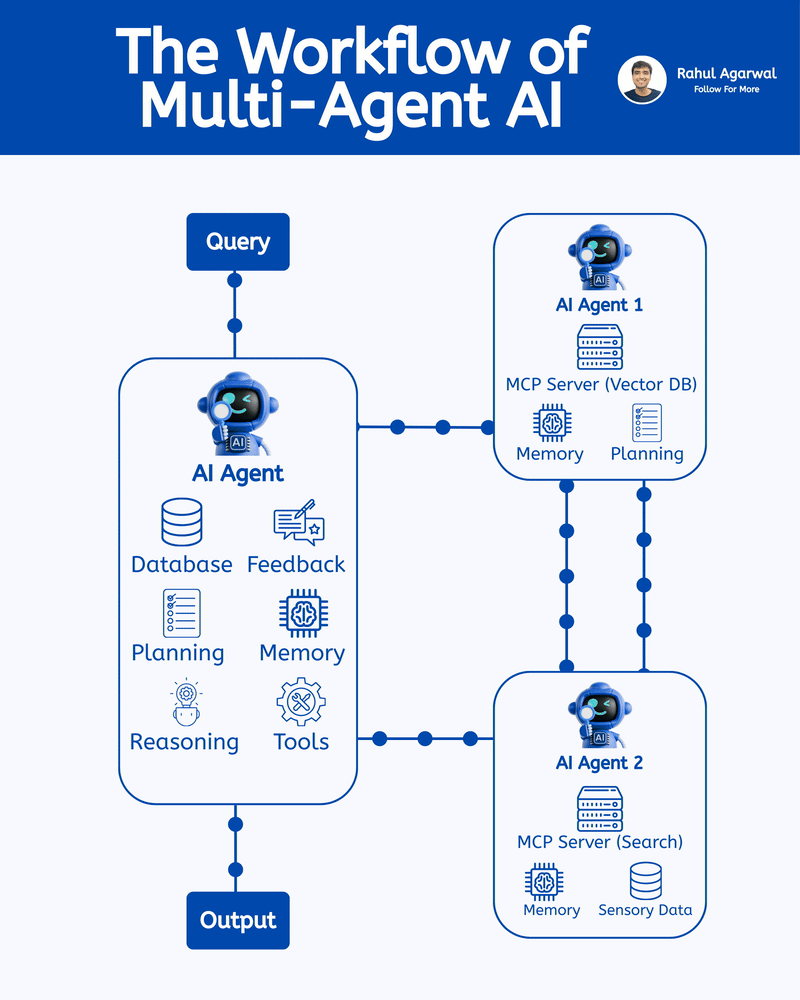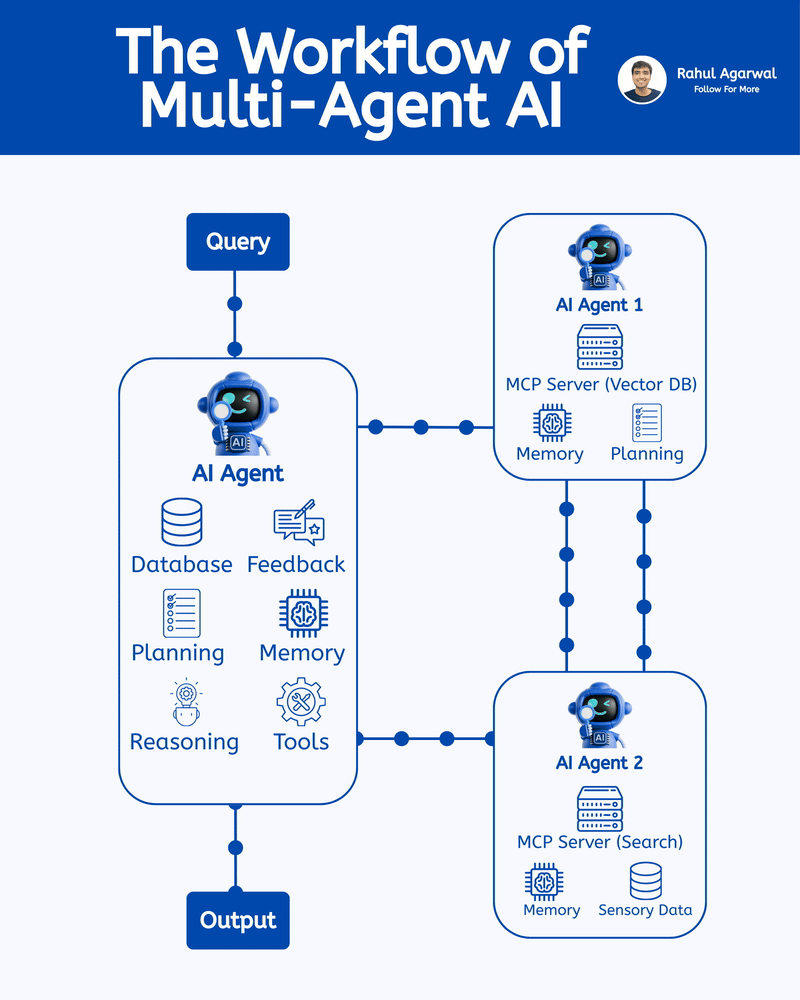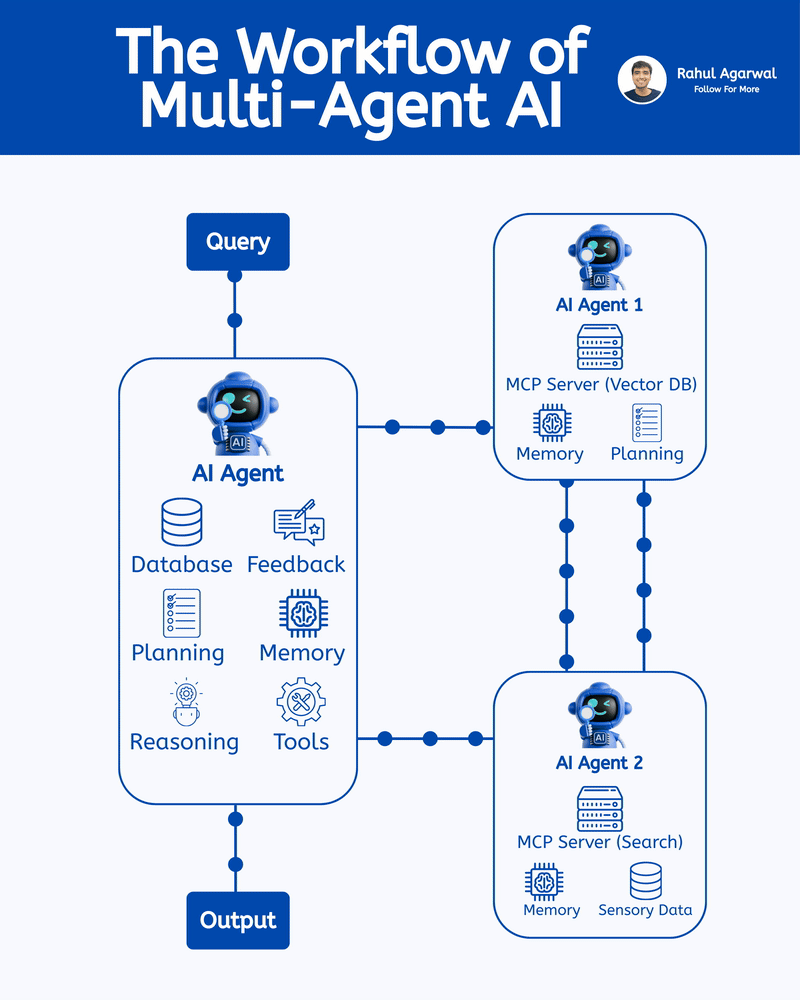
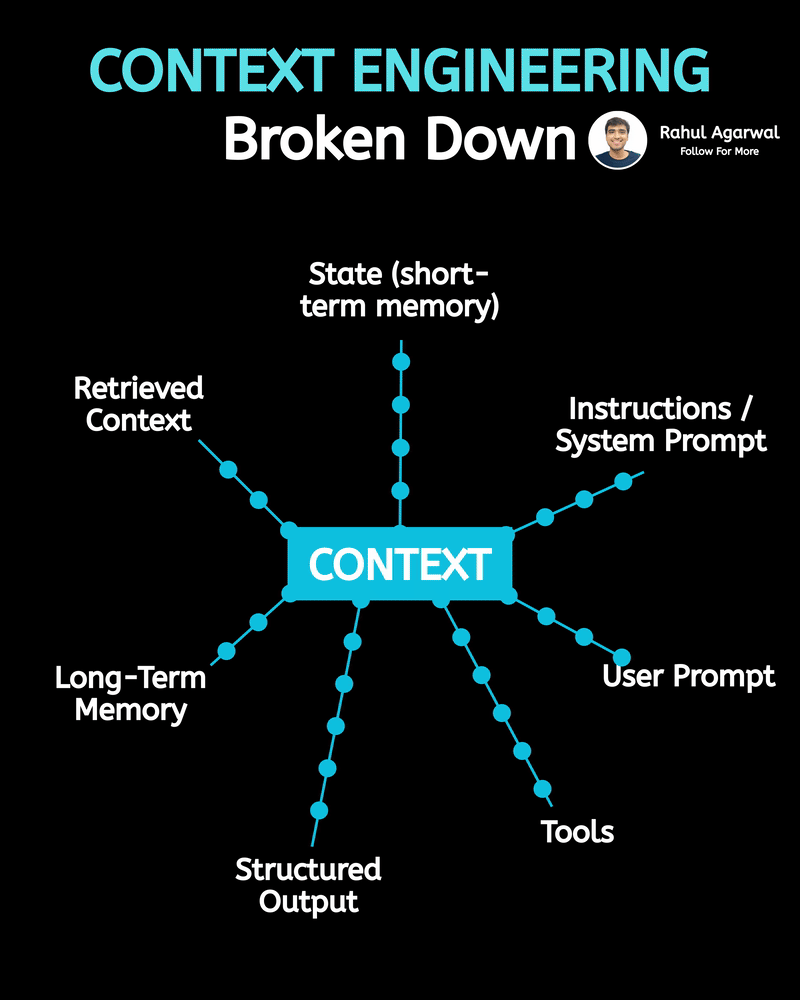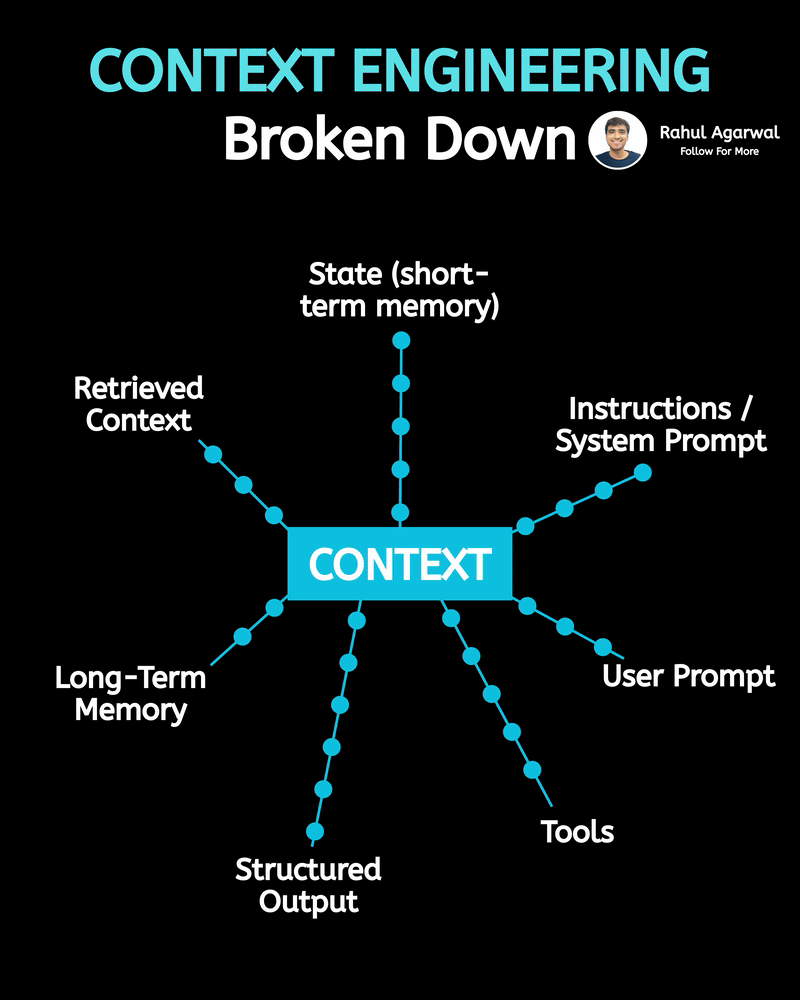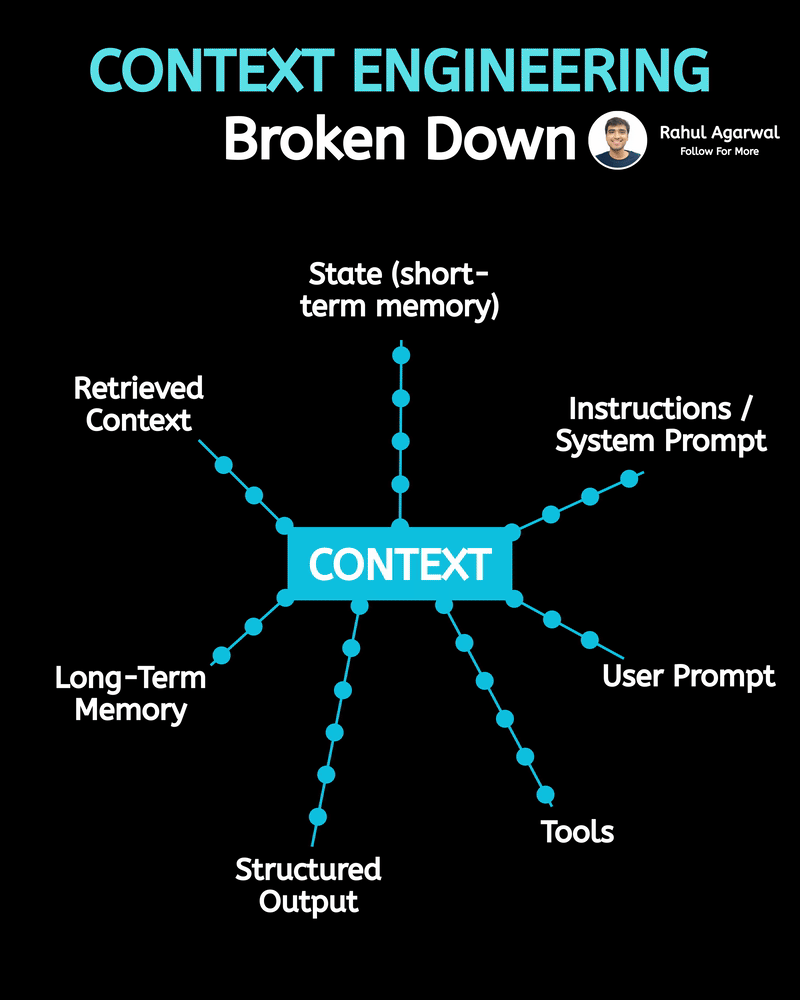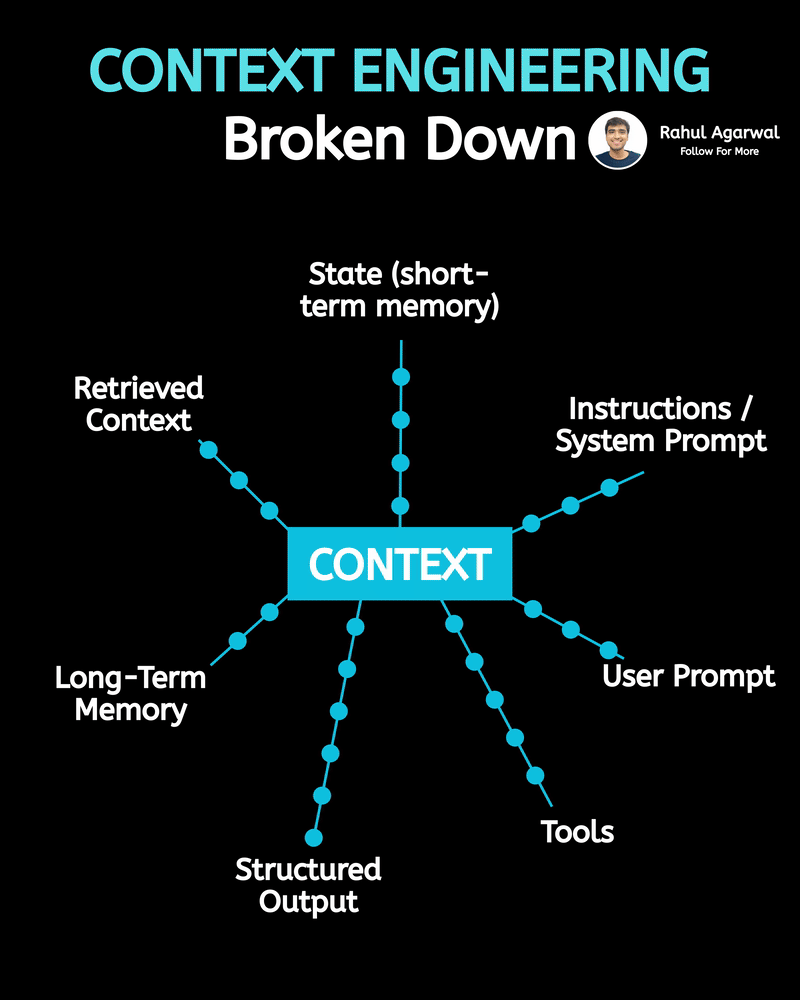
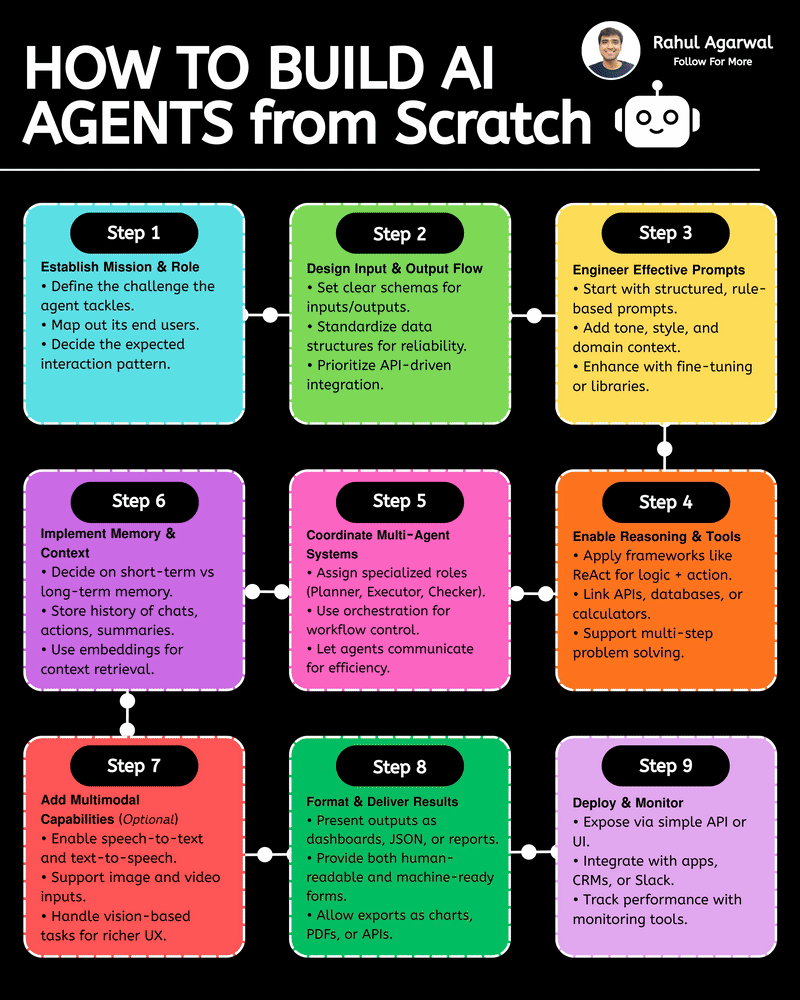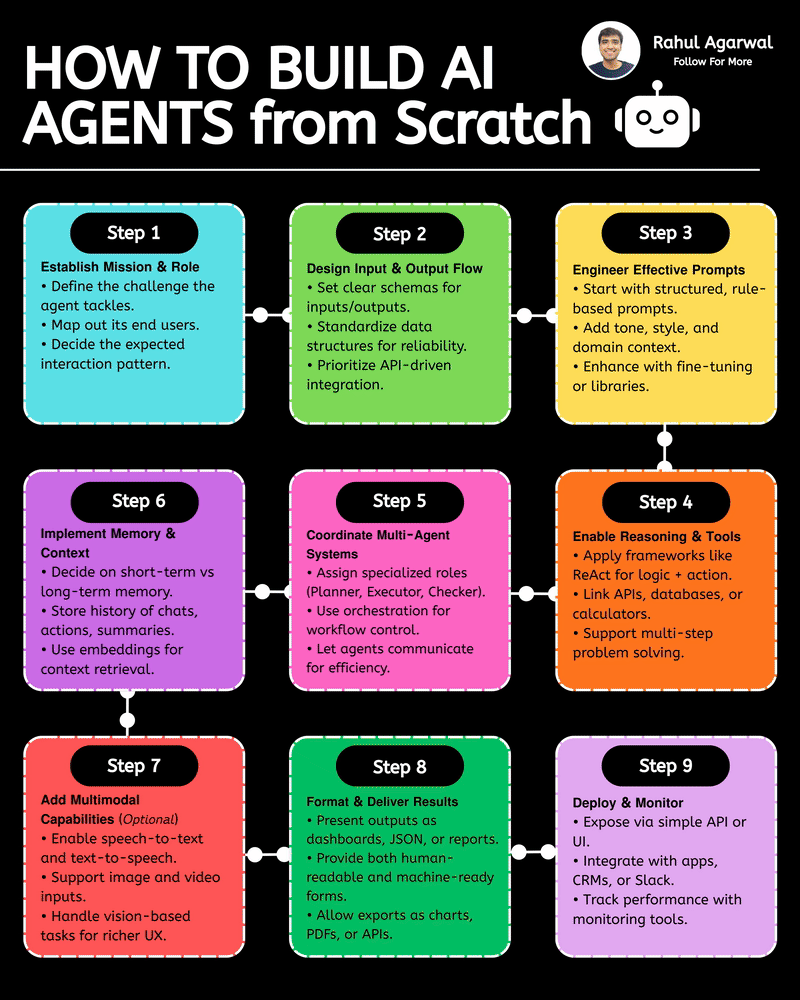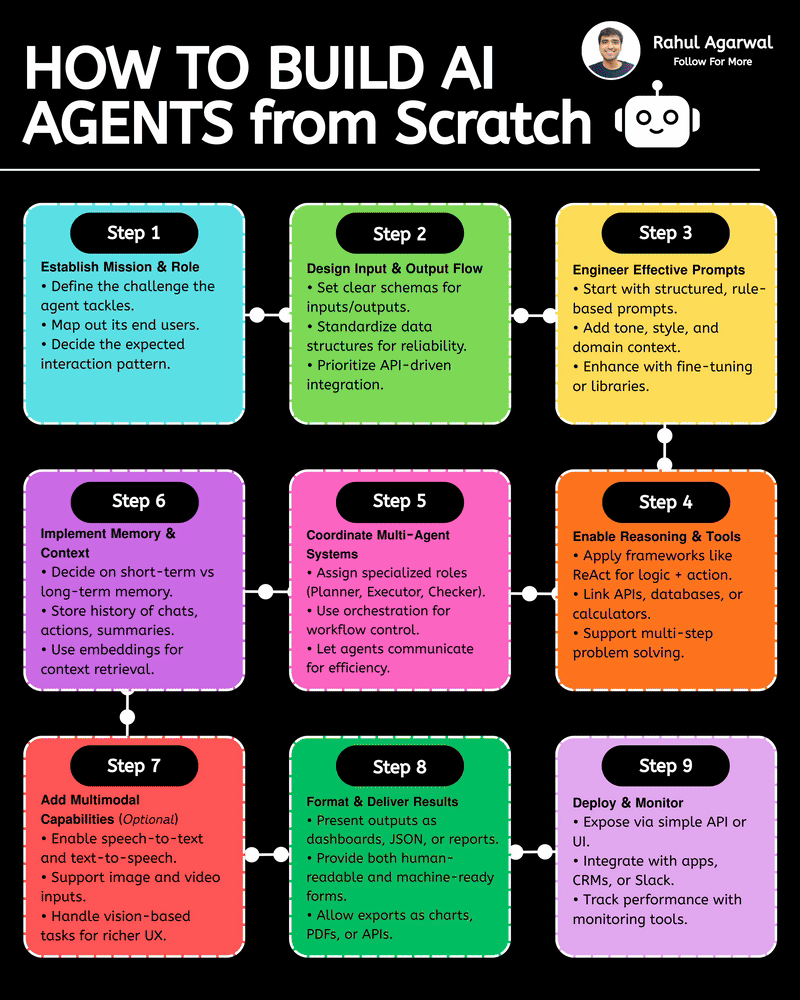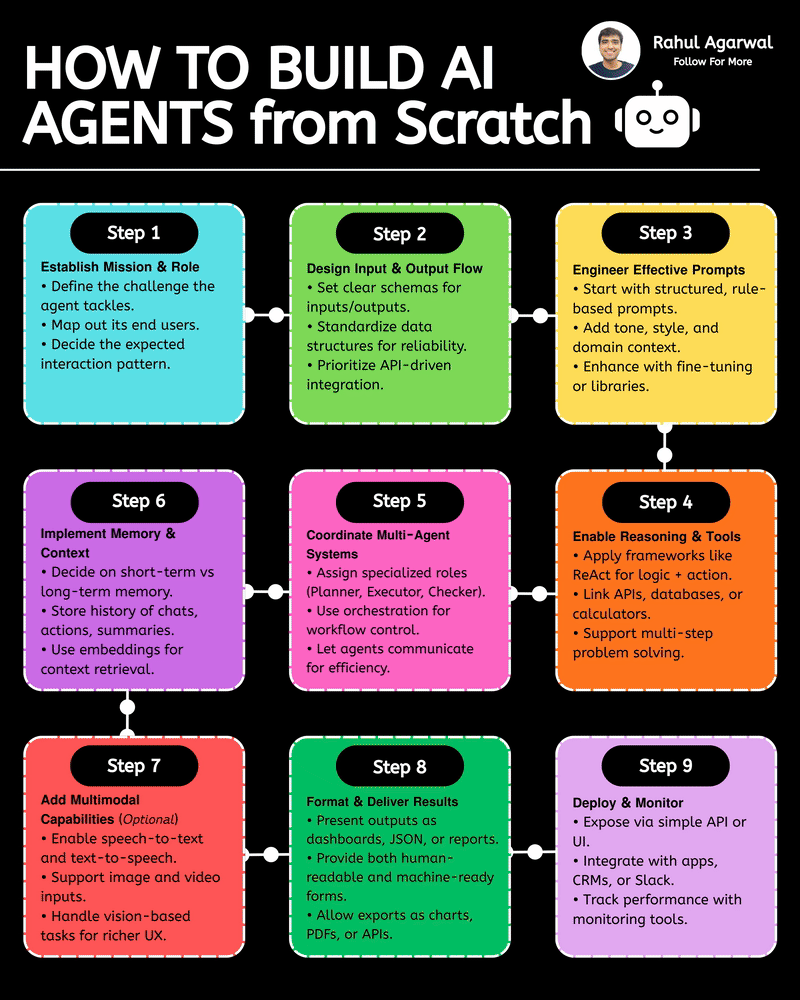
Hands down the simplest explanation of AI agents using LLMs, memory, and tools. A user sends an input → the system (agent) builds a prompt and may call tools and memory-search (RAG) → agent decides and builds an answer → the answer is returned to the user and important context is saved into short-term or long-term memory. 1) 𝗨𝘀𝗲𝗿 → 𝗜𝗻𝗽𝘂𝘁 User sends a message, which becomes the system’s input. This starts the whole process. 2) 𝗜𝗻𝗽𝘂𝘁 → 𝗔𝗴𝗲𝗻𝘁 The agent receives the input and decides what action to take. It plans how to respond. 3) 𝗔𝗴𝗲𝗻𝘁 → 𝗥𝗔𝗚 (𝗿𝗲𝘁𝗿𝗶𝗲𝘃𝗮𝗹) The agent searches long-term memory for relevant information. This helps it use real stored knowledge instead of guessing. 4) 𝗔𝗴𝗲𝗻𝘁 → 𝗔𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗧𝗼𝗼𝗹𝘀 If needed, the agent calls tools/APIs to perform tasks. This allows it to do more than just generate text. 5) 𝗨𝗽𝗱𝗮𝘁𝗲 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝗺𝗽𝘁 The agent builds a final prompt using the input, retrieved memory, and tool results. A better prompt leads to a better answer. 6) 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝗱𝘂𝗰𝗲 𝗔𝗻𝘀𝘄𝗲𝗿 The system generates the final answer based on the prompt. This is what the user receives. 7) 𝗦𝗮𝘃𝗲 𝘁𝗼 𝗦𝗵𝗼𝗿𝘁-𝗧𝗲𝗿𝗺 𝗠𝗲𝗺𝗼𝗿𝘆 The conversation is stored in chat history for the current session. This helps the agent remember context during the chat. 8) 𝗔𝗱𝗱 𝘁𝗼 𝗟𝗼𝗻𝗴-𝗧𝗲𝗿𝗺 𝗠𝗲𝗺𝗼𝗿𝘆 (𝗼𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝗮𝗹) Important facts are saved permanently in long-term memory. This allows personalization and continuity across sessions. Short definitions of the main boxes (super simple): • 𝗔𝗴𝗲𝗻𝘁: the brain/manager that decides what to do. • 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝗺𝗽𝘁: the full context and instructions given to the LLM to produce an answer. • 𝗥𝗔𝗚 (𝘃𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗼𝗿 𝘀𝗲𝗮𝗿𝗰𝗵): fast search for similar past bits of text in long-term storage. • 𝗔𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗧𝗼𝗼𝗹𝘀: external capabilities (APIs, scripts, calculators). • 𝗦𝗵𝗼𝗿𝘁-𝗧𝗲𝗿𝗺 𝗠𝗲𝗺𝗼𝗿𝘆: current chat history (keeps the session coherent). • 𝗟𝗼𝗻𝗴-𝗧𝗲𝗿𝗺 𝗠𝗲𝗺𝗼𝗿𝘆: persistent store of facts/notes across sessions (searchable with vectors). • 𝗠𝗖𝗣 (𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝘁𝗲𝘅𝘁 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝘁𝗼𝗰𝗼𝗹): the layer that manages what the model should remember, how context is stored, and how information is organized for retrieval (metadata, permissions, indexing). Why this design is useful: • 𝗞𝗲𝗲𝗽𝘀 𝗰𝗼𝗻𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘀𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀 𝘀𝗺𝗮𝗿𝘁 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗽𝗲𝗿𝘀𝗼𝗻𝗮𝗹: short-term for flow, long-term for personalization. • 𝗖𝗼𝗺𝗯𝗶𝗻𝗲𝘀 𝗿𝗲𝗮𝘀𝗼𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 + 𝗮𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀: the agent can think (LLM), fetch facts (RAG), and act (tools). • 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝘂𝗹𝗮𝗿: you can add new tools or storage without redesigning the whole system. ✅ Repost for others who struggle to understand the basic workflow of AI agents.

More like this
Recommendations from Medial
Baqer Ali
AI agent developer |... • 2m
🚨 BREAKING: Anthropic just dropped the tutorial on "Building AI Agents with Claude Agent SDK" Here's what it covers: > Agent Loop Gather context → Take action → Verify work → Repeat. Your agent searches files, executes tasks, checks its output, t
See More
The next billionaire
Unfiltered and real ... • 8m
Greg Isenberg just shared 23 MCP STARTUP IDEAS TO BUILD IN 2025 (ai agents/ai/mcp ideas) and its amazing: "1. PostMortemGuy – when your app breaks (bug, outage), MCP agent traces every log, commit, and Slack message. Full incident report in seconds.
See MoreDaksh Sikarwar
Make your idea to a ... • 2m
AI Prompt That Never Fails (RTCCO) Role • Task • Context • Constraints • Output. “Act as a performance marketer. Task: write 3 ad angles. Context: yoga studio in Agra. Constraints: 60–80 chars, no clichés. Output: table with hook + CTA.” Try once, yo
See More
Download the medial app to read full posts, comements and news.